Advantages and Disadvantages of Mendeleev's Periodic Table
Mendeleev's periodic table refers to the table which interprets elements in a rising atomic mass order in a tablet pattern, such that it expresses likeness order and movements in the behavior of components.
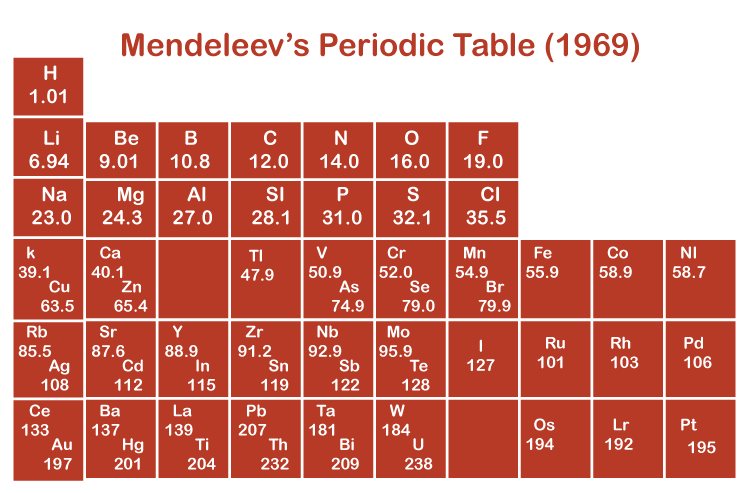
The Scientist Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev provided an apparent fundamental notion before creating the table, and thus he is referred to as the Father of the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was enlisted in 1869, heeding the denial of Newlands Octave Law. Elements in Mendeleev's periodic chart were situated according to their basic and essential properties, atomic mass, and chemical factors. This periodic table brought into the world 63 elements as members. In the periodic table, the elements were organized horizontally in 10 series in the decree of their gaining atomic weights. These series were split into 7 horizontal columns (period) and 8 vertical columns (groups).
Mendeleev's periodic law
Based on his investigations, he evolved a standard known as Mendeleev's Periodic Law. This law affirms that "The physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic function of their atomic weights". Mendeleev's periodic physical and chemical properties of the components depend on the atomic weight of the components, in which they are arranged in rising order of their atomic weight and the ones with like properties repeat after regular intervals of rising atomic weight.
Features of Mendeleev's periodic table
- Mendeleev constructed the elements in a table and referred groups to columns and rows as periods.
- There are nine groups in the table which are named in Roman numbers I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII, and 0.
- There are two subgroups in the first seven columns. Elements on the left side of each group belong to subgroup A and on the right side belong to subgroup B.
- In order to adjust more elements, periods IV, V, VI, and VII are divided into two halves.
- First period in the table is considered the shortest one because of containing only one element Hydrogen.
Advantages of Mendeleev's periodic table
- Mendeleev's periodic table symmetrically categorized the components. By recognizing the properties of one element, the properties of other elements and their compounds in the group are imagined, which makes the analysis of elements simpler.
- When Mendeleev's periodic table was proposed, only 63 elements were inferred. Therefore, while categorizing the elements according to their properties, Mendeleev vacated some empty positions. These empty positions illustrated hidden elements. Moreover, Mendeleev anticipated the properties of these unknown elements based on their position. Eka-aluminium and Eka-site cons can be contemplated as an example.
- Accurate atomic masses of numerous elements were discerned with the support of Mendeleev's periodic table.
Disadvantages of Mendeleev's periodic table
- The position of hydrogen is its primary demerit. Based on its properties, hydrogen should have been positioned in both parties, IA and VIIA. Even today, hydrogen displays the properties of alkali metals (IA group) and halogens (VIIA group). But, hydrogen has been set in the IA group in this periodic table.
- The position of isotopes is another con faced in this table. In Mendeleev's periodic table, components are adapted to the rising atomic masses. Therefore, isotopes of an element need to be positioned at different places. But this will be unreliable because isotopes hold up identical chemical properties.
- Position of lanthanides and actinides again came as a problem in the table. The 14 elements obeying lanthanum, atomic numbers 58 to 71, are lanthanides and the 14 elements pursuing actinium, atomic numbers 90−103, are actinides. These configurations are bizarre in Mendeleev's periodic table since Mendeleev's periodic law is unfollowed.
- Elements with variable valency had become a major issue in this table. An enormous amount of elements exhibit more than one valency. But this was not spoken of in Mendeleev's periodic table.
- Related elements are not placed in the same factions. The elements such as silver and thallium, barium and lead, and copper and mercury demonstrating identical properties are positioned in a varied faction in Mendeleev's periodic table.
- Irregular pairs of elements are placed in the table. Various elements are not organized in the intensifying atomic mass, i.e., not seated according to Mendeleev's periodic law.
- Dissimilar elements are positioned in the same groups. Subgroups A and B of a particular group display varied physical and chemical properties, but they are situated in the exact faction in Mendeleev's periodic table.
- No adequate justification has been proposed for the truth that why the elements seated in a faction display likeness in their properties.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










