Adjective PhraseAdjectival phrases refer to one of the various types of phrases which you may use in your oral and written communication on a regular basis. Adjectives are utilized to define, describe and express the nouns. 
Adjective phrases are employed to define, describe and express the adjectives. So conclusively, adjective phrases enhance the sentences by giving a richer description for nouns. What Is an Adjective Phrase?Let's analyze an adjective phrase to master the concept and to know what it is. A phrase is a collection of words that isn't quite a statement but communicates a coherent notion. They are used to offer context and clarity in sentences. Following are few phrases that can help you to begin understanding;

An adjective is a term that is used to characterize a noun. Adjectives include the following:
An adjective phrase refers to the phrase which comprises adjectives, but it is also a phrase that works as an adjective by characterizing the nouns in the sentence. Examine the highlighted adjective phrases in the below-mentioned statements:
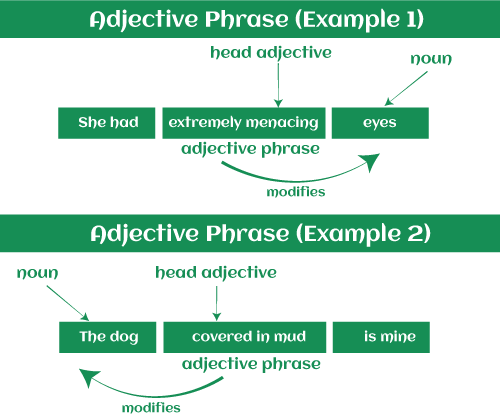
As you can see from these instances, an adjective phrase might come before or after the noun it is defining. The Purpose of Adjective PhrasesWondering about what are the functions of adjective phrases and it's purpose? Adjective phrases can change nouns or pronouns and work in the same way with both. 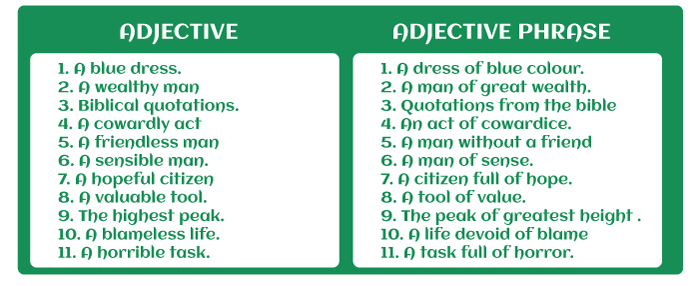
How to Recognize an Adjective PhraseThe key to recognizing an adjective phrase is to recognize a set of terms within a sentence that works together to characterize a noun or pronoun.
Constructing an Adjective PhraseSeeing this type of statement in action is the greatest way to grasp it. Adjective phrases can be constructed by stringing together many adjectives, or these might start with the prepositions or adverb intensifiers. The adjective phrase has been highlighted in the statements below, whereas the nouns or pronouns it modifies is Italicised. Adverb Intensifier with AdjectiveAn adjective phrase is made by mixing the adverb that serves as an intensifier and an adjective.
Adjective Phrase with a PrepositionA preposition or prepositional phrase can be used with another term to characterize a noun in a statement to make an adjective phrase.
Several Adjectives in a RowSometimes one adjective was not enough to describe something. An adjective phrase is formed by a string of numerous adjectives.
Adjective Phrase PositioningAdjective phrases can come before or after the nouns that they change. However, their function is to change nouns or noun phrases within sentences. Adjective Phrases That Come Before a Noun or a PronounAdjective phrases are frequently used in statements to change nouns or noun phrases. They are frequently used before the word or pronoun that they describe.
Adjective Phrases Following a Noun or a PronounIn a statement, adjective phrases need not have to occur prior the nouns or pronouns they alter. It is common for adjective phrases to come after the noun or pronoun they change. Let us have a look at some of the examples of adjective phrases following the nouns or pronouns;
Adjective Phrases vs. Solo AdjectivesIf you want to change a noun in a more sophisticated way than a basic adjective, consider employing an adjective phrase. This can be accomplished without changing the meaning of the statement or sentence, but it can also be done in a manner that restricts or expands the noun. Determine the following examples, where the adjectives and adjective phrases are highlighted, and the noun is Italicised. Beautiful: Alone or in a PhraseAll of these statements convey the same thing. The first sentence, however, contains one adjective, but the succeeding sentences have adjective phrases.
Angry: Individually or in a PhraseAgain, the two statements mentioned below are interchangeable. The first employs only an adjective, whereas the second uses an adjectival phrase.
What Is the Distinction Between an Adjective Phrase and an Adjective Clause?
A phrase is a collection of terms or words that cannot function as a sentence on their own since they lack a subject and a predicate. A clause, on the contrary, comprises a subject and a predicate and, in some situations, can serve as an independent sentence. Adjective clause and adjective phrase both serve the same purpose: they describe a noun. An adjective phrase, on the other hand, is only a few extra words that "bulk up" an adjective, whereas an adjective clause repeats the noun. An adjective clause will frequently do this with a pronoun. Here are a few instances of bolded adjective clauses within sentences:

Here are the identical sentences, but with adjective phrases in place of the adjective clauses:
Examples of Adjective PhrasesAdjective Phrases have been bolded for easy identification.
Adjective Phrases Provide More DetailsA well-chosen adjective phrase can add life and personality to a statement. A single adjective can be sufficient. However, if it can be expanded into an adjective phrase, you can give your readers more information and details. Once you're ready to incorporate certain adjective phrases into your writing, make sure to practice and learn the concept adjective phrase examples for more guidance.
Next TopicComparative and Superlative Adjectives
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










