What is the full form of AMLAML: Acute Myeloid LeukemiaAML stands for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. It is a type of blood cancer that starts in the bone marrow where it affects the immature blood cells (myeloid cells) that are precursors to other blood cells like red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. It causes the myeloid cells to mutate and form leukemic blasts. Thus, it affects the formation of normal healthy cells. Eventually, there will be a shortage of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in the body of the affected person. 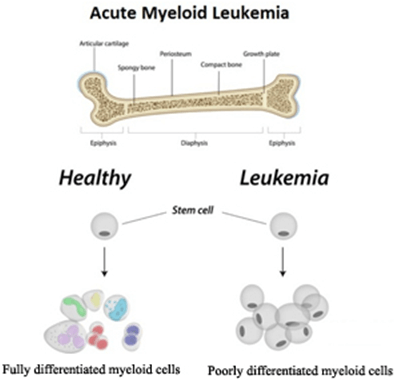
There are different types of AML based on the type of leukemic cells present in the blood and bone marrow. It is also known as acute myelogenous leukemia, acute myeloblastic leukemia, and acute nonlymphocytic leukemia. AML is caused by unfavorable changes (mutations) in the genes of the DNA of myeloid cells present in the bone marrow. The exact reasons for these mutations are not known. Symptoms
Risk Factors
Various AML subtypes:The majority of AML subtypes are determined by the cancer cells' maturity (development) and degree of divergence from normal cells at the time of diagnosis. A subtype of AML is acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL). An aberrant gene termed PML-RARA is created when several genes on chromosome 15 switch places with a few genes on chromosome 17, resulting in this leukaemia. A message is sent by the PML-RARA gene that prevents the maturation of promyelocytes, a kind of white blood cell. Blood clots and major bleeding issues could develop. This is a major health issue that requires immediate attention. APL typically affects individuals in their middle years. Number of factors for prognosis (chances of recovery) and available treatments:The prognosis and available therapies rely on:
Acute leukaemia must receive immediate medical attention. Treatments:
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










