What is the full form of ABGABG: Arterial Blood GasABG stands for Arterial Blood Gas. It refers to a test that is performed to measure the levels of oxygen and carbon and acidity (pH) in the blood of an artery. This test checks how efficient your lungs are in moving oxygen into the blood and removing carbon dioxide from the blood. When blood passes through the lungs oxygen from the air present in the lungs moves into the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood moves out into the lungs. 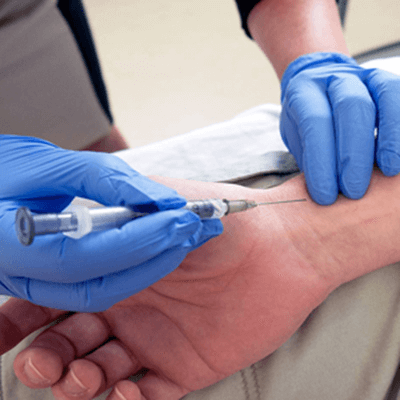
In this test, blood is drawn from an artery before it enters into body tissues. This provides you with the following information or it measures: Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2): It is the pressure of oxygen dissolved in the arterial blood. The pressure of oxygen shows how efficiently oxygen is moving into the blood from the lungs. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): It is the pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in the arterial blood. It shows how efficiently the carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the lungs. pH: It is a measure of the hydrogen ions (H+)/pH in the blood. pH less than 7 indicates acidic solution and more than 7 indicates basic/alkaline solution. In general, arterial blood pH ranges from 7.38 to 7.42. So, it is slightly basic in nature. Bicarbonate (HCO3): It is a chemical (buffer) that helps maintain the pH of the blood. It prevents blood from becoming too acidic or too basic. Oxygen content (O2CT) and oxygen saturation (O2Sat) values: O2 content value is the measure of the amount of oxygen in the blood. Oxygen saturation value tells how much of the total haemoglobin in the red blood cells are carrying oxygen. In general, the normal values of an ABG test are as follows:
An arterial blood gas test may also be referred to as:
What circumstances call for an arterial blood gas (ABG) test?The following situations or fields of medicine see a lot of arterial blood gas (ABG) test orders: Emergency medicine: Emergency medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with treating injuries or illnesses that need to be treated right away. Anaesthesiology: Anaesthesiology is the branch of medicine that deals with caring for patients prior to, during, and following surgery. It includes anaesthesia, critical emergency medicine, intensive care medicine, and pain medicine. Pulmonology: The field of medicine known as pulmonology deals with illnesses that affect your respiratory system. Who performs an arterial blood gas (ABG) test?Blood is frequently drawn from an artery in your hand or forearm by a physician known as a respiratory therapist in order to perform arterial blood gas testing. The sample is subsequently processed by the respiratory therapist or rapidly sent to a lab where medical laboratory professionals process it. In what ways an ABG test is carried out?A respiratory therapist may perform a blood circulation assessment known as the Allen test prior to taking a sample from your wrist for an arterial blood gas test. An Allen test requires you to raise your hand while clenching it. The respiratory therapist will next exert pressure for a brief amount of time on the arteries in your arm. This quick examination verifies that your wrist's two arteries are healthy and open. If you are undergoing therapy for additional oxygen, the oxygen might be turned off by the respiratory therapist for around 20 minutes for collecting the blood sample. An air test in a room is what this is. They won't perform this test if you require supplemental oxygen to breathe. Do arterial blood gas tests carry any risks?When the respiratory therapist administers an arterial blood gas test properly, there is little risk involved. It may be more challenging to draw blood from some persons than from others due to differences in artery size between individuals and between the left and right sides of the body. When an arterial blood gas test is going on, it carries a small but possible risk of:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










