Basal Ganglia AnatomyThe brainstem, cerebellum, and cerebrum are the three main components of our central nervous system. The cerebral hemispheres, which make up the cerebrum's two almost symmetrical halves, are where the basal ganglia are located. The cerebral cortex is an organ which is composed of greyish colour made up of millions of neuronal cell bodies, it is represented as the outermost region on a coronal or axial section of the brain. The white matter of the brain, which is the innermost region, is made up of the axons that are attached to these cell bodies. 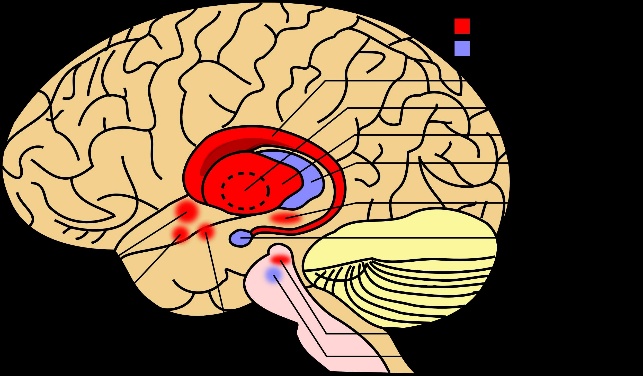
The internal capsule, which functions as a highway for signals and information to go to and from the cerebral cortex, is one major white matter fibre bundle. We can discern patches of subcortical grey matter that make up the basal ganglia on both sides of the internal capsule. In order to initiate and govern voluntary movements, the motor cortices need a feedback system from the basal ganglia. Your prefrontal cortex is used to organise your motions first, and this sends a message to both the motor cortex and the basal ganglia. The motor cortex is now assisted by the basal ganglia in planning and executing the action. As a result, your arm is in the proper position for you to begin writing. In addition, the basal ganglia can aid in the acquisition of new procedural motor abilities, such as bicycling. The caudate nucleus, which resembles the letter C, comes first. The head, body, and tail are the three organs that can make up the caudate nucleus. It curls around the thalamus and travels medially down the lateral ventricle of the brain. The internal capsule encircles the caudate nucleus laterally. The head can easily be seen in making of the lateral wall of anterior horn of the lateral ventricle on a transverse section of your brain. The body of the caudate is seen with the lateral ventricle's body wall on a coronal side. The lateral ventricle's ceiling is formed by the caudate tail, which follows the inferior horn of the ventricle and bends around the thalamus's posterior end. The lentiform, or lenticular, nucleus are the term which is used to describe the putamen along with the globus pallidus externus and internus. The wide base of this wedge-shaped nucleus points laterally. We can see that the internal capsule is near to the lentiform nucleus and separates it from the caudate nucleus and the thalamus on transverse and coronal sections of your brain. The lentiform nucleus' three parts are separated by thin white matter sheets that run vertically through it. First, the globus pallidus, which appears lighter because it has more myelinated nerve fibres, is the nucleus that is located most medially. The globus pallidus is either divided into the globus pallidus externus, which is related to the putamen, and the globus pallidus internus, which is lateral to the internal capsule, by a layer of whitish matter. The putamen is the darker-looking and most lateral of the lentiform nuclei. It is located near to the external capsule and lateral to the globus pallidus externus in body. The corpus striatum, or simply the striatum, is another name for the putamen and the caudate nucleus. Except anteriorly is, where the head of the caudate nucleus is connected with the internal capsule, these two nuclei are separated by the internal capsule. The internal capsule is crossed by tiny grey matter bridges that are superior to this connection, giving the corpus striatum its striated appearance. Take a quick pause and try to determine the purpose of the basal ganglia and the basal nuclei that make up the basal ganglia. Now that we have discussed the basal ganglia, let's shift gears and discuss other nuclei that are connected to them. The substantia nigra, which means "black substance" in Latin, is a darkly pigmented region located ventrally within the midbrain, between the tegmentum and the crus cerebri. This area appears darker in colour because of the presence of cells that carry neuromelanin-filled granules in their cytoplasm. There are two components of the substantia nigra which are known as the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr). Dopaminergic neurons are found in the SNpc, and these neurons form the nigrostriatal pathway by extending their axons to the corpus striatum, where they release dopamine.
Next TopicBasal Ganglia Calcification
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










