What is the full form of BMTBMT: Bone Marrow TransplantBMT stands for Bone Marrow Transplant. It refers to a medical procedure in which diseased or damaged bone marrow is replaced with healthy bone marrow. It is mainly performed to treat blood cancers like leukemia, Thalassemia, and lymphomas and in the treatment of various other types of cancers. Bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue inside your bones that contains stem cells. These stem cells differentiate into different types of blood cells like WBCs, RBCs and platelets. Its main job is to produce blood cells or blood components. The blood cells that give rise to new blood cells are called stem cells. The most fundamental kind of stem cell is the pluripotent one. The following characteristics set this blood cell apart from others:
A bone marrow transplant requires stem cells. 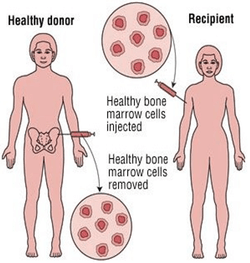
Why is a bone marrow transplant required?The goal of a bone marrow transplant is to treat a variety of illnesses, including cancer. A bone marrow transplant may be required when the amount of chemotherapy or radiation needed to treat cancer is so high that the patient's bone marrow stem cells could be irreparably damaged or killed by the treatment. If a condition has destroyed the bone marrow, bone marrow transplants may also be required. Using a bone marrow transplant, one can:
Before the procedure, you should have a thorough conversation with your doctor and bone marrow transplant experts to consider the risks and advantages. Types of Bone Marrow Transplant:Autologous transplant: In this transplant, the person's own stem cells are used in the transplant. So, before starting this procedure, a person's stem cells are harvested and stored. Then chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used to kill the cancer cells. After the high doses of chemo or radiation, the harvested stem cells are transferred back to the body of the person. Allogeneic transplant: In this transplant, the stem cells of a donor are transferred to the recipient. There should be a close genetic match between donor and recipient. This type of transplant is needed when a person's bone marrow cells (stem cells) are damaged due to a medical condition. The success of an allogeneic transplant depends on how closely the donor cells match with the recipient cells. A brother or sister is most likely to be a good match for allogeneic bone marrow transplants. Syngenic transplant: In this transplant, the recipient receives stem cells from his or her identical twin. The donor cells are not rejected by the recipient's body and the recipient's cells are also not attacked by the donor cells. What conditions could be helped by a bone marrow transplant?The conditions that benefit from bone marrow transplants most frequently are the following:
However, because everyone with these conditions experiences sickness differently, not everyone will benefit from a bone marrow transplant.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










