Biology DefinitionThe study of living beings is the simplest definition of biology. It is concerned with anything that is alive and livable. A living matter is something that exhibits life, as opposed to things that are inert. For instance, an item that is made up of a cell or a collection of cells would be considered living. 
Each of these cells is capable of performing activities, such as anabolic and catabolic responses, to maintain life. A substance that can respond to stimuli, adapt to its surroundings, reproduce, and develop would also be considered to be life. These processes need energy. Homeostatic methods are also used to control them. Animals, fungus, bacteria, archaea, and fungi are the five primary groups of living beings. Biology is interested in the structure, function, distribution, evolution, and categorization of these organisms. Modern Principles and Concepts of BiologyThe basic principles of biology accepted until today are cell, genetic, and evolutionary theories. Cell TheoryCell Theory is a scientific theory proposed by scientists Theodor Schwann, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, and Rudolf Virchow. It is intended to disprove the old theory of spontaneous generation. It proposes the following principles: 
Gene TheoryThe gene is the fundamental unit of inheritance. The Punnett Square diagram illustrates how a specific phenotype of an offspring relies on the parentally inherited alleles. In this instance, children that inherit the Y allele will have the yellow hue as their dominant feature. The recessive characteristic will, however, be expressed by the offspring that receives yy but lacks the dominant gene. 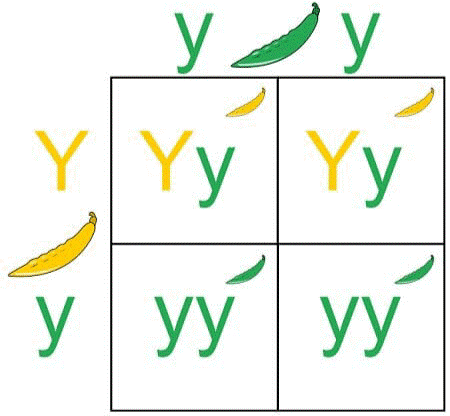
According to gene theory, the basic, physical, and functional unit of inheritance is the gene. It has DNA within and is situated on a chromosome. The genetic code, or the sequence of nucleotides that defines a protein's or RNA's structure, is stored in the gene. Due to the fact that it is passed down across generations, a gene is a unit of heredity. It is the foundation upon which an organism's phenotypic characteristic is founded. 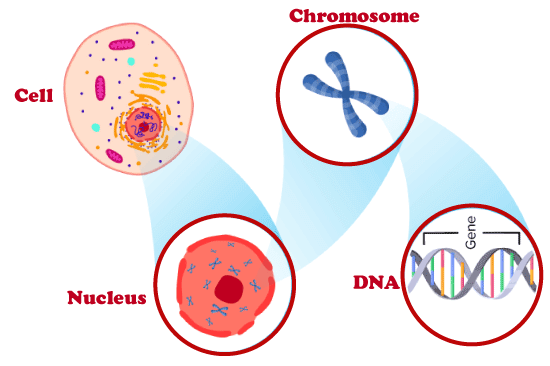
Gregor Johann Mendel was one of the key founders who helped establish genetics as a science. He is considered as the founder of the stated field as a result. He was able to identify unit variables that were handed down from one generation to the next and are now known as genes. These unit factors, according to him, come in pairs. There will be a dominant pair among the two couples (recessive). To explain how heredity happens, he created the Mendelian rules. Evolutionary Theory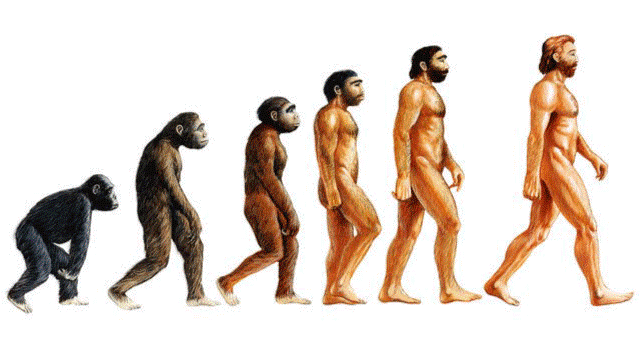
The term "evolution" refers to the gradual genetic alterations that occur in a population over many generations as a result of natural selection, mutation, hybridization, or inbreeding. This image illustrates how mutation and selection function as important elements in evolution. One of the key proponents of the idea of evolution is Charles Darwin. During his Beagle expedition, he became famous for his book Origin of Species by Natural Selection. He had the ability to observe numerous plant and animal species. Based on his study, he hypothesized that living things had an innate propensity to create children of the same sort. As a result, the species' survival ability depends on the amount of food and space available. As a result of the habitat's limited capacity to support a large population, creatures must compete with one another. As a result, survival or the battle for existence becomes a personal achievement. The History of BiologyAll sciences have seen periods of time in their histories where they achieved outstanding development in very little time. These discoveries are generally the result of two things: first, the existence of a creative mind, one that is perceptive enough to reject preconceived notions and develop original hypotheses; and second, the accessibility of technology to carry out the required tests to test the ideas. Without the right equipment to perform an inquiry, even the most creative and curious mind is severely constrained; on the other hand, even the most advanced technical apparatus cannot by itself provide insights into any scientific process. 
The discovery of the cell is an illustration of how those two elements are related. There has been conjecture for hundreds of years about the basic structure of both plants and animals. Yet it wasn't able to establish a comprehensive theory, the cell theory, that adequately explained how plants and animals are organized until optical tools were sufficiently advanced to disclose cells. Similarly, until technical advancements made it feasible to uncover chromosomes and the role they play in cell division and heredity, the relevance of Gregor Mendel's findings on the mechanism of inheritance in the garden pea was overlooked for many years. This is a result of the relatively recent invention of very complex tools, like the ultracentrifuge, the electron microscope, and automated DNA sequencing devices. Additionally, biology has evolved from a science that primarily focused on whole cells and organisms?one that was largely descriptive in nature?to a field that places an increasing emphasis on the subcellular and molecular characteristics of organisms and aims to reconcile structure and function at all levels of biological organization. The Earliest HeritageAlthough the origin of the study of biology is unknown, it is assumed that early people were at least somewhat familiar with the local fauna and flora. Identifying non-poisonous food plants and comprehending the behaviors of deadly predators were essential for human survival. According to archeological evidence, humans had practically domesticated every amenable animal at their disposal before civilization even began, and they had also created an agricultural system that was reliable and effective enough to meet the needs of large populations of people living in close quarters. It follows that a significant portion of biological History predates humans' invention of writing and record-keeping. Scope of BiologyBiology is practically used in many fields, such as agriculture, health, genetic engineering, and the food business. The fields of medicine, nursing, pharmacology, science, and research are among the professional spheres of biology. Many other educators speak out, including professors and speakers. 
In the 19th century, scientists claimed that all living things had some fundamental traits, leading to the establishment of biology as a distinct field of study. Every year, over a million papers are published in various medical journals, and biology is now a required course of study at institutions all around the world. Branches of Biology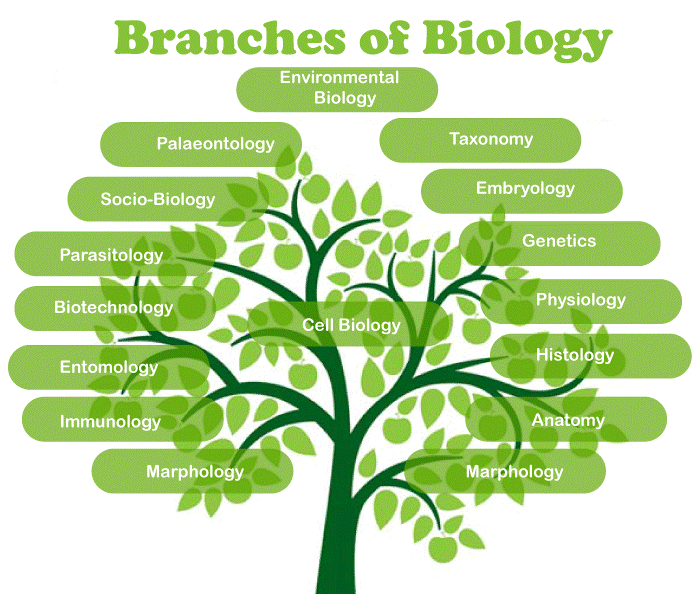
The scientific study of life is known as biology. It has a number of pertinent branches. The major biological subfields are listed below, along with a brief explanation of each: Main Branches of BiologyThe following is a quick discussion of some of the major biological fields: 1. Taxonomy: Taxonomy is the study of recognizing, naming, and categorizing different living things. 2. Morphology: This branch of biology focuses on studying the outward characteristics of diverse living organs, including their size, shape, color, and relative location. 3. Anatomy: When a body has been dissected, it is possible to view the interior structure without the help of a telescope. 4. Histology: Using a light microscope, this field of research examines the structure and organization of tissues. 5. Cytology: This field of research examines the shape and composition of cells and the function of their organelles, especially their nuclei. 6. Cell Biology: Cell biology is the scientific study of the morphological, organizational, biochemical, physiological, genetic, developmental, pathological, and evolutionary characteristics of the cell and its component elements. 7. Molecular biology: It is the study of the composition, dynamics, and interactions of the biomolecules that generate and control the wide range of protoplasmic activities. It also covers the investigation of these molecules' physicochemical organization. 8. Physiology: This field of study examines various bodily processes and activities. 9. Embryology: This field of research examines how zygotes are fertilized, grow, divide, and differentiate into embryos or early stages of the development of living things before they reach their final form and size. 10. Ecology: Ecology is the study of how living things interact with one another and with their surroundings. 11. Genetics: This field of research examines heredity, or the transmission of traits, and genetic variations. The study of how qualities are expressed and passed from parents to children is known as heredity. 12. Eugenics: This branch of research examines elements that affect the improvement or deficiency of a race, particularly that of humans. 13. Evolution: It investigates the origin of life as well as how genetic mutations and adaptations result in the emergence of new types of organisms. 14. Palaeontology: This field of study examines the fossils, imprints, and remnants of extinct creatures found in rocks of various ages. 15. Exobiology: The area of science examines if there is a chance for life in the universe. 16. Virology is the scientific study of viruses in all their manifestations. Why Study Biology? Why is Biology Important?
It might not be fully able to persuade you of the importance of biology if I tell you that this is the study of "All Life". Let's continue to make it easier to think about. James Right provides six of what he considers to be the most crucial justifications for studying biology.
The other sciences are closely related to biology on many levels. The other scientific disciplines can only be understood if one has a basic grasp of biology, which is more than merely helpful. Biology Is a Social and Economic Issue for ManyBiology courses often deal with issues in and out of the laboratory. The connection of biology to vital issues such as food distribution, commerce, and public health means you must recognize biology and still be an important and active member of society. When questioned about biology's influence on significant issues whether they are a biology student or not, they should pay attention, Visick, (A biology professor responded), "We don't have to go much farther than what's occurring right now, do we? 
Half of our country is still unvaccinated because a tiny number of people have been effective in disseminating so much false information about COVID-19, the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, and the COVID vaccine (movement). Such efforts can succeed mainly because people need to learn more biology to distinguish between good knowledge of disinformation and disinformation. However, COVID is by no means the only biological problem we face today. A basic understanding of biology is increasingly required to address a wide range of challenges, including those related to environmental policy, healthcare, diet and nutrition, agriculture, reproductive health, and medicines. Hence, even though it is important for us to all have a basic understanding of biology, anyone who has earned a degree in biology and possesses strong communication and teaching abilities has a wonderful chance to educate the public and aid in making important life-changing decisions. How Biology Helps to Treat IllnessesModern medicine and biology are closely related, and pharmacology, a branch of biology, is a crucial component of contemporary medicine and healthcare. Research and the production of analgesics and antidepressants are both included in the field of pharmacology. Knowing about numerous diseases, their cause of them, and their effects on the human body is useful information that can be found in fields like pathology. Although still focusing on how viruses affect humans, virology accomplishes the same thing. You must recognize how biology affects genetics. Science has advanced because of technological advances to the point that it is now possible to anticipate diseases, understand how they are passed down through generations, and even treat them at the smallest scale. Said the range of applications biology provides is astounding, particularly in the areas of medicine and health. ConclusionBiology studies living organisms and the processes that keeps them alive. Biology is separated into branches as it is such a vast science. The current strategy is based on the levels of biological organization involved (for example, molecules, cells, people, and populations) and the particular subject being researched (e.g., structure and function, growth and development). According to this system, the major divisions of biology are morphology, physiology, taxonomy, embryology, genetics, and ecology. Each of these categories has further subgroups. The study of one type of living thing, in particular, can be the focus of a particular branch of biology, such as botany (which studies plants), zoology (which studies animals), ornithology (which studies birds), entomology (which studies insects), mycology (which studies fungi), microbiology (which studies microorganisms), and bacteriology (bacteria).
Next TopicBiosphere Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










