Copy and Rotate commandCopyThe copy command is used to copy the objects. The concept is the same as Ctrl + C to copy and Ctrl + V to paste, which can also be used in AutoCAD. The objects are copied in a specified direction and at a specified distance. The Copy icon on the ribbon panel looks like the below image: 
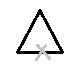
The steps to copy the objects are listed below: 1. Select the copy icon from the ribbon panel. Or Type co or copy in the command line or command prompt and press Enter. 2. Select the objects. To select it, click on the boundary of objects through a small square cursor. 3. After the selection is completed, press Enter. 4. Specify the displacement or base point. Base Point 5. Specify the base point of the objects. 6. Specify the second base point. It is the point where we want to move that object. The process is shown in the below image: 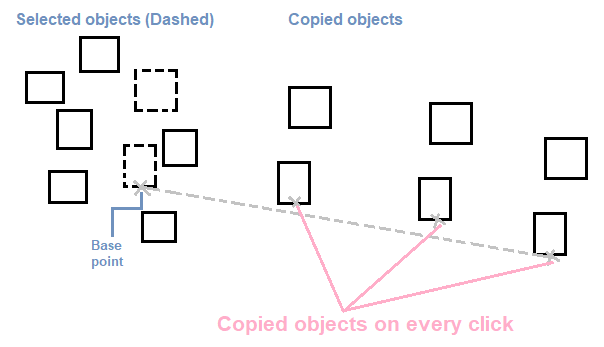
7. To continue copying objects, repeat steps 5 and 6. 8. To Exit, press the Esc button. Or 5. Specify the base point of the objects. 6. Type the displacement value, such as, 5. The distance 5 will be measured from the original object. 7. Press Enter. 8. To continue copying objects, repeat steps 6 and 7. Or Displacement 5. Type D on the command line. 6. Specify the value of displacement in the form of (X, Y, Z), for example, 2, 3. In this, the object will be moved 2 units in the X-axis and 3 units in the Y-axis from the original or current position. 7. Press Enter. Single/Multiple modes to copy objectsThe single-mode allows copying the objects once. The command exits automatically after it. The multiple mode allows copying the objects number of times. We need to press Esc to exit. Steps for single-mode The steps to implement the single-mode are listed below:
The process is shown in the below image: 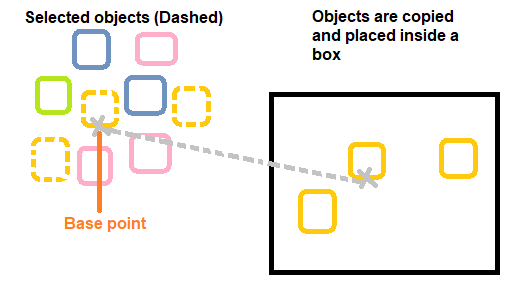
Steps for multiple mode The steps to implement the multiple mode are listed below:
The process is shown in the below image: 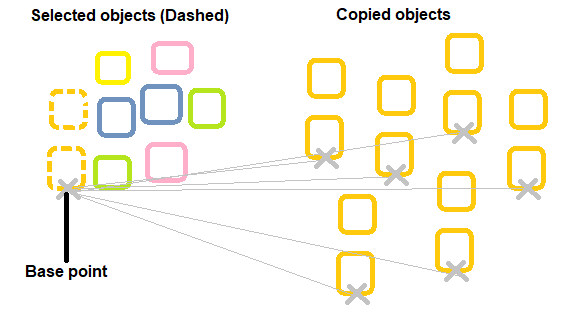
Example: To copy triangles in the boxes The image for such an example is given below: 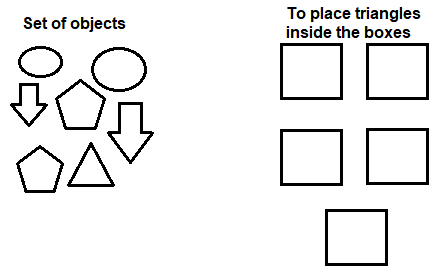
In the above image, we need to copy the triangles from the set of figures and place them inside the boxes. The steps for such an example are listed below:
The process is shown in the below image: 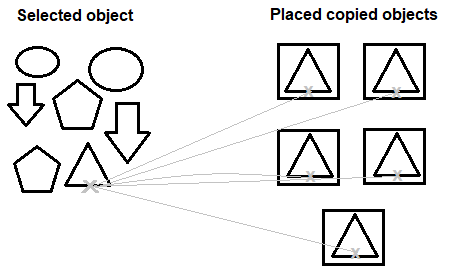
Copying objects in the form of an arrayThe objects can be copied in the form of the array as well. Here, the selected objects will be first arranged in the form of an array (copies placed in parallel) and then placed on the specified position. The objects can be copied in a straight line and diagonally with respect to the axis of the specified base point. Let's understand with an example. Example: To copy the square 6 times in a straight line The set of figures is shown in the below image: 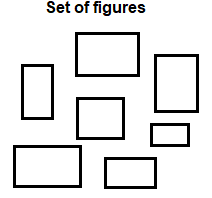
The steps for such an example are given below: 1. Type co or copy in the command line or command prompt and press Enter. 2. Select the square from the set of figures, as shown in the below image: 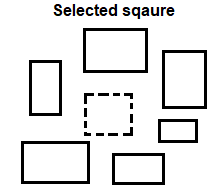
3. After the selection, press Enter. 4. Type mo or mode in the command line and press Enter. 5. Type M or multiple in the command line and press Enter. 6. Specify the base point on the square. We can specify any point on the boundary of the square. 7. Type A or Array and press Enter. 8. Specify the numbers of items to the array, which means enter the number of items to be copied (including the object). For example, to create 2 copies of an object, enter value =3 (2 copies + object). 9. Specify the gap between the objects through the cursor. The distance between objects will be the distance between the original object and the first copy of the object, as shown in the below image: 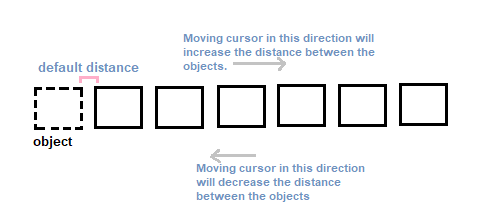
The above objects can also be copied diagonally by moving the cursor diagonally. 10. Click on the viewport when the distance is adjusted. 11. Continue clicking on the points to place the copied object. But after the next click the object will be copied only once per click, as shown in the below image: 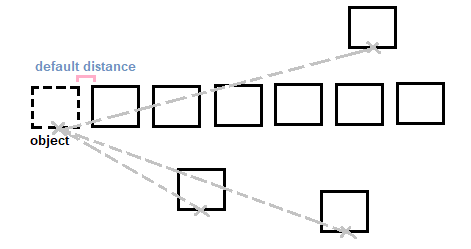
For array, we need to follow the above steps again. 12. Press the Esc button to exit from the copy command.
Next TopicRotate Command
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share