Application Layer in OSI Model
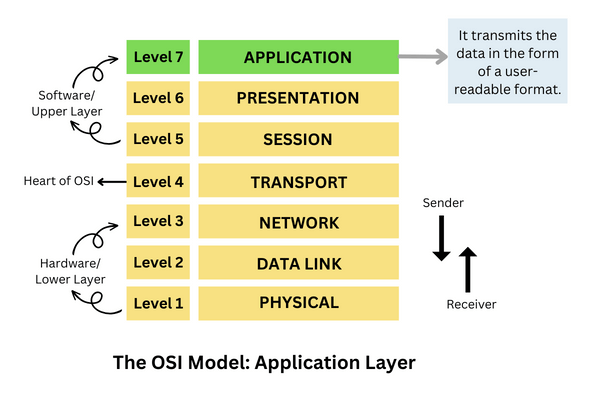
The application layer is the last and 7th layer from the bottom of the OSI model. It is a layer through which the end user can communicate directly with the software. The application layer transmits the data in the form of a user-readable format. It provides many services to the user. It transfers data to the presentation layer. Furthermore, it either provides services to the presentation layer or takes services from the presentation layer.
Not only that, but it is the responsibility of the application layer that the communication between two hosts is taken place smoothly without any disturbance. The application layer ensures that the required media is available on both hosts. It determines which protocol is to be used while communicating between the hosts.
It delivers the standard interface that applications can use to transmit and obtain information to communicate with each other over the network. The application layer includes different protocols that are used in email communication, file transfer, web browsing, and more. These protocols deliver a standardized method for applications to convey messages to each other.
Functions of the application layer in the OSI model
- The application layer determines the communication partner to whom data will be transmitted.
- This layer specifies the availability of resources, i.e., it checks whether adequate network resources are available or not.
- This layer delivers protocols that are accountable for creating seamless transmission between applications.
- This layer serves as an interface between user applications and the network.
- This layer delivers directory services, which means it permits access to any sort of data from a distributed database.
- This layer delivers several facilities to the users for multiple email forwarding and storage facilities.
- This layer lets users log into a remote host and access any type of application.
- This layer lets the user access the files in the remote host.
- This layer provides email services.
- This layer provides file transfer access and management.
- This layer communicates with the operating system and guarantees that data is saved properly.
- This layer enables users to communicate with other software applications.
Protocols of the application layer in the OSI model:
- SMTP: It is an abbreviation for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol which is a TCP/IP protocol used to organize email. With the use of this protocol, data is sent from one email address to another. It is accountable for the transmission of email messages over the Internet. It is a valid protocol for ensuring the delivery of email messages. It also provides security for email transmission by supporting authentication mechanisms.
- HTTP: It is an abbreviation for Hypertext Transfer Protocol that allows users to access Internet data. It is accountable for the conversation between the client and the web server. When a user requests data, the browser transmits an HTTP request to a server hosting the data. The server replies with an HTTP response, which holds the requested data or an error notification if the data is not found or cannot be accessed.
- FTP: It is the short form for File Transfer Protocol which is used to send files between server and client using the internet. It uses a client-server model, where the client requests a file, and the server responds with the requested file. It uses TCP to share data as TCP delivers error-free transmission of data.
- TFTP: It is the short form for Trivial File Transfer Protocol. It is a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) based protocol, which means it is unreliable and connectionless. It transmits all commands and data over a single UDP port. It is used when a lightweight and fast file transfer protocol is required. It is uncomplicated to use and configure.
- DNS: It is the short form for Domain Name System that translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses so that web browsers can comprehend what a user desires to access on the Internet.
- SNMP: It is an abbreviation for Simple Network Management Protocol used for managing and monitoring network devices and systems. Using this protocol, network administrators gather data about network performance, identify and troubleshoot problems, and remotely configure network tools.
- TELNET: It is an abbreviation for telecommunication network that delivers remote access to a network appliance. It is a client-server protocol that uses TCP to establish a link between a client and a server. It uses a simple text-based interface that enables users to execute commands and obtain feedback from the server.
Conclusion:
- In this article, you have studied the Application Layer in OSI Model. It is the 7th layer in the OSI model which provides communication to end-user applications. The primary role of this layer is to support interoperability between applications on different devices on a network.
- You have learned about the functions of the application layer, such as file transfer, email services, directory services, and remote login.
- You have gained knowledge of several protocols of the application layer, such as Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Telecommunication Network (TELNET), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Domain Name System (DNS), and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










