ABAP Database TablesWhat is the database table in ABAP?
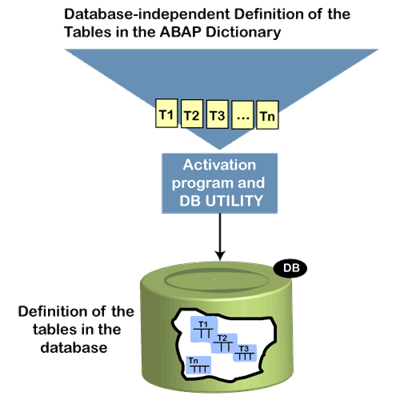
Note: To better understand the ABAP tables, first learn about the data elements and domain given in previous chapters.Components of Table in ABAP DDICThe components of the ABAP table are given below: 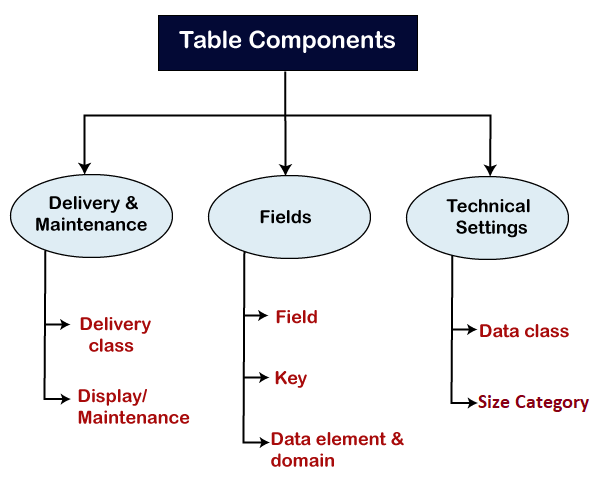
Delivery Class:
Display/Maintenance:
Field Name: The name which we provide to each field in the table is known as the field name that consists of a maximum of 16 characters. Similar to the table name, it must start with a letter, and can have a letter, numbers, and underscore. Key Flag: It specifies whether that particular field belongs to the Key field or not. Field Length: It defines the number of characters that can be entered into the field. Decimal Places: It specifies how many digits are permitted after the decimal point, and it can only be used for the numeric data. Short text: It specifies the meaning of the particular field entered within the table. Data class: It defines the actual area of the table inside the database. The options available for the data class are given below, which we can select according to our table:
Domain: The domain is an object that defines the technical information of the field, such as data type and length. Learn More. Data Element: The data element is an object that specifies the semantic information of the field, such as description, labels, etc. Learn More. Types of ABAP TablesIn the ABAP dictionary, we can create three types of tables:
We can also create some special table types apart from these three tables, such as table pools and clusters. These two table types store the information of other tables such as program parameters, temporary data, documentation text, etc. The explanation of the ABAP tables is given below: 1. Transparent TableABAP transparent table contains the application data that represents the master data or transaction data used by an application. A table of vendors or table of customers is an example of the master data. In transparent tables, the database table has the same name and the same number of fields with field names as the data dictionary table. The transparent table shows the one-to-one relationship with the table definition in the SAP database. The below image is showing the transparent table in ABAP: 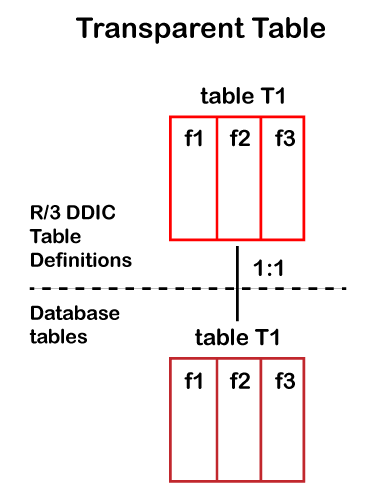
2. Pooled TablesThe pooled table in ABAP shows the many-to-one relationship with the table definition in the database, which means for a single table defined in the SAP database, there are various tables in the ABAP dictionary. The names of the tables stored in the Dictionary and the database must be different. The SAP database stores all the Pooled tables in a single table, which is known as a table pool. The pooled tables in the data dictionary may or may not have a common primary key field. Below image shows the relation between the Pooled tables and table pools: 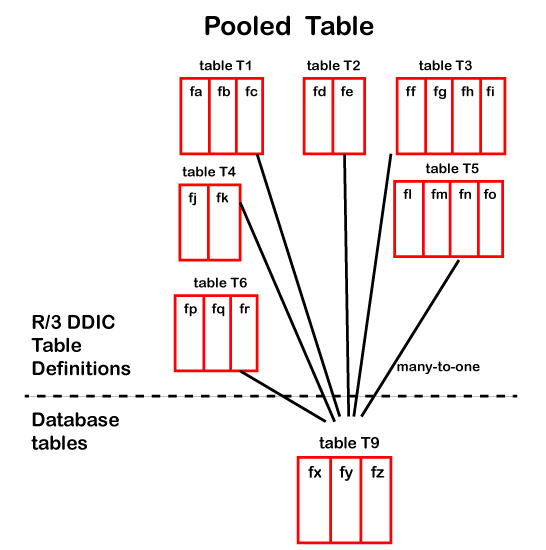
3. Cluster Tables:Cluster tables are similar to the Pooled tables, as they also show the many-to-one relationship with the table definition in the SAP database. All the cluster tables are stored in a single table in the database, and that table is known as a table cluster. The tables in the data dictionary must have at least one primary key field in common, and the table is usually accessed simultaneously. The relationship between the cluster table and table clusters can be understood by using the below diagram: 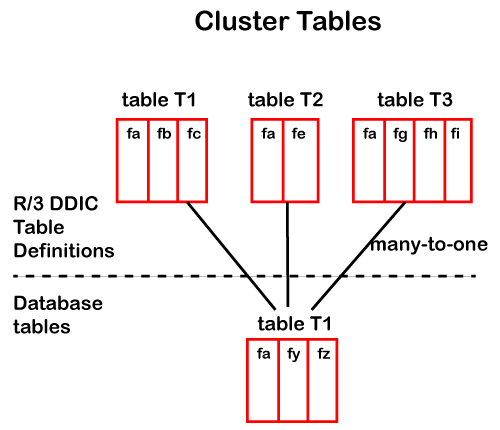
The key difference between the Pooled, Cluster, and Transparent tables:Pooled and cluster tables do not usually hold the application data as the transparent table; instead they are used to store the system data, such as system configuration information, historical data, etc. Creating a table in ABAPThe basic steps are given below; the practice of this is given in further topic:
Creating Records in the Table:Once we create the table successfully in DDIC, we can now enter data in the table. Below are the steps for creating records in the table:
Displaying the Records of TableAfter creating the records in the table, we can easily display all the records saved in the table.
Note: In this section, we have only provided the theory about creating and editing table. But the practical Implementation for creating a table and displaying is given in further topic. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










