Advantages and Disadvantages of FloodA flood is an overflow of water (or, in rare cases, other fluids) that normally covers the dry ground. The word can also refer to the tide's inflow when used in the sense of "flowing water." Floods are a research topic in the hydrology field and are very important to agriculture, civil engineering, and public health. Human modifications to the environment frequently lead to an increase in the severity and frequency of flooding, particularly when it comes to land use changes like deforestation and the removal of wetlands, modifications to waterway courses or flood defenses like levees, as well as more serious environmental issues like climate change and sea level rise. The increased rainfall and extreme weather events brought on by climate change make other causes of flooding more severe, leading to more violent floods and a higher risk of flooding. Flooding can happen when water from bodies of water, like rivers, lakes, or the ocean, overflows and breaches levees, allowing some of the water to stray outside its customary confines. Additionally, it can result in flooding when rainfall gathers on soggy soil. Although the size of lakes and other bodies of water will vary depending on the quantity of precipitation and snowmelt that falls at various periods of the year, these variations are unlikely to be important unless they result in property flooding or domestic animals drowning.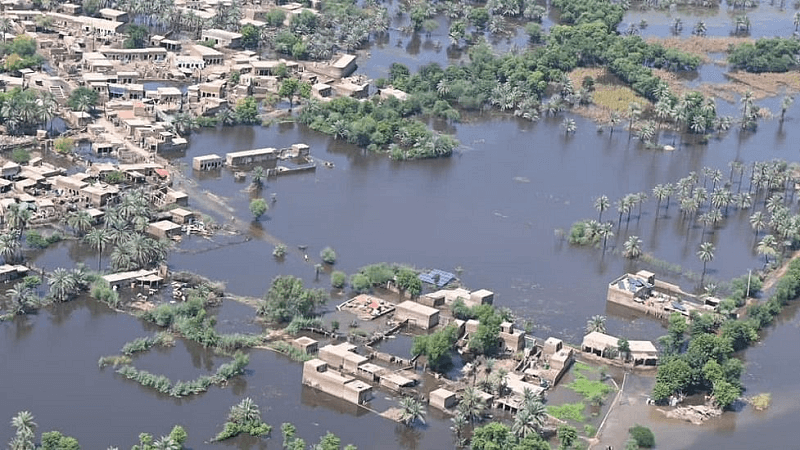 
Floods can also occur in rivers when the flow rate is greater than the capacity of the river channel, especially around bends or meanders in the waterway. Floods commonly cause damage to a building or business if it is situated in a river's natural floodplain. Because the land around rivers is usually flat and fruitful and because rivers provide convenient access to trade, industry, and transportation, people have traditionally lived and worked near rivers. Moving away from rivers and other bodies of water can, however, lessen the harm caused by riverine floods. In addition to causing physical damage, flooding can have unintended consequences, including forcing long-term evictions of communities and accelerating the spread of mosquito- and water-borne diseases. Types of FloodsArealFlooding may result when water is produced by snowmelt or rainfall in low-lying areas more quickly than the ground or runoff can absorb it. A dangerous depth can sometimes be reached by excess accumulation. Where the water table is low, such as on a floodplain, or due to heavy rain from one or more storms, the surface soil may become saturated and become impermeable, preventing penetration. Ice, rock, concrete, asphalt, and roofs all have sluggish to nonexistent infiltration rates. Since the speed of overland flow depends on the surface's slope, local depressions and flat places like floodplains are where areal flooding first occurs. When precipitation is more than evaporation, endorheic basins may experience area flooding. Estuarine and CoastalLarge waves meeting high upstream river flows and storm surges brought on by strong winds and low barometric pressure frequently results in estuaries flooding. Storm surges, high tides, and major wave events at sea can cause waves to exceed flood barriers and coastal flood regions. A tsunami or tropical cyclone can cause serious flooding in more catastrophic circumstances. This category includes storm surges that result from either tropical or extratropical cyclones. According to NHC (National Hurricane Center) research, storm surge is an additional rise in water caused by a storm above and beyond the anticipated astronomical tides. It's critical to understand the difference between storm tide and surge, which is the increase in water level caused by a combination of storm tide and the astronomical tide. When storm surge and spring tide coincide, causing storm tides to reach 20 feet or more, this spike in water level can result in severe flooding in coastal communities. Urban FloodingUrban flooding is a condition that can affect any community, regardless of whether or not it is situated within a designated floodplain or close to any body of water. Urban flooding occurs when land or property inside a built environment overflows due to severe rainfall that exceeds the capacity of drainage systems like storm sewers, especially in more densely populated areas. Besides the possibility of rivers and lakes overflowing, snowmelt, stormwater, or water from burst water mains may collect on private property and in public rights-of-way, seep through building walls and floors, or backup into buildings through sewer pipes, toilets, and sinks. Circumstances like flash flooding or snowmelt sometimes bring it on. 
Advantages of Floods1. Flooding Makes the Land Fertile The fact that flooding makes the soil fruitful may be one of the most widely acknowledged advantages of floods. Eventually, as the water recedes, fine sand, clay, silt, and organic debris are left behind. Because of this, floodplains are among the world's most productive agricultural regions. The ancient Egyptians were aware of this idea as they cultivated along the Nile. Thus, they referred to the Nile's periodic flooding as "The Gift of the Nile." Additionally, many crops, including rice, may be grown in the flooded soil. Nearly half of the world's population consumes rice as a staple food typically grown on paddy fields by Asian communities. 2. Dislodges Accumulated Debris Additionally, the power of the floodwater's rushing can move items that obstruct rivers and estuaries. Debris-like branches, logs, and boulders frequently impeded river water flow. They can occasionally completely obstruct water flow, which can cause droughts downstream. During the dry season, when there is minimal water flow, this can be quite disastrous. This can cause zebras, impalas, and other animals to pass away from dehydration, starvation, and exhaustion. So, during the rainy season, flooding fills waterways and clears them of any unnecessary material. 3. Supplies Sediment to Deltas Deltas develop when sediment builds up across rivers faster than the sea can remove. Deltas are strengthened by sediment that is dumped on them as floodwaters hit estuaries. Additionally, to shield the coast from storms and waves, they are incredibly productive areas. 4. Floods Recharge Groundwater More floodwater recharges groundwater resources. Aquifers allow water to seep into the earth when the terrain is porous (loose rocks and sediment). This underground water might subsequently surface as natural springs or flow into rivers. Disadvantages of Floods1. Floods Damage-Built Infrastructure Without a doubt, the force of moving water is immense. Floods can destroy everything in their path, resulting from a river overflow or a dam failure. They cause property damage by flooding homes, buildings, and bridges. They can start fires that end in explosions. They frequently harm sewage networks as well as drainage systems. Waste material consequently overflows, causing contamination. Or they contaminate water sources, rendering the water unsafe for human consumption. 2. Flooding Leads to Economic Losses Such damage causes significant financial losses. Hurricane Katrina's $81 billion cost makes it the most expensive flood in US history. Floods prohibit people from working because they disrupt transportation and communication systems. They also destroy agricultural land and infect livestock with illnesses. Two storms in 2019 destroyed 780,000 hectares of agricultural land by flooding Malawi, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe. Significant losses can occur in regions that depend on seaside tourism and related industries. Floods may badly damage their properties or possibly stop tourists from going there. Even though these companies frequently have insurance coverage to rebuild, obtaining that money is a further challenge. 3. Loss of Lives and Social Disruption Floods can kill thousands to millions of people all at once if they are not well prepared for the floods. This is particularly true in Asia, where the population comprises farmers who live close to floodplains. Actually, in 1931, China had one of the greatest floods on the Yangtze River. Around 4 million people died directly and indirectly due to torrential rain flooding a 1300 km2 area. In addition, floods may result in physical or mental health problems for many people. They frequently lead to water pollution, which in turn causes illness outbreaks, including diarrhea and gastroenteritis. They also disturb the livelihoods of numerous populations by destroying farms and crops. 4. Extreme Floods Cause Erosion As it is, severe flooding incidents can potentially remove a sizable amount of sediment. The steep terrain may eventually result in bank erosion, collapse, or even landslides. For instance, in the Indian state of Assam, substantial erosion is brought on by monsoon flooding. The Brahmaputra River's width has risen by 15 kilometers due to bank erosion! 5. Flooding Causes Algal Blooms Regrettably, flooding can also cause algal blooms in lakes, rivers, and oceans. The abundance of nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, encourage algae to grow and reproduce quickly. They eventually cover the water's surface, preventing oxygen from entering. As a result, inner-living organisms die. ConclusionIt is surprising that this natural disaster continues to ravage the globe on a regular basis, leaving an ever-growing path of devastation and death in its wake. Unrestrained migration into flood-prone areas is the biggest contributor to this, especially in developing nations. While accepting that such mobility is required for survival, the public must be made aware that flood warnings should be listened to and that fundamental safeguards should be taken seriously and correctly. The only option in the current situation is to launch and sustain a robust, well-received, and well-funded educational campaign focused on reducing future flood-related losses. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










