Bacterial Infection SymptomsSometimes, certain germs that cause disease can infiltrate the body. Once inside, they might spread and infect the area. The location of the infection within the body will frequently affect the symptoms that manifest. 
This article will list a few bacterial infection symptoms and indicators according to where they manifest in the body. Additionally, it will offer guidance on when to visit a doctor as well as details on treating and preventing bacterial illnesses. General Symptoms of a Bacterial InfectionThe signs and symptoms of the infections vary with the disease and also the type of people. It also varies with where the infection is occurring in the body. Nevertheless, a few of the most typical general indications of infection include:
The Signs by the BodyAlthough bacterial illnesses can manifest themselves everywhere in the body, they frequently happen close to points where germs can enter the body. The most typical symptoms and indicators of bacterial infections in various body areas are described in the following sections. 
Digestive Tract InfectionsAlthough various bacterial species induce somewhat different symptoms, the majority of them frequently cause many of the following:
Infections of the Upper Respiratory TractThe sinuses and nasal tubes are part of the upper respiratory system. The skull's sinuses are a network of hollow spaces. Bacteria or viruses can occasionally infect the sinuses. Sinusitis is the medical word for sinus infection and sinus inflammation. The following are typical sinusitis symptoms and signs:
Components Make Up the Lower Respiratory TractThe following bodily components make up the lower respiratory tract

Possible Pneumonia Symptoms And Indicators Include:
Throat InfectionsThe class of bacteria which causes the tonsils and throat through infections with germs are streptococcus. Strep throat is another name for this ailment. Strep throat's most typical signs and symptoms include:
The sour throat is most common in children and teenagers. As many as 3 in 10 youngsters in the United States with a sore throat have strep throat, according to a reliable source. Infections of the WombA bacterial infection of the vagina is known as bacterial vaginosis (BV). It is a typical vaginal ailment affecting females between the ages of 15 and 44. Bacterial vaginosis symptoms and signs include: A strong, fishy smell, especially after sex, a thin, white or grey vaginal discharge, discomfort, itching, or burning inside the vagina, itching surrounding the vagina, and burning feelings after peeing. 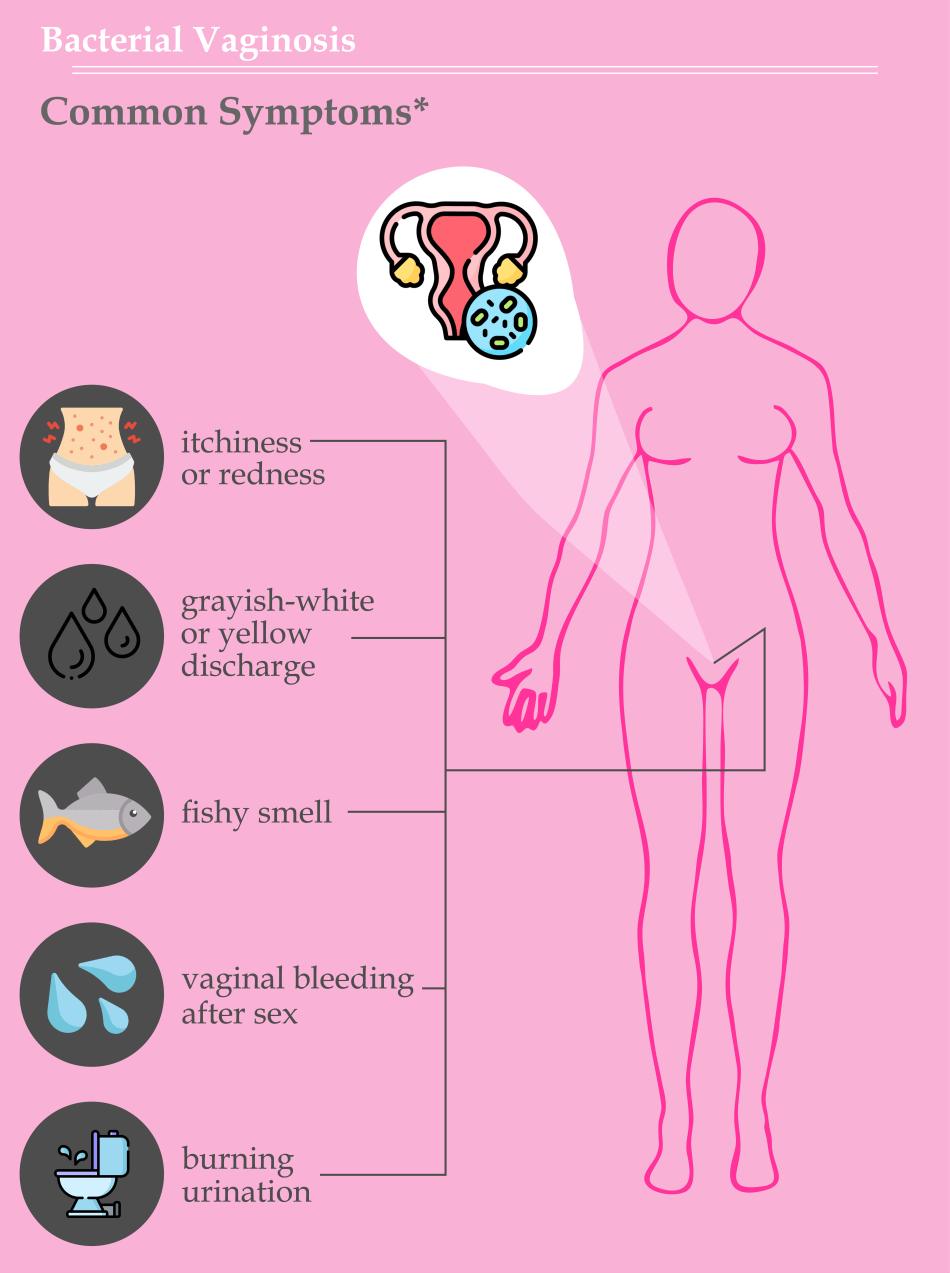
Sexually Transmissible DiseasesBacteria are responsible for the development of some STIs. Most bacterial STIs are contagious to all people. Among the typical bacterial STIs are:
Although each STI has a somewhat distinct set of symptoms, the majority can result in the following:
Skin InfectionsMost skin infections are brought on by germs entering the body through skin tears. These fractures might be the consequence of surgical incisions or wounds like burns, scratches, and cuts. Cellulitis and impetigo are two typical skin infections. Cellulitis
ImpetigoAnother typical bacterial skin illness is impetigo. Although it frequently affects the hands and face, it can also affect other body areas. Some of the common symptoms of impetigo are: Flushed, itchy lesions that ooze clear fluid are the result of impetigo. The lesions develop a honey-coloured crust over the course of many days.
Infections of the Urinary TractBacterial infections called urinary tract infections (UTIs) can appear anywhere in the urinary system. About 60% of women and 12% of men get these infections at least once in their lives. UTI warning signs and symptoms include: Cloudy discomfort in the lower back, pelvis, and lower abdomen pee leaks, painful or burning feeling when urinating, a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying after urinating, the need to urinate more frequently than usual, a strong need to urinate but being unable to produce much urine. 
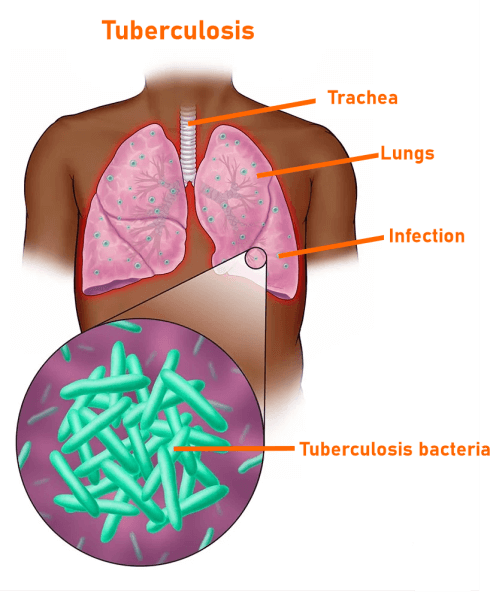
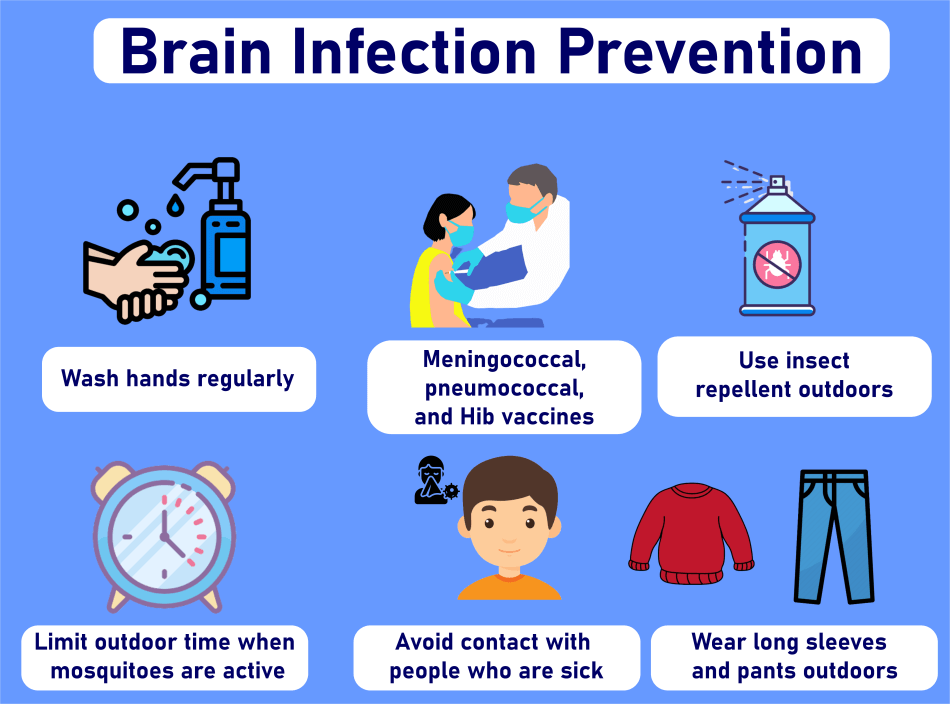
Additional signs and symptoms that might be brought on by a kidney-related UTI include:Upper back discomfort, frequently on one side of the body, nausea, and fever Infections of the Spinal Cord and Brain The medical name for a bacterial infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord is meningococcal meningitis. It is a potentially fatal disorder that needs immediate medical attention. Meningitis Symptoms and Signs Include:Fever, a sore neck, sensitivity to light, nausea, and disorientation Among the signs of meningitis in newborns and young children are the following:
MedicationViral infections differ from bacterial illnesses. For the right kind of medication to be administered, it is essential to identify the type of bacteria producing the symptoms. A course of antibiotics is often used to treat bacterial illnesses. Although few antiviral drugs are available, doctors may prescribe them for certain viral illnesses. Some diseases frequently arise as a result of either bacteria or viruses. Typical bacterial infections include:

Virus-related infections frequently occur as follows:Common cold, flu, and sore throats that are not strep throat-related Treatments Antibiotics are necessary for the majority of bacterial illnesses. For a specific bacterial infection, a doctor's recommendation for an antibiotic will often be based on the following:
There are several different antibiotic formulations. They can be used topically in creams or ointments or orally in the form of tablets. An intravenous antibiotic infusion may be necessary if a person has a serious bacterial illness. PreventionThe greatest approach to help avoid bacterial illnesses is to practise excellent hygiene. In order to practise good hygiene, one must regularly and thoroughly wash their hands and body as well as keep their personal belongings tidy. Prevented advice:
When to Visit the DoctorConsult a doctor if you believe you have a bacterial infection, especially if your symptoms worsen or continue. With timely treatment, the majority of bacterial infections disappear without any additional problems. However, infections that are left untreated or inadequately treated can worsen and develop potentially fatal consequences. If a person notices any of the following signs, they need to get quick medical attention:
Infections or other risks are more likely to occur in certain categories of people. At-risk groups that often need more close supervision or care include:
ConclusionIn conclusion, bacterial infections can result in certain common symptoms, including discomfort, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes. Apart from different signs in response to a different place in the body, an infection can also produce additional symptoms in response to the infection. The infections caused by bacteria are treated with antibiotics. The kind of antibiotic a patient gets will depend on where and how bad their illness is. Bacterial infections left untreated might result in serious or even fatal consequences. If a person has any symptoms that need quick medical attention or if their current symptoms worsen or continue, they should consult a doctor.
Next TopicTransfusion of Blood
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










