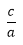Aptitude Algebraic Expressions Concepts and FormulasPoints to Remember:1. Quadratic Equations:(i) An equation of the type ax2 + bx + c =0 is called the quadratic equation. (ii) The highest power of the variable is called the degree of an equation. (iii) An equation will have as many solutions as its degree. If an equation is of n degree, it will have 'n' solutions. (iv) The solution of an equation is the value by which equation is satisfied. The values of the solution of an equation are also called the roots of the equation. This quadratic equation has two solutions. 2. Solving Quadratic Equations:Any quadratic equation can be either solved by the factor method or by formula. (i) By the factor method: First find the factors of the given equation making the right-hand side equal to zero and then by equating the factors to zero, we get the values of the variable. (ii) By Formula: Consider a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0,for finding the roots of the equation, we use the following formula: 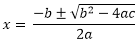
Here + and - in the above formula is used to get the two values of x. Here the quantity b2 - 4ac is called the discriminant. 3. Roots of the Quadratic Equation:The value of the x that we obtain from a quadratic equation is called the root of the equation; α and β are used to denote the roots of the equation. (i) Sum of the roots of a quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0is equal to (ii) The product of the roots is equal to α*β = (iii) Consider a quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0. 4. Whenever we are given the roots of a quadratic equation, then the equation will be 5. (i) When a quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c =0, has one root equal to zero, then c = 0. (ii) A quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c = 0, will have reciprocal roots, if a = c. (iii) When the roots of a quadratic equation, ax2 + bx + c, are negative reciprocals of each other, then c = -a. (iv) When both the roots are equal to zero, b = 0 and c = 0. (v) When one root is infinite, then a = 0 and when both the roots are infinite, then a = 0 and b = 0. (vi) When the roots have equal magnitude but are opposite in sign, then b = 0. (vii) When two quadratic equations, ax2 + bx + c = 0 and a1x2 + b1x + c1 = 0, and have a common root, then (bc1- b1c) (ab1 - a1b) = (c1a - ca1)2. (viii) When they have both the roots common, then 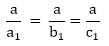
6. Linear Equations:A statement of equality that contains an unknown quantity or variable is called an equation. In a linear equation the pattern of numbers increases or decreases by the same amount every step of the way, so the graph of a linear equation is always a straight line. Aptitude Algebraic Expressions Test Paper 1 Aptitude Algebraic Expressions Test Paper 2 Aptitude Algebraic Expressions Test Paper 3 Aptitude Algebraic Expressions Test Paper 4 |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share





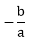 i.e.,α+β=
i.e.,α+β=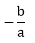
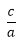 , i.e.,
, i.e.,