Blockchain and distributed ledger technologyOne of the biggest technological stories of the last ten years is Blockchain. Although it appears like everyone is talking about it, the actual meaning and operation of Blockchain are sometimes obscured under the surface of discussion. Although Blockchain has a reputation for impenetrable, its core concept is quite straightforward. Additionally, it has the power to completely transform entire sectors. Blockchain is a system that makes it possible to share information securely. A database obviously contains data. A ledger is an account book where transactions are entered. The ability to update the Blockchain is shared among the nodes, or individuals, of a public or personal computer network. A blockchain is a sort of decentralised database or ledger, one of today's top technological developments. Distributed ledger technology, also known as or DLT, is what this is. Digital tokens or money are used as incentives to encourage nodes to update blockchains. Three main features define a blockchain. A blockchain database must, first and foremost, be cryptographically secure. Therefore, two cryptographic keys are required in order to enter or contribute data to the database: a key that is publicly accessible, which is essentially the database address, and a secret key, which is a unique key that must be verified by the network. Distributed ledgerA sort of information that is shared, copied, and synchronised among the participants in a decentralised network is known as a distributed ledger. The distributed ledger keeps track of all interactions between network participants, such as trading goods or information. The ledger's records are updated by consensus among network participants, who also regulate the system. There needs to be involvement from a centralised authority or a neutral third party, such a clearinghouse or financial institution. The distributed ledger is an auditable, immutable record of all network transactions since each record includes a date and distinctive cryptographic signature. Users at every node in the network can evaluate distributed ledgers, and they can have an exact copy of the files that circulate across the network. If the ledger is modified or added to, the participants are notified and copied on the changes. The database is synchronised to ensure that it is accurate. Bitcoin and distributed ledgers both make use of the same technology. Blockchain/DLT are the foundation of the "internet of value," allowing peer-to-peer "value" transfers and recording interactions without the need to establish a centrally coordinating body. The term "value" refers to every record of ownership of an asset, such as money, securities, or property titles, as well as ownership of certain information, such as an individual's identity, health information, or other personal data. 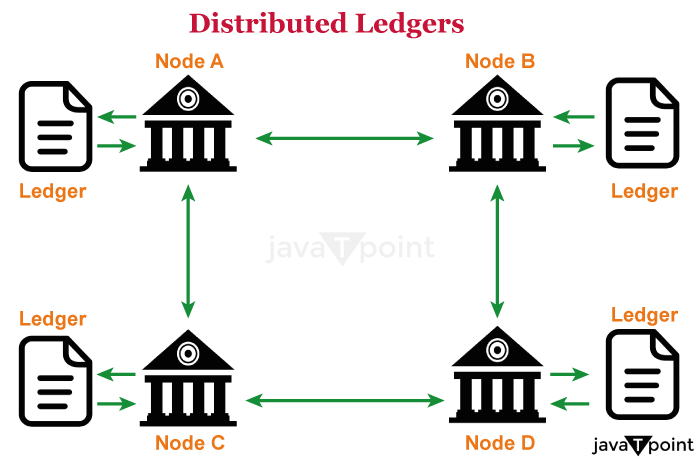
DLT has the potential to significantly improve the financial sector's efficiency, resiliency, and reliability.
Workings of Distributed LedgersIndividuals known as nodes hold, manage, and alter distributed ledgers. Every node independently builds the database. Each node processes every transaction on the network, drawing conclusions about how the database develops. 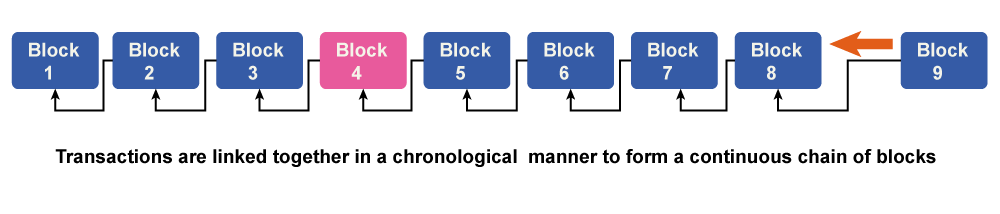
Voting is done on the database modifications that have been made based on the transaction. All nodes take part in the voting process, and a new transaction is approved on the database if a minimum of 51% of them concur. After that, all of the nodes refresh the database versions to ensure that every device or node is running the same version. The newly created transaction is added to a blockchain block. In a Proof-of-Work blockchain, nodes are also known as miners. A miner is rewarded for successfully adding a new transaction to a block. It needs devoted computer power available constantly. Miners are in charge of calculating the digital signature for new blocks. The reward goes to the miner who correctly locates the hash first. The success of miners who devote more computing power to finding the hash will increase. Finding new hash scales, however, gets more challenging as blocks continue to generate. The objective is to generate blocks at a steady rate. Distributed ledger technology typesThere are three different types of distributed ledgers:
Features of Distributed Ledgers
ExamplesA very well-known instance of a distributed database is bitcoin. It is a form of digital currency that can be used to make purchases on a network that lets users to make irreversible purchases for less money than they would pay using more traditional online payment methods. Ethereum is a well-known distributed ledger that lets programmers build custom apps. Since it introduced smart contracts, it is incredibly well-liked. The self-executing smart contracts are activated when specific real-world circumstances are met and pertinent data is added to the Blockchain. Ripple is another instance of a distributed database that focuses on payments, particularly cross-border transactions. Ripple is an open-source ledger. It was designed with banks in mind initially. How do decentralized finance, cryptocurrencies, and Blockchain relate to one another?Without the help of banks or other middlemen, buyers and sellers can trade cryptocurrencies online thanks to blockchain technology. Cryptocurrencies and all other digital assets are built on the blockchain technology. A series of blockchain or cryptocurrency applications known as "decentralised finance" (DeFi) is intended to take the role of the present financial intermediaries with services based on smart contracts. Decentralized means that anybody with access to a program has control over whatever changes are made to it, just like Blockchain. Users may now have a more significant direct influence over their money as a result. ConclusionDLT is marketed by experts in this field as a remedy for numerous online issues that will radically resolve all of these issues. "Internet of Value" is a concept used to describe distributed ledger technology. The Internet will be used to facilitate real-time transactions and processes. With its efficient solutions, the use of distributed ledgers has a chance to have a positive impact on issues in the finance or banking, online safety, healthcare, government, and data security sectors. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










