Advantages and Disadvantages of Global Positioning System
Your forefathers relied on the night sky to pinpoint their locations. A Thomas guide was then employed. Modern technological advancements allow us to utilize cell phones or other navigational aids to determine our whereabouts. Today, all it takes is one miraculous piece of technology to acquire driving directions, communicate your outdoor location to a companion who got lost or keep track of your workout distance. The Global Positioning Systemcommonly referred to as GPS, is the name of such technology. You may already be familiar with GPS, but in this part, we will examine its operation, benefits, and drawbacks.
What is GPS?
- The Global Positioning System, or GPS, was initially invented by the military.
- The US Department of Defence (USDOD) commissioned the first 11 GPS satellites in 1978 for military use under Navstar.
- However, not all the Navstar satellites were capable of reaching their orbits. Thus, there was still to be accomplished.
- GPS was completely operational in the US by 1995, and it was first implemented in automobiles in 1996.
- Until May 2000, the finest quality frequencies were solely used for military operations. Then, they were made freely reachable to people.
- The US air force now administers GPS.
- To get absolute accuracy anywhere, many contemporary receivers rely on GPS and the Russian GLONASS satellite.
What is GPS?
- A cluster of satellites circles the globe every 11 hours and 58 minutes at an altitude of more than 20,000 kilometers.
- These satellites repeatedly transmit messages back to us on the ground, which are gathered by things like your cell phones or the GPS systems in your vehicles and enable us to know where you are in the world.
- GPS is practically everywhere.
- For proper operation, GPS does not necessitate a phone signal or an internet connection. But when they're around, it works better.
- You can now get GPS Insoles to monitor family members or elderly people with Alzheimer's.
Types of Navigational Systems
- Foreign powers throughout the world utilize various kinds of navigational satellite systems.
- However, the Navstar, an American system, is the most well-known and frequently employed system.
- Although the Indian and Chinese systems are not global because they are stationed in geosynchronous orbits over their respective territories, there are similar Russian,and European systems.
- The positioning of the GPS satellites is such that you should be able to see at least four of them directly overhead from practically any place on the planet's surface. This is significant since calculating three location coordinates and the clock deviation using GPS point positioning requires at least four satellites.
How does it work?
- Through trilateration, GPS operates.
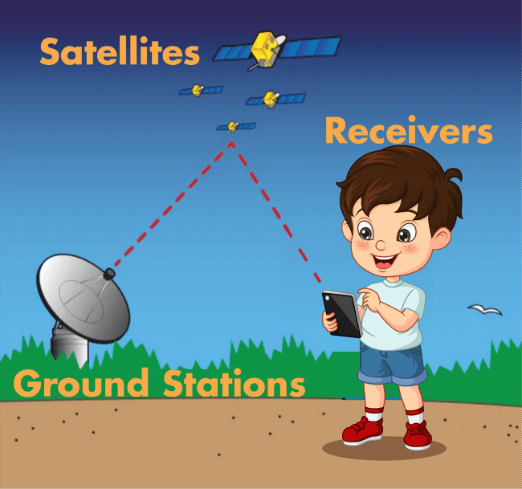
- So, to put it plainly, the three fundamental components of the GPS are satellites, ground stations, and receivers.
- The stars and constellations that our predecessors relied upon to determine their position are like today's modern satellites.
- They must show up where they are expected to and at what time.
- Ground stations locate radars to confirm that the satellites are actually where they claim to be.
- Your smartphone or vehicle's receiver monitors the satellite's pulse to calculate its distance from you.
- It can pinpoint your location within a foot or even less precision when it determines how distant you are located from four or more GPS satellites.
- There are 32 operational satellites in orbit for the GPS.
- 24 are fundamental satellites, and the remaining one's act as backups if something happens to the others.
- They frequently require repairs as well as ongoing upkeep. Even yet, they only have a lifespan of about ten years.
- GPS is weather-proof.
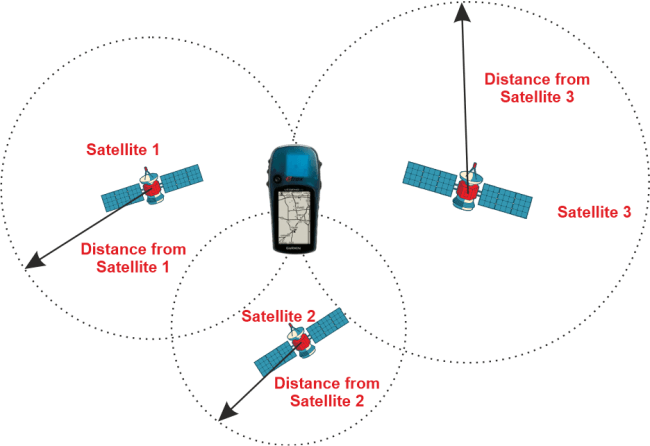
- Because the GPS uses a trilateration system, a receiver on the planet must recognize at least four satellites to pinpoint its precise location.
- Predicting its latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates on a map is what 2D and 3D trilateration entail.
- There will be spheres rather than circles on your drawings regarding 3D trilateration; otherwise, everything is the same.
- Latitude, longitude, and altitude are components of 3D locations.
- If you know that you are located 50 miles near satellite A, you can presume that you are somewhere inside a hypothetical hemisphere with a 50-mile radius.
- Additionally, you are certain that you are 20 miles from satellite B.
- A circle results from the intersection of two spheres.
- You can construct a second sphere by multiplying the distance from the third satellite by two to get two points of intersection.
- Let's use the Earth itself as the fourth sphere since you are aware that just one of the two potential points is what you require and that you are on the ground.
- The accuracy of your position will increase as you employ more satellites.
- The GPS satellites broadcast their time and location information to a GPS receiver at regular intervals.
- Transmissions are employed to convey data to the receiver.
- The receivers evaluate the radio signals from the GPS satellites to determine two crucial things:
- The position and separation between you and at least three satellites in the region above you.
- Radio waves propagate at a similar speed as light.
- Based on the time needed for the signals to traverse from orbit to the planet, the receiver estimates the distance the signal has traversed.
- It's not that easy, though.
- Atomic clocks employed by GPS satellites to guarantee the most accurate time are not capable of being installed in every receiver.
- They range in price from 50,000 to 10,000 USD. Your cellphone would become quite pricey as a result.
- The receiver, therefore, has standard quartz clocks that are constantly updated or modified to deliver the most precise time.
- They can do this because of the data that the satellites send them.
- The concern here is that, according to Einstein's general theory of relativity, time advances more rapidly for entities that are distant from the effects of gravity.
- Every day, the satellite's atomic clock advances earth clocks by 38 microseconds.
- GPS position would be inaccurate by an additional 6 kilometers per day if scientists did nothing.
- But the issue can be resolved, as well as the precise placement of objects can be possible, by using at least three or four satellites.
- Even if you picked the wrong numbers, they would eventually intersect when we employ three satellites and three spheres. There is no possibility that we will obtain the incorrect measurements when we have four spheres.
- Several circumstances may influence the GPS signal and accuracy.
- For instance, in a location with plenty of tall structures the GPS signal will be impeded by reflective windows in addition to being blocked by dense buildings, which will reduce GPS accuracy.
- Similarly, as they get too numerous, things like thriving trees, power stations, cell sites, electric cables, and poles obstruct the GPS signal.
Advantages of GPS
- Because GPS tells you which way to go for every turn you make or must make to get to your destination, it makes navigation incredibly simple.
- A survey can be completed more quickly and with more accuracy with GPS, which also helps to minimize the overall completion time.
- Manual measurement is also made easier with GPS because there is minimal room for any errors.
- GPS operates in all weather, so you don't have to bother about the weather as you would with other navigational devices.
- The best navigational system for boats is this one because we frequently get lost in bigger water bodies due to a lack of clear directions.
- It also helps us find nearby restaurants, hotels, and gas stations.
- The US government updates the system frequently and is, therefore, very advanced.
- It can be integrated into other technologies due to its extremely low cost.
- Finally, GPS is very affordable compared to other navigational devices.
Disadvantages of GPS
- Higher capital expenses; specific hardware and software requirements; vulnerability to orbital and atmospheric multipath disruptions.
- Required ambiguity-fixed or continuous locks
- These current GPS techniques have two drawbacks:
- They are more prone to multipath disturbance than the traditional static technique, which can impact the receiver signals during both kinematic and static changes in the tracking.
- Short observation sessions produce results that are more vulnerable to poor satellite geometry than traditional static procedures, making multipath during the ambiguity resolution period particularly risky as incorrect ambiguities may occur.
Applications of GPS
- GPS's free, open source, and reliable nature have led to the development of numerous applications influencing every part of modern life.
- Everything from mobile phones and smartwatches to bulldozers, cargo containers, and ATMs now incorporates GPS technology.
- GPS boosts productivity in many sectors of the economy, including farming, construction, mining, and package delivery.
Practice Questions
What is GPS?
They are cluster of satellites that orbit the planet every 11 hours and 58 minutes at an altitude of more than 20,000 kilometers.
What are the different navigational systems available?
Navstar, GLONASS and the systems of India, China, and Europe.
What are the advantages of GPS?
Affordable, error free, operates in all weather, free, open source, and reliable in nature.
What are the applications of GPS?
- Everything from mobile phones and smartwatches to bulldozers, cargo containers, and ATMs now incorporates GPS technology.
- GPS boosts productivity in many sectors of the economy, including farming, construction, mining, and package delivery.
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now












