Ascorbic AcidAscorbic Acid, which is also called Vitamin C, is a natural water-soluble vitamin. It is an odorless, white to pale yellow crystalline powder with an acidic taste. Ascorbic acid is also a potent antioxidant that fights off free radicals and thus protects your cells from the damage caused by free radicals. Our body cannot make produce vitamin C, so we have to get it from food or supplements. Vitamin C is abundantly found in citrus fruits, potatoes, berries, tomatoes, cabbage, broccoli, peppers, spinach, etc. Ascorbic acid tends to darken when exposed to light. It is stable in a dry state but quickly oxidizes in a solution. Its chemical name is L-ascorbic acid. Its chemical formula is C6H8O6. Its other chemical names include ascorbate and antiscorbutic vitamin. Chemical Structure of Ascorbic AcidThe ascorbic acid molecule is made of asymmetrical six-carbon atoms (C6H8O6), which is related to glucose in terms of its structure. 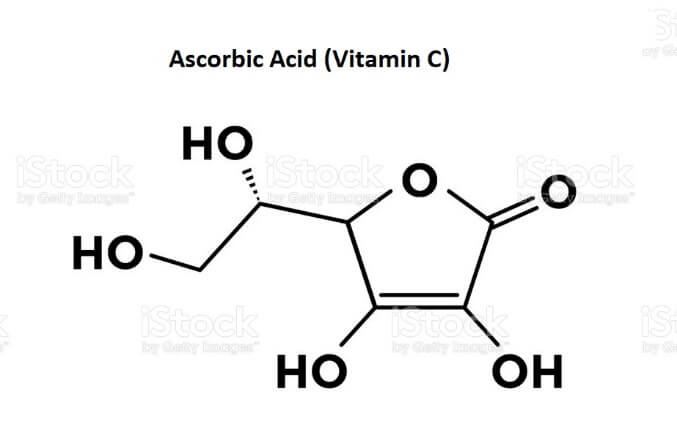
Why is Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) prescribed?It is generally prescribed when we are not getting a sufficient amount of vitamin C from the diet. It is also recommended to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by the deficiency of vitamin C and which causes fatigue, anemia, bleeding gums, joint pain, and affect wound healing, and more. The required amount of vitamin C can be obtained from a healthy diet. Further, the deficiency of vitamin C is common in people who:
Recommended Daily Dose of Vitamin CFor adult men: 90 milligrams For adult women: 75 milligrams Safety and side effectsThe appropriate dose of vitamin is usually considered safe. However, taking a large amount of vitamin C can cause the following side effects:
Further, in some cases, too much consumption of vitamin C may lead to kidney stones, and when taken over 2,000 mg per day for a long time it may cause severe side effects. Also, before any medical test, inform your doctor that you are taking vitamin C supplements. This is because the high levels of vitamin C may affect the outcome of some medical tests such as stool tests for occult blood or glucose tests. Interactions of Ascorbic Acid in the bodyHere are the possible interactions of ascorbic acid: Aluminum: The intake of vitamin C supplements can increase the absorption of aluminum from medicines that contain aluminum such as phosphate binders. It may lead to severe health issues in people with kidney problems. Chemotherapy: It is believed that intake of antioxidants like vitamin C may reduce the effect of drugs during chemotherapy. Estrogen: It may increase the estrogen hormone levels if taken with oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy. Protease inhibitors: if taken orally, vitamin C may reduce the effect of these antiviral drugs. Statins and niacin: The benefits of niacin and statins can be less if they are taken along with the vitamin C supplements. Warfarin (Jantoven): The response to warfarin (an anticoagulant) may reduce if you are taking high doses of vitamin C. Health Benefits of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) offers lots of health benefits as it plays many vital roles in our body. Here are some of the major health benefits of ascorbic acid or vitamin C.
Furthermore, people who consume alcohol regularly and also have other illnesses often have a deficiency of vitamin C. They may need to take vitamin C for a longer time than normal duration to restore the vitamin C levels to normal. PrecautionsFollowing types of patients should not take vitamin C over an extended period of time.
Side effects of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)
The physical and chemical properties of ascorbic acid are based on its chemical structure. Physical Properties of Ascorbic Acid
Chemical Properties of Ascorbic Acid
Uses of Ascorbic AcidIt is widely used in the food industry as being a potent antioxidant it functions as a preservative that delays food spoiling due to bacteria, fungi, yeasts, mold and exposure to air. Further, the low pH of vitamin C helps prevent microbial growth. So, it is a popular natural preservative. According to the FDA, antioxidants helps prevent fats and oils in foods from tasting bad and becoming rancid. According to WHO, milk fortified with iron and vitamin C helps reduce iron deficiency in infants and young children as it promotes iron absorption. Difference between Ascorbic Acid and Citric AcidCitric Acid is also a weak organic acid with antioxidant properties like ascorbic acid. But, it is not a vitamin or nutrient like ascorbic acid. So, although these acids have lots of things in common, they are different from each other. Here are some of the major differences between ascorbic acid and citric acid.
Next Topic#
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










