Advantages and Disadvantages of artificial vegetative propagation
Introduction
Almost every living thing on the earth increases or multiplies itself with reproduction. The process of reproducing a new generation is called reproduction. There are two types of reproduction: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction: This method is adopted by humans and animals to produce a new generation.
Asexual reproduction: This method is adopted by plants and some species of animals.
"When a single plant reproduces with some natural process or asexually with its stem, roots and leaves, the process is called vegetative propagation."
With vegetation propagation, the plant can produce new species genetically identical to the parent plant, apart from its seed. Fruits, vegetables and flowers reproduce with this, such as sweet potatoes, bananas, apples, pineapples, etc., as some of the real-time vegetative propagation. In the vegetative propagation process, only one plant is involved and can be reproduced by two methods of vegetative propagation, i.e. fragmentation and regeneration.
| Fragmentation |
When humans fragment parts of plants or either break accidentally or naturally, that detached part grows into a new plant. |
| Regeneration |
It is a biological or physiological process in which parts of the plant get repaired or renewed by its tissues. The damaged and unhealthy tissues are replaced with new healthy cells. |
This vegetative propagation is further divided into types:
a) Natural vegetative propagation
- It has been a natural process of plant reproduction since the earth's existence. In this plant reproduce naturally without human intervention. Plants can grow and develop by themselves and start this process by developing adventitious roots. From the roots, new plants may sprout up or from stem or leaves of a parental plant. In most cases, vegetative plant propagation sources are modified stems. Plant stem produces vegetative plant structure that includes runners, tubers, rhizomes, bulbs and corms.
- Natural vegetative production can be conducted from roots, stem and leaves.
- Natural vegetative propagation techniques
- Bulbs: These are underground stems to which leaves are attached, present above the ground and capable of storing food. Daffodils bulbs are from lateral buds that produce new smaller bulbs or bulbels in subsequent years. Monocot plants use these bulbs for production and storage.
- Corms: Underground bulb-shaped stems larger than the rest, known as corms, can produce adventitious roots. Corms' structures are surrounded by papery foliage and have buds that can develop into new plant shoots. Corms store nutrients in fleshy, hard stem solid tissue?for example, Gladiolus, crocus and taro.
- Tubers: Vegetative organs made from stems and roots known as stem tubers and root tubers.
Stem tubers are formed from rhizomes or runners that become swollen due to vital nutrients. The upper surface of the tuber creates a new shoot system, and the bottom creates a root system. Examples: yams and potatoes
Root tubers: Created by modifying roots to store nutrients which further expand and give rise to new plants. For example, dahlias and sweet potatoes.
- Rhizomes: An underground stem that can also be grown horizontally on the ground. These are the stems where proteins and starch are stored and can produce roots and shoots?for example, grasses, irises, lilies, turmeric and ginger.
- Tuberous roots are part of tubers that display the characteristics of a typical root internally or externally. These are present in peonies, dahlia, taro, sweet potato, daylilies, asparagus and many others.
- Plantlets: These are tiny, young plants made from plant leaves by meristem tissue present at leaf margins. Roots are developed when these tiny plants reach maturity and set beneath the soil to form a new plant?for example, spider plant and kalanchoe.
b) Artificial vegetative propagation
- Artificial vegetative propagation is a method of genetically modifying and growing plants inside a clinical setup by humans. When human intervention is present in the process of vegetative propagation, considered artificial vegetative propagation, this method is an invention of scientists in agriculture. Here, scholars and scientists prepare tests and solutions to carry out the process of artificial vegetative propagation inside laboratories. Some techniques are used for artificial vegetative propagation, such as grafting, layering, cutting, tissue culturing and suckering. Horticulturists and farmers use these to produce crops with desirable qualities.
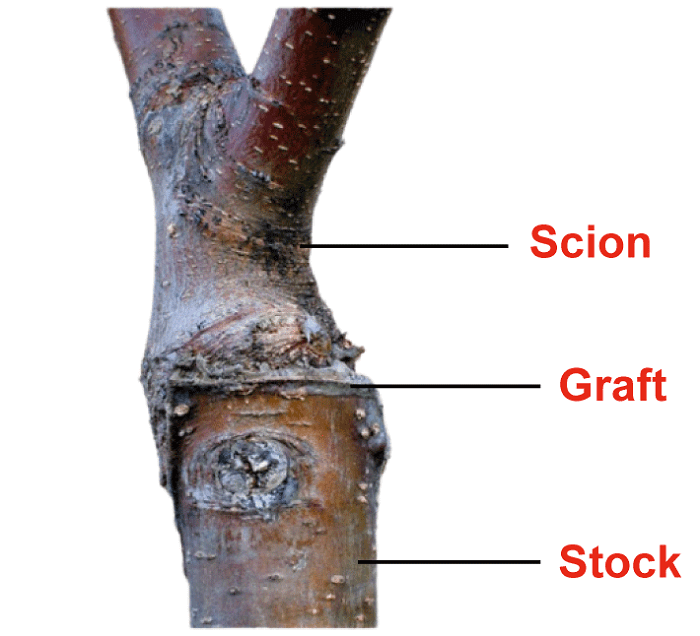
- Grafting - In this technique, one plant is rooted in the ground, and a cutting from another plant is attached to that rooted plant. A cut was made in the plant to attach the other plant, and they were kept after combining. In some time, the tissues of grafted plants combine with the tissue of a rooted plant, and with time, a new plant is developed.
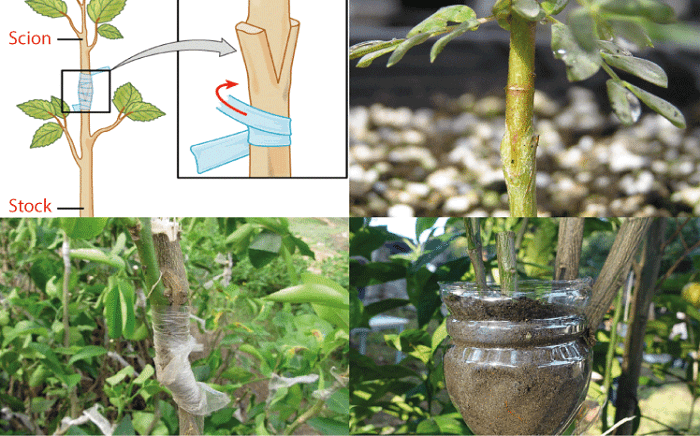
- Cutting- A most common and easiest method in which a part of a plant's leaf or stem is cut and rooted in the soil. This rooted part grows into a new plant called an adventitious root. This technique is used to increase the growth of plants by indulging growth promoters or hormones in the process. These chemicals, like IBA (Indol Butyric acid) and NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid), are injected into the adventitious roots for nurturing and quick plant development. Cutting can be implemented in two ways:
| Cutting by root |
Cutting by leaf |
In this, long pieces of roots are used to propagate a new plant artificially. Example:
Orange
Lemon
Raspberry
Blackberry
boysenberry |
This leaf is cut from the rooted plant, broken into two or three parts and planted in a vertical position in the soil at another place to do artificial propagation of the new plant. Examples of cutting are:
Sansevieria (snake plant)
Bryophyllum
Begonia |
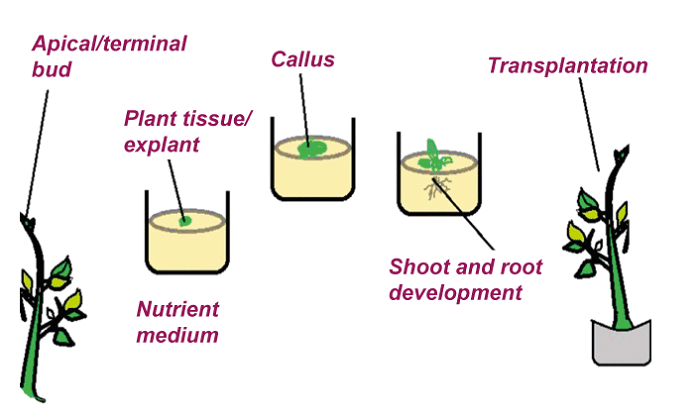
- Tissue culture- This technique is proper artificial propagation where the plant grows in an artificial environment. Every natural condition is not suitable for a plant to grow. To overcome this tissue culture method is very useful. In this, a technician segregates the parts of plants and cultures them in a clinic where tissues are placed in a sterilized container. These tissues are nurtured in a special medium until a callus (mass of cells) is formed. In a hormone-laden medium, this callus is cultured ad developed into plantlets, which mature (develop into fully grown plants). This is mostly experienced in banana plants.
A technique used in tissue culture is termed: micropropagation.
In this technique, artificial vegetative propagation of plant and fruit trees takes place in test tubes using an artificial medium where growth takes place in controlled conditions, regardless of the seasons. This technique is best suited for sterile plants that couldn't produce via sexual reproduction. With micropropagation, thousands of propagules are produced as they have a high-frequency fecundity rate that is impossible by traditional approaches as they generate a fraction of that. It is the only method of reproducing genetically modified cells or cells after protoplast fusion where millions of plantlets can be kept alive. Rare and endangered plant species are multiplied, and germplasm stocks can be kept for many years.
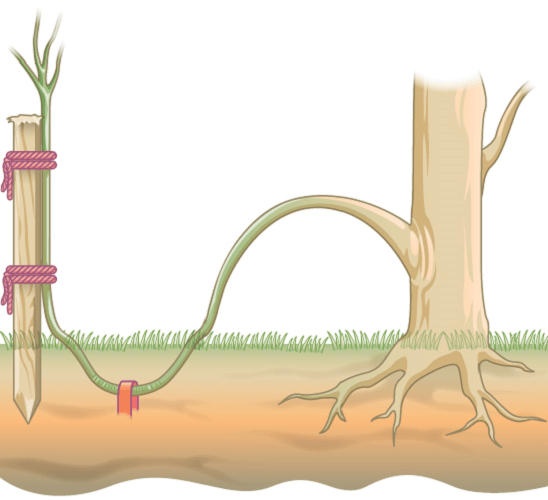
- Layering- In the layering technique, the branches or stems of plants are bent to the ground. A bent plant stem or branch touches the ground and is covered with soil. Adventitious roots or extended roots are developed in part covered by the soil, and the attached shoot with new roots is termed as a layer, and naturally, this layering occurs. Air layering is a part of layering in which branches are scraped and covered with plastic to reduce moisture. Examples of layering propagation are boxwood, honeysuckle and wax myrtle.
- Suckering -It is a technique in which parent plant suckers are attached and form a dense, compact mat. They cut away from a parent plant when they grow into small crop sizes. The detached small plant is transplanted to a new area where they sprout new plants. These new shoots are developed, and nutrient-sucking buds are removed that can prevent the main plant from growing.
Advantages of artificial vegetative propagation
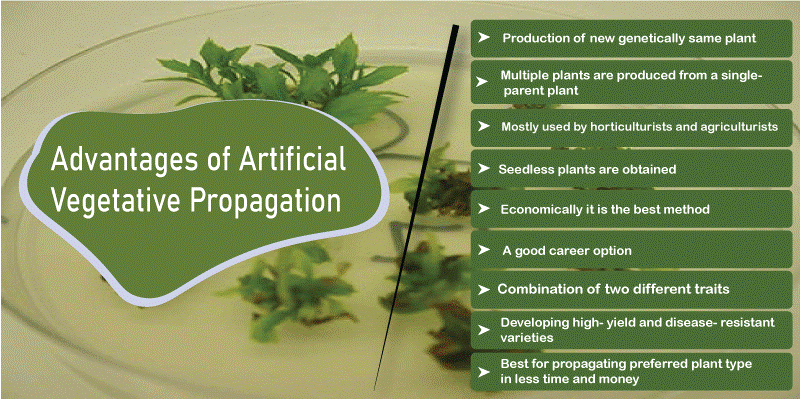
a. Production of new genetically same plants
Like natural vegetation, artificial vegetative propagation also enables the production of new plants genetically identical to parent plants. All the features of the parent are inherited in new plants.
b. Multiple plants are produced from a single-parent plant
Multiple genetically same plants can be produced from a single parent plant with artificial propagation. Using a part of the plant
c. Mostly used by horticulturists and agriculturists
With a motive of expanding the quality and quantity of products, agriculturists and horticulturists use artificial vegetative propagation by using two ways:
- Mass production: when horticulturists want to grow the same plant with desired quality of flower seed or entire plants, does mass production
- Developing new varieties with desirable characteristics: with the hybridization process, a new variety and characteristic of the plant can be propagated further.
d. Seedless plants are obtained.
Plants that produce few seeds or do not produce viable seeds are reproduced by artificial vegetative propagation. Here production is done in bulk.
e. Economically it is the best method.
As we know, artificial vegetative propagation is used in agriculture and horticulture. Horticulture is a science or branch of agriculture in which diverse crops are produced. Scientists or horticulturists have this art of development, marketing, use of high values, and sustainable production of intensively cultivated food and ornamental plants (plants used for decorations). It adds beauty, quality, and sustainability to our life and rehabilitates our environment and the human condition. Horticulture crops include landscape, fruits & vegetables, decorative indoor plants and annual & perennial species.
An agriculture-based country that earns major income benefits the country economically worldwide. Agriculture crops are also yielded with artificial propagation. This increases the option of business and earning in the field of agriculture.
f. A good career option
Some countries' maximum population depend on agriculture for their livelihood; therefore, artificial vegetative propagation gives new methods and a way to agriculture. It is considered a good career opportunity for people interested in agriculture, plantation and horticulture.
g. Combination of two different traits
With artificial vegetative propagation techniques, i.e. cutting, budding, grafting, and tissue culture, two varieties of plants are combined to form a new variety of plants.
h. Developing high-yield and disease-resistant varieties
With artificial vegetative propagation, scientists can develop disease-resistant and high-yield varieties of fruit trees or flowers. These are produced under a protected environment, and with tissue culture, thousands of plants are grown free from infections.
i. Best for propagating preferred plant type in less time and money
Yes, new plants are grown in less time with artificial vegetative propagation. For example, fruit trees grown by a natural process, i.e. by its seed, may take years to bear fruits, but the same trees grown from cutting or by grafting may start bearing fruit after a few growing seasons.
Disadvantages of artificial vegetative propagation
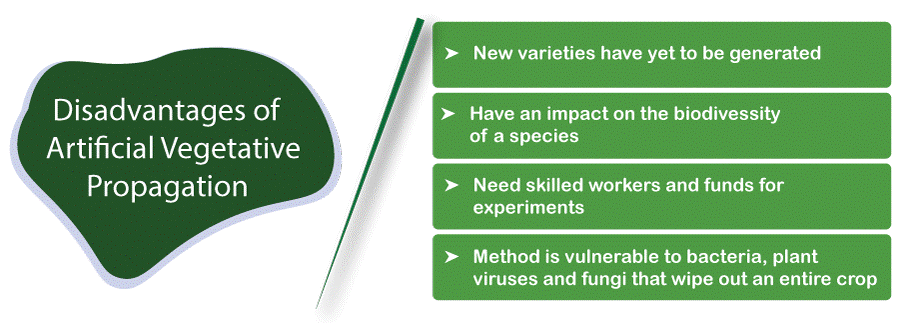
a. In some cases, new varieties have yet to be generated.
People generate the same varieties of plants (genetically the same) with artificial propagation. In asexual reproduction, no recombination of genetic material takes place. Due to this, no variation or genetic variability was seen in the production.
b. Have an impact on the biodiversity of a species
Rather plants are genetically identical in artificial vegetative propagation, but they can't beat natural growth. This method may reduce some species' genetic diversity, resulting in lower food yields.
c. Need skilled workers and funds for experiments.
Artificial vegetative propagation is a sensitive process that needs extra care and knowledge; therefore, trained agriculturists are required for this process. Agriculturists or scientists keep experimenting in this field for which they need funds. Government and private labs have been opened for them, but regular maintenance and continuation of experiments need funds.
d. Production from this method is most vulnerable to bacteria, plant viruses and fungi that wipe out an entire crop.
The plant clone can be susceptible to some disease that has the potential to infect the entire crop and can destroy the whole crop. Clone plants are genetically weak and vulnerable to bacteria, fungi and other diseases. Plants get affected by viruses too.
Conclusion:
At last, we can conclude that artificial vegetative propagation is an essential type of vegetative propagation that make humans develop plants artificially and fulfil the demand. The artificial propagation method is adopted worldwide for producing fruits, flowers and vegetables such as jasmine, roses, apple, mango etc. advantage and disadvantages of it help you have a clear understanding of artificial vegetative propagation.
|




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now














