What is the full form of ERPERP: Enterprise Resource PlanningERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a business management software that is implemented by many business houses to increase their productivity and performance. It is a very powerful business tool. It is used to collect, store, manage and, interpret data from many business activities like Product planning, cost, Manufacturing or Service delivery, Marketing and Sales, Inventory management, Shipping, and payment, etc. ERP software is very useful for large organization. It comes in many modules:
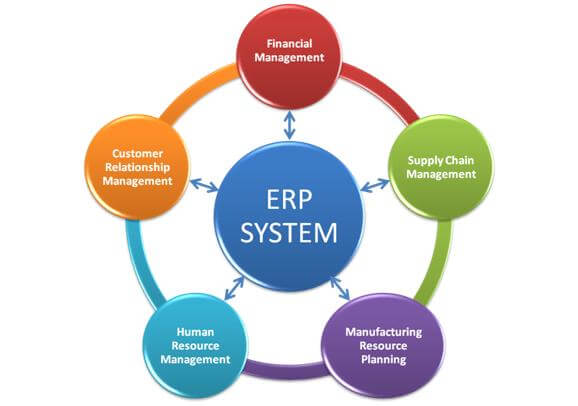
Each ERP software module has its own functional area and is used by the organization for better productivity and performance. Features of ERP systemsThe main feature of an ERP system is a shared database that supports multiple functions used by different units. For example, Accounting and sales can rely on the same information. Advantages/ Benefits of ERP
ImplementationTime and Cost are important factors that need to be considered before buying or implementing an ERP system. The implementation can take several months to a couple of years. The cost is also not fixed and varies on the basis of your requirements and the features provided by the vendor. So, it is advisable to thoroughly analyze the vendor's ERP package modules, features, and supporting infrastructure before implementing the ERP. ERP implementation is the process of installing, configuring, and deploying an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system in an organization. ERP systems integrate all aspects of an organization's operations, including finance, manufacturing, supply chain management, human resources, and more, into a single, centralized system. ERP implementation can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring careful planning and management to ensure success. Here are the key steps involved in ERP implementation: Project Planning: The first step in ERP implementation is project planning, which involves defining the scope of the project, identifying the objectives and goals, and outlining the timelines and resources required. The project team should be selected, and a project manager should be appointed to oversee the implementation. System Selection: The next step is to select the ERP system that best meets the organization's needs. This involves evaluating different vendors and software solutions based on factors such as functionality, ease of use, scalability, and cost. Configuration: Once the ERP system has been selected, the next step is to configure it according to the organization's requirements. This involves customizing the system settings, workflows, and business processes to match the organization's needs. Data Migration: Data migration is the process of transferring data from the old system to the new ERP system. This involves mapping the data fields and ensuring that the data is accurate and consistent. Integration: The ERP system needs to be integrated with other systems and applications, such as CRM software, inventory management systems, and e-commerce platforms. This ensures that data is consistent and accurate across all systems. Testing: Once the ERP system has been configured and integrated, the next step is to test it thoroughly. This involves running tests to ensure that the system functions as expected and that data is accurate and consistent. Training: The final step is to train the employees on how to use the new ERP system. This involves providing training materials, conducting workshops and training sessions, and offering ongoing support to ensure that employees can use the system effectively. ERP implementation can be a challenging process, but by following these key steps and working with experienced consultants and vendors, organizations can ensure a successful implementation that delivers the expected benefits and improvements in efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. Top ERP Vendors
Customization in ERPCustomization in ERP refers to modifying an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to meet the specific needs and requirements of an organization. ERP systems are designed to provide a standard set of features and functions that are applicable across multiple industries and business types. However, every organization is unique and may have specific business processes, workflows, and data requirements that are not fully addressed by the standard ERP system. Customization is the process of modifying the ERP system to meet these specific needs. Here are some key aspects of customization in ERP: Business Process Customization: Every organization has its unique set of business processes that reflect its operations and requirements. ERP customization can help organizations tailor the system to their specific business processes by modifying workflows, creating new data fields, or adding custom applications. Data Customization: Organizations may have unique data requirements that are not addressed by the standard ERP system. Customization can help organizations modify data fields or add new ones to capture the required data. User Interface Customization: ERP systems have a standard user interface that may not meet the specific needs of every organization. Customization can help organizations modify the user interface to improve usability and efficiency. Integration Customization: ERP systems need to be integrated with other systems and applications such as CRM software, e-commerce platforms, and inventory management systems. Customization can help organizations modify the integration process to ensure that the data is accurate and consistent across all systems. The benefits of customization in ERP include the following: Meeting specific business needs: Customization can help organizations tailor the ERP system to their specific business processes, workflows, and data requirements. Improved efficiency and productivity: Customization can help organizations improve their efficiency and productivity by automating processes, reducing manual data entry, and streamlining workflows. Competitive advantage: Customization can help organizations gain a competitive advantage by improving their ability to respond to market changes and customer needs. However, there are also some challenges associated with customization, such as: Increased cost and time: Customization can be a time-consuming and costly process, requiring significant resources to implement and maintain. Compatibility issues: Customization can sometimes result in compatibility issues with other systems or future software updates, which can cause problems with data integrity and system stability. Overall, customization in ERP can be an effective way for organizations to tailor the system to their specific needs and requirements, but it is important to carefully consider the costs and benefits before embarking on customization projects. Working with experienced consultants and vendors can help organizations make informed decisions about customization and ensure that the system is customized in a way that maximizes its benefits while minimizing its risks.
Next TopicETA Full Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










