Advantages and Disadvantages of LVDTLinear Variable Differential Transformer is referred to as LVDT in short form. It is a typical electromechanical transducer that may transform the rectilinear motion of an element to which it is mechanically connected into an associated electrical signal. 
There are commercially available LVDT linear position sensors that can estimate movements as little as a few hundredths of an inch up to a few inches. Still, they can also measure positions up to 30 inches (or 0.762 meters), which is the maximum measurement range. Types of LVDTThe various types of LVDTs include all the following:
Linear Variable Displacement Transducers are frequently employed in modern automated, robotic, or motion control systems, avionics, and manufacturing machines. Specifications can be used to evaluate the selection of a suitable LVDT type. LVDT ConstructionThe LVDT consists of a cylindrical former with two minor LVDT windings coiled on the surfaces and one main winding inside the hub of the former. Both minor windings have an equal number of twists but are wound in opposite directions, such as clockwise and anticlockwise. 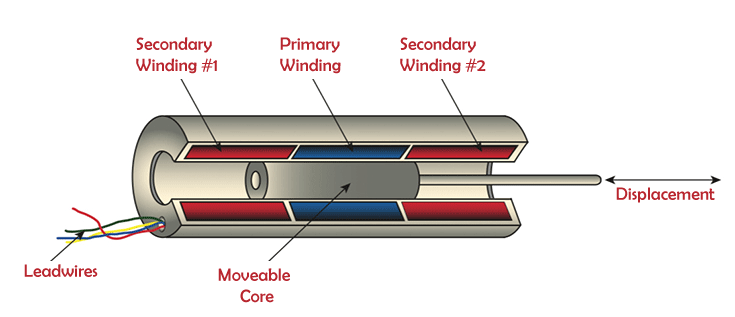
The change in voltages between the two minor coils will thus be the o/p voltages. S1 and S2 are used to classify these two coils. The cylindrical former's Esteem iron core is at the centre of it. The operating frequency of AC is provided by 50 to 400 HZ, and the excitation voltage is 5-12V. LVDT Working PrincipleMutual induction is the working principle behind how the linear variable differential transformer, or LVDT, operates. The dislocation is the transformation of nonelectrical energy into electrical energy. The functioning of an LVDT also goes into great depth regarding how the energy is changed. LVDT's workingDepending on where the iron core is located in the insulated former, there are three ways the LVDT circuit design can operate. 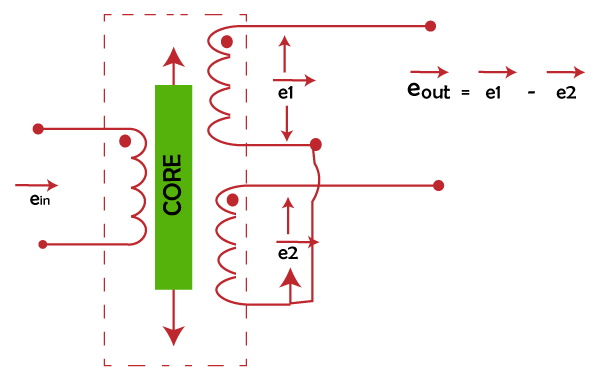
CASE IThe induced EMF is the same in both windings whenever the core is at a null position (for no displacement). The flux coupling with both secondary windings is equal when the core is null. Since e1 and e2 are identical, the output value is zero when there is no displacement. Therefore, it demonstrates that there was no displacement. CASE IIIn this case, the flux connecting with secondary winding S1 is greater than the flux connecting with S2 when the core is displaced upwards of the null position (for movement upward of the reference point). This causes the output voltage to be positive. As a result, e1 will resemble e2 more. CASE IIIWhen the core is shifted to the downward Null position(for movement downward of the reference point), the magnitude of e2 in this situation will be greater than e1's magnitude. Because of this, the output will be negative & will be below the reference point. Output of LVDTA sine wave with an amplitude proportional to the location's off-centeredness and 1800 degrees out of phase, depending on which side of the core is the output of a measurement device such as an LVDT or linear variable differential transformer. Here, the signal is demodulated using full-wave rectification. When the core displacement is maximum from the centre position, the engine out (EOUT) value is highest. It is an amplitude function of both the primary side excitation voltage and the sensitivity parameter of the particular LVDT type, and it is quite significant at RMS. Use of LVDTA position sensor like an LVDT is the best choice for many applications. These are some of the uses listed below.
LVDT GraphThe LVDT graph diagrams display the shaft changes and their effects on the magnitude of the differential AC output from a null point and the direct current output from electronics. 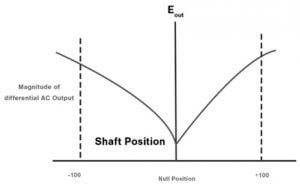
The key factors affecting the maximum shaft displacement from the core position are the sensitivity factor and the amplitude of the primary excitation voltage. The shaft remains null until a comparable primary excitation voltage is applied to the coil's main winding. Advantages of LVDT (Linear variable differential transformer)
A few more advantages include the following:
Disadvantages of LVDT (Linear variable differential transformer)Need for extra setup: Extra setup is necessary because the LVDT is delicate to stray magnetic fields; as a result, additional configuration is needed to shield it from these fields. As a result, it gets a little pricey. Affected by several factors:
LVDT applications
Next TopicAdvantages and Disadvantages of Machine
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










