Bash ArrayIn this topic, we will demonstrate the basics of bash array and how they are used in bash shell scripting. An array can be defined as a collection of similar type of elements. Unlike most of the programming languages, arrays in bash scripting need not be the collection of similar elements. Since Bash does not discriminate the string from a number, an array may contain both strings and numbers. Bash does not provide support for the multidimensional arrays; we cannot have the elements which are arrays in themself. Bash provides support for one-dimensional numerically indexed arrays as well as associative arrays. To access the numerically indexed array from the last, we can use negative indices. The index of '-1' will be considered as a reference for the last element. We can use several elements in an array. Bash Array DeclarationArrays in Bash can be declared in the following ways: Creating Numerically Indexed Arrays We can use any variable as an indexed array without declaring it. To explicitly declare a variable as a Bash Array, use the keyword 'declare' and the syntax can be defined as: where, ARRAY_NAME indicates the name that we would assign to the array. Note: Rules of naming a variable in Bash are the same for naming an array.A general method to create an indexed array can be defined in the following form: where keyword 'index' is used to define positive integers. Creating Associative Arrays Unlike numerically indexed arrays, the associative arrays are firstly declared. We can use the keyword 'declare' and the -A (uppercase) option to declare the associative arrays. The syntax can be defined as: A general method to create an associative array can be defined in the following form: where index_ is used to define any string. We can also write the above form in the following way: Bash Array InitializationTo initialize a Bash Array, we can use assignment operator (=), by specifying the list of the elements within parentheses, separated by spaces like below: Note: Here, the first element will have an index 0. Also, there should be no space around the assignment operator (=).Access Elements of Bash ArrayTo access the elements of a Bash Array, we can use the following syntax: Print Bash ArrayWe can use the keyword 'declare' with a '-p' option to print all the elements of a Bash Array with all the indexes and details. The syntax to print the Bash Array can be defined as: Array OperationsOnce an array is assigned, we can perform some useful operations on it. We can display its keys and values as well as modify it by appending or removing the elements: Reference ElementsTo reference a single element, we are required to know the index number of the element. We can reference or print any element using the following syntax: Note: Curly braces ${} are required to avoid shell's filename expansion operators.For example, let's print an element of an array with an index of 2: Bash Script Output Javatpoint If we use @ or * in the place of a specified index, it will expand to all members of the array. To print all the elements, we can use the following form: Bash Script Output Welcome to Javatpoint The only difference between using @ and * is that the form is surrounded with double quotes while using @. In the first case (while using @), the expansion provides a result in a word for each element of the array. It can be better described with the help of "for loop". Assume we have an array with three elements, "Welcome", "To" and "Javatpoint": Applying a loop with @: It will produce the following result: Welcome To Javatpoint Applying a loop with *,a single result will be produced holding all the elements of the array as a single word: Welcome To Javatpoint It is important to understand the usage of @ and * because it is useful while using the form to iterate through array elements. Printing the Keys of an ArrayWe can also retrieve and print the keys used in indexed or associative arrays, instead of their respective values. It can be performed by adding the ! operator before the array name as below: Example Output 0 1 2 Finding Array LengthWe can count the number of elements contained in the array by using the following form: Example Output The array contains 3 elements Loop through the ArrayThe general method to iterate over each item in an array is by using the 'for loop'. Example Output 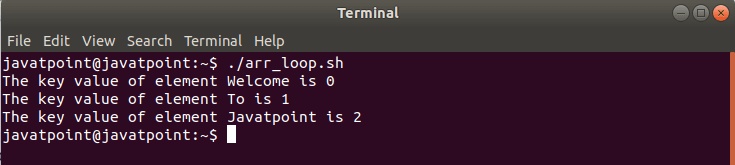
Another common method to loop through an array is to retrieve the length of the array and use the C-style loop: Bash Script Output 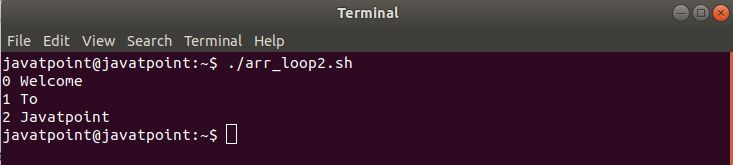
Adding Elements to an ArrayWe have an option to add elements to an indexed or associative array by specifying their index or associative key respectively. To add the new element to an array in bash, we can use the following form: Example Output Java Python PHP HTML JavaScript Another method for adding a new element to an array is by using the += operator. There is no need to specify the index in this method. We can add one or multiple elements in the array by using the following way: Example Output Java Python PHP JavaScript CSS SQL Updating Array ElementWe can update the array element by assigning a new value to the existing array by its index value. Let's change the array element at index 4 with an element 'Javatpoint'. Example Output We welcome you on Javatpoint Deleting an Element from an ArrayIf we want to delete the element from the array, we have to know its index or key in case of an associative array. An element can be removed by using the 'unset' command: An example is shown below to provide you a better understanding of this concept: Example Output Java HTML CSS JavaScript Here, we have created a simple array consisting of five elements, "Java", "Python", "HTML", "CSS" and "JavaScript". Then we removed the element "Python" from the array by using "unset" and referencing the index of it. The index of element "Python" was '1', since bash arrays start from 0. If we check the indexes of the array after removing the element, we can see that the index for the removed element is missing. We can check the indexes by adding the following command into the script: The output will look like: 0 2 3 4 This concept also works for the associative arrays. Deleting the Entire ArrayDeleting an entire array is a very simple task. It can be performed by passing the array name as an argument to the 'unset' command without specifying the index or key. Example Output 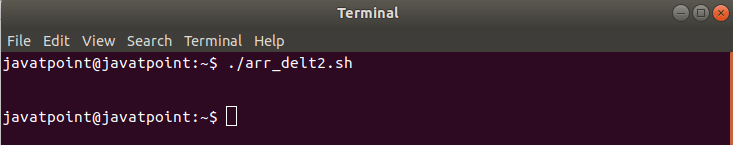
There will be no output if we try to print the content of the above script. An empty result is returned because the array doesn't exist anymore. Slice Array ElementsBash arrays can also be sliced from a given starting index to the ending index. To slice an array from starting index 'm' to an ending index 'n', we can use the following syntax: Example Output 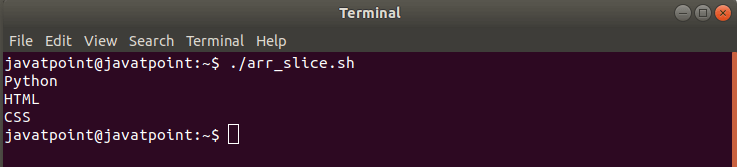
Next TopicBash Read File
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










