Accounting Principles
Meaning
Accounting principles refer to various rules and guidelines that a company is bound to follow while preparing and reporting financial data. These principles aim to make the financial statements complete, consistent, and comparable. This makes things easier for the insiders as well outsiders who have an interest in the business. The financial performance helps the creditors in deciding whether to give the loans to the company and helps the investors in deciding whether they should invest in the company or not. They also mitigate accounting fraud by increasing transparency and allowing red flags to be identified.

Characteristics of Accounting Principles
- These principles are the set of rules and guidelines which are prepared to bring uniformity and easy availability and understanding of the accounting information.
- These principles are derived from experience and reasons. They are not tested in the laboratory unlike principles of science and hence are not universally applicable, i.e., their use can vary in a different business environments.
- Accounting principles are not static, meaning they can change over time to reflect changes in corporate practices, government legislation, and the demands of accounting information users.
- There are three criteria that decide the general acceptance of the accounting principles. They include:
- Relevance
These principles are relevant because they provide useful information to accounting users.
- Objectivity
Any principle is called objective if there are not any personal biases or judgments of the person who is furnishing information. On this basis, accounting principles are objective. Also, these principles are variable.
- Feasibility
Accounting principles are feasible as they can be applied without any cost or undue complexity.
Need for Accounting Principles
Accounting information must be reliable and comparable so that a meaningful conclusion can be derived from it by internal and external users. The information is required to be comparable in order to compare the performance of the firm with other firms as well as with the previous year's performance of the firm. This can be possible only if the accounting information is based on some particular set of rules which are known as policies, principles, and conventions. These rules are usually known as GAAP and they bring uniformity and consistency to the accounting process. These principles also help in enhancing the utility to various users.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
GAAP is a set of commonly accepted accounting principles, standards, and procedures that are formed by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). These principles are accepted by accountants all over the world as general guidelines for preparing accounting statements. FASB has developed these principles over a period from usage, reason, common experiences, historical precedents, individual statements, professional bodies, and regulation of government agencies.
These principles aim to bring clarity, consistency, and comparability to accounting information. GAAP is based on ten principles which are given below:
- Principle of Regularity
- Principle of Consistency
- Principle of Sincerity
- Principle of Permanence of Methods
- Principle of Non-Compensation
- Principle of Prudence
- Principle of Continuity
- Principle of Periodicity
- Principle of Materiality
- Principle of Utmost Good Faith
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
IFRS standards are issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) which is used in more than 120 countries. These standards are also useful in determining how the transactions and other accounting events should be reported in the financial statements. IFRS was introduced to bring uniformity to the financial environment so that the financial statements can be easily interpreted from company to company and country to country. The primary difference between GAAP and IFRS is that GAAP is rules-based and IFRS is principle-based.
Various Accounting Principles
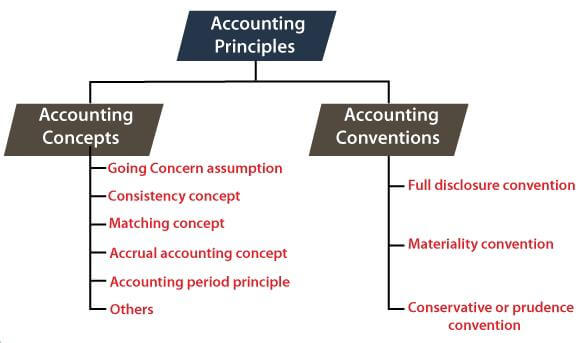
Accounting principles are known by different terms such as assumptions, conventions, concepts, doctrines, postulates, etc. There are mainly two categories in which these principles can be divided. They include:
1. Accounting Concepts or Assumptions
To make the accounting language more meaningful, a set of accounting concepts is made by various accountants which are used to prepare the financial statements. These concepts provide a foundation for the accounting process and help in knowing how the transaction should be recorded and reported. Some of the basic accounting concepts as per the Accounting Standard (AS-1) issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India are as follows:
- Going Concern Assumption
It is presumed that the business is a going concern, i.e., it continues to exist for an estimated period. This presumption is necessary because all the business transactions are recorded in the books on this basis. As per his concept, fixed assets are recorded at their original cost, and depreciation is charged on these assets without reference to their market value. Because of the going concern, exterior parties enter into long-term contracts with the enterprise.
- Consistency Concept
As per this Concept, the accounting principles and methods should remain consistent from year to year. This is because if a company applies different accounting principles in two accounting periods then it will be difficult for the company to compare the profits of the current year with the preceding year.
- Matching Concept
The matching principle states that there must be a comparison made between the income and corresponding expenditure for a particular financial year so that the company can figure out the actual profit that occurred during that period.
- Accrual Accounting Concept
According to this principle, both revenue and expenditure must be recorded in the actual incurred instead of at the time when the cash or cash equivalent is received or spent. Irrespective of the successive cash flow, income and expenditure are significant.
- Accounting Period Principle
This principle states that the accounting process of the company will be completed within a certain period. This period is usually a financial year or a calendar year. Thus, every transaction that takes place within that particular period of accounting must be included or can say recorded in the financial statement of the company.
- Other Accounting Principles
The list of some other important accounting principles is given below:
- Cost Principle or Historical Cost Concept
- Economic Entity Principle
- Monetary Unit Principle
- Reliability Principle
- Revenue Recognition Principle
- Time Period Principle
- Dual Aspect Concept
- Business Entity Concept
2. Accounting Conventions
These are the customs or generally accepted practices that accountants follow after reaching a general agreement or consensus. The following are types of accounting conventions:
- Convention of Full Disclosure
According to this norm, all relevant information pertaining to the company's financial concerns must be fully revealed. In other words, the information that is of material relevance to the users of the financial statements should be disclosed. These users can be proprietors, present and potential creditors, investors, and others. According to the Companies Act, the contents of the Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account are to be disclosed.
- Convention of Materiality
This convention states that the company should not disclose such items which have an insignificant effect or are irrelevant. This is an exception to the general rule of full disclosure. These useless elements are either left out or integrated with other relevant items to remove unneeded burdens from the accounting statement.
- Convention of Conservatism or Prudence
As per this convention, the company should record all anticipated losses in the books of accounts but it should ignore all the unrealized gains. In short, it is the policy of playing safe. The company should make provision for all known liabilities or losses to recover them even if the amount is not known.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










