Benzoic AcidBenzoic acid is an organic acid with the chemical formula C6H5CO2H. It is a simple aromatic carboxylic acid, since it contains a carboxyl group bonded to a benzene ring. It got its name from gum benzoin, which served for a long time as the only source of benzoic acid. Benzoic Acid Structure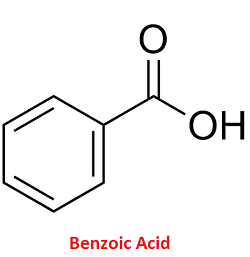
Its molecule comprises a benzene ring which is linked to a carboxyl group. Further, the molecule is made of 7 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Physical properties of benzoic acid
Chemical properties of benzoic acid
Laboratory Preparation of Benzoic Acidi) From Grignard reagent Bromobenzene is converted into benzoic acid by the carboxylation of the intermediate phenylmagnesium bromide (Grignard reagent). The steps are as follows;
ii) Oxidation of benzyl compounds It can be produced through the oxidation of benzyl derivatives, benzyl alcohol and benzyl chloride. Industrial Preparation of Benzoic AcidIn the industries, it is produced on a large scale by partial oxidation of toluene using oxygen. Cobalt or manganese naphthenates is used as a catalyst in this method. In this process, benzotrichloride is reacted with calcium hydroxide in water. Iron or iron salts are used as catalysts here. It produces calcium benzoate which is then acidified to form benzoic acid. Benzoic Acid Chemical Reactionsi) Formation of Salt Owing to the presence of a carboxyl group, which is acidic, benzoic acid tends to react with bases like sodium hydroxide to form a salt, sodium benzoate C6H5COO-Na+ (NaC6H5COO). ii) Formation of Esters Esters are formed when benzoic acid is reacted with alcohol in the presence of sulphuric acid, which acts as a dehydrating agent. iii) Formation of Acid Halides Benzoic acid forms acid halide, benzoyl chloride, upon reacting with thionyl chloride (SOCl2) or Phosphorus pentachloride PCl5. iv) Sulfonation Benzene ring's sulfonation takes place when benzoic acid reacts with the fuming sulphuric acid H2SO4. Here, the functional group SO3H replaces the hydrogen atom located at meta-position to the carboxylic acid group. v) Nitration During nitration, when sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst, the nitro NO2 group occupies a meta-position to the position of the carboxyl group in the benzene ring. vi) Halogenation In this reaction, chlorine (Cl2) reacts with benzoic acid in the presence of ferric chloride (FeCl2), which acts as catalyst, to form meta chlorobenzoic acid (Cl-C6H4-COOH). vii) Decarboxylation In this, carbon dioxide is removed. Sodium carbonate reacts with sodium benzoate using soda-lime and forms benzene. viii) Reduction Benzoic anhydride converts into benzoic acid and benzyl alcohol upon reacting with sodium borohydride and followed by acid hydrolysis. Uses of Benzoic AcidIn food: It is used as a preservative in foods like soft drinks, fruit juices, pickles, etc. Processed food contains benzoic acid in order to prevent the growth of bacteria, mould, yeast, etc. It does not change the flavor or odor of the food items. However, it is used in acidic foods as its antifungal and antibacterial properties are effective even at low pH. So, it is good as a preservative in an acidic environment. In an alkaline medium, it breaks into ions and thus cannot perform the role of a preservative. In medicine and healthcare: It is used in drugs as a preservative. It is also found in baby products, soaps, detergents, skin products, and more. In treatment: It is used to prevent bacterial infections including ringworm and athlete's foot. It is produced as hippuric acid in the liver. This acid is not toxic and is used to treat skin irritation caused by insect bites, burns, and more. It also helps in the treatment of infections of the urinary tract and bronchitis. Other uses of benzoic acid
Precautions while using Benzoic AcidAlthough benzoic acid is non-toxic under normal circumstances, it still causes health risks, so, the following precautions could be taken while handling it.
Storage of Benzoic AcidThe container should be tightly closed and kept in a cool, dry and well-ventilated area. It should not be close to heat, stoves, and incompatible substances like oxidizing agents and strong bases.
Next TopicFormic Acid
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










