Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud ComputingHere, we are going to discuss some important advantages of Cloud Computing- Advantages:Business operations are being transformed by the transformational technology known as cloud computing. With its extensive advantages and possibilities, cloud computing has emerged as a crucial strategic tool for businesses in a range of sectors. Businesses can take advantage of various benefits that promote development, innovation, and operational effectiveness by leveraging the power of the cloud. 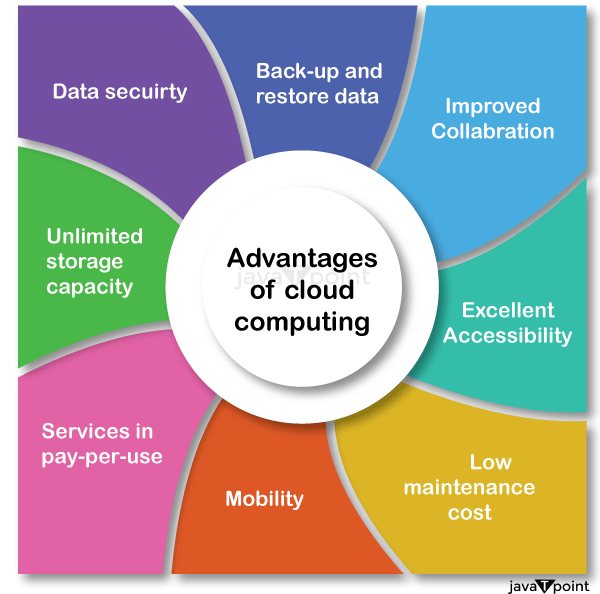
Let's explore the advantages that cloud computing has to offer: Data Backup and Restoration: Cloud computing offers a quick and easy method for data backup and restoration. Businesses may simply access and restore their data in the event of any data loss or system failure by keeping it in the cloud. Improved Collaboration: Collaboration is improved because cloud technologies make it possible for teams to share information easily. Multiple users may work together on documents, projects, and data thanks to shared storage in the cloud, enhancing productivity and teamwork. Excellent Accessibility: Access to information stored in the cloud is made possible. Users can access their data from anywhere in the world with an internet connection, making remote work, flexibility, and effective operations possible. Cost-effective Maintenance: Organizations using cloud computing can save money on both hardware and software upkeep. Because cloud service providers manage the maintenance and updates, businesses no longer need to make costly infrastructure investments or set aside resources for continuous maintenance. Upkeep and Updates: Cloud service providers take care of infrastructure upkeep, security patches, and updates, freeing organizations from having to handle these duties themselves. This frees up IT teams' time and resources to work on higher-value projects like application development, data analysis, or strategic initiatives rather than wasting them on rote upkeep and updates. Mobility: Cloud computing makes it simple for mobile devices to access data. Utilizing smartphones and tablets, users can easily access and control their cloud-based applications and data, increasing their mobility and productivity. Pay-per-use Model: Cloud computing uses a pay-per-use business model that enables companies to only pay for the services they really utilize. This method is affordable, eliminates the need for up-front investments, and offers budget management flexibility for IT. Scalable Storage Capacity: Businesses can virtually store and manage a limitless amount of data in the cloud. The cloud offers a scalable and centralized storage option for all types of data, including documents, photos, audio, video, and other kinds of files. Enhanced Data Security: Cloud computing places a high focus on data security. To guarantee that data is handled and stored safely, cloud service providers offer cutting-edge security features like encryption, access limits, and regular security audits. Businesses can rest easy knowing that their important data is secure. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud computing provides reliable options for these two issues. Businesses can quickly bounce back from any unforeseen disasters or disruptions thanks to data redundancy, backup systems, and geographically dispersed data centers. Agility and Innovation: Businesses can continue to be innovative and nimble thanks to cloud computing. Organizations may quickly embrace new solutions, test out emerging trends, and promote corporate growth with access to a variety of cloud-based tools, services, and technology. Green Computing: By maximizing the use of computer resources, lowering energy use, and minimizing e-waste, cloud computing may support environmental sustainability. By utilizing technologies like virtualization and load balancing to maximize the use of computer resources, cloud providers can operate large-scale data centers built for energy efficiency, resulting in lower energy usage and a smaller carbon footprint. These benefits of cloud computing give companies the ability to use cutting-edge technology offered by cloud service providers while maximizing productivity, cost savings, scalability, and data security. They also enable them to concentrate on their core capabilities. Disadvantages of Cloud ComputingWhen we talk about the "disadvantages of cloud computing," we're talking about any potential drawbacks or difficulties that businesses might have when utilizing cloud computing services. These drawbacks draw attention to some restrictions or risks related to cloud computing that businesses should take into account before making a choice. Some of the Disadvantages of Cloud Computing are as follows:
Because of technological difficulties, maintenance needs, or even cyberattacks, cloud service providers can face outages or downtime. Users may not be able to access their data or applications during these times, which can interfere with business operations and productivity.
A dependable and fast internet connection is essential for cloud computing. Business operations may be delayed or interrupted if there are connectivity problems or interruptions in the internet service that affect access to cloud services and data.
Using standardized services and platforms offered by the cloud service provider is a common part of cloud computing. As a result, organizations may have less ability to customize and control their infrastructure, applications, and security measures. It may be difficult for some organizations to modify cloud services to precisely match their needs if they have special requirements or compliance requirements.
Concerns about data security and privacy arise when sensitive data is stored on the cloud. Businesses must have faith in the cloud service provider's security procedures, data encryption, access controls, and regulatory compliance. Unauthorized access to data or data breaches can have serious repercussions, including financial loss, reputational harm, and legal obligations.
Although pay-as-you-go models and lower upfront costs make cloud computing more affordable, businesses should be wary of hidden charges. Data transfer fees, additional storage costs, fees for specialized support or technical assistance, and expenses related to regulatory compliance are a few examples.
When an organization depends on a cloud service provider, it is dependent on that provider's dependability, financial security, and longevity. Users may have disruptions and difficulties switching to alternate options if the provider runs into financial difficulties, changes their pricing policy, or even closes down their services.
When data is stored in the cloud, it frequently sits in numerous data centers around the globe that may be governed by multiple legal systems and data protection laws. This may pose compliance issues, especially if some sectors of the economy or nations have stringent data sovereignty laws. Organizations should carry out a comprehensive risk assessment, thoroughly examine the dependability and security procedures of possible cloud service providers, and build backup and disaster recovery strategies to counteract these drawbacks.
Next TopicHistory of Cloud Computing
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










