Budget DefinitionA budget is an allocation of resources based on revenue and expenses. In other words, it is an estimate of your income and spending for a specific time frame, such as a month or a year. (Alternatively, if you monitor the inflow and outflow of funds for your household, it is a family budget.) 
There is no perfect way to Budget; what works for one person might not work for someone else. Making a complete list of spending or focusing on a few key areas can both be included in budgeting. While some people favour using a spreadsheet or other technology for budgeting, others favour writing out their budgets by hand. What Is the Purpose Of A Budget?Budgeting is not about starving yourself; it's about taking control of your finances. It shouldn't seem like a punishment to create a budget. Remember that it's a strategy for all your money, including cash for fun pursuits. Budgets don't have to be rigid. In reality, it should alter when your circumstances do, such as when you obtain a promotion or become a homeowner. Your Budget should be as unique and flexible as you can. Why Is Budgeting Important?
Everyone, not only those struggling financially, benefits from having a budget. It encourages you to stick to your monetary objectives and maximize your resources. A budget might serve as a stepping stone toward your financial objectives. You might benefit from it if you: 1. Recognize your relationship with finances - You can clearly see how much you have to save or spend by keeping track of your income and spending. Once you recognize trends, you can determine where corrections need to be made. 2. Make enough long-term investments - A good Budget pushes you to save money for both an emergency fund and other goals like a trip or retirement. How much money you need to set away each month can be calculated in this manner. 3. Pay - off debt or continue to do so - Creating a budget in advance will help you avoid overspending and assist with debt repayment. 4. Reduce tension - While budgeting is not a solution, it may help you manage your finances and get ready for difficulties. Different Types of Budgets
1. Master BudgetA master budget is made up of smaller budgets created by several organizational and functional divisions. As inputs, financial plans, projections of cash flow, and financial statements are employed. Master budgets are used by management teams to specify the actions required to meet their organizational goals. In larger firms, senior management is in responsible of creating many versions of the master budget prior to its finalization. After a final review and analysis, funds may be allocated for a certain business activity. Smaller businesses usually use spreadsheets to create their master budgets, but upgrading to efficient budgeting software typically reduces errors. 2. Operating BudgetA business's anticipated income and related costs are displayed in an operational budget for a certain time period. A profit and loss report would be a good analogy. It consists of non-operating expenses as well as fixed and variable costs, and capital expenditures. Each line item in this Budget is supported with important details, despite the fact that it is a high-level summary report. To determine if the company is spending in accordance with its plans, this information is helpful. This Budget is created by management at the start of each year in the majority of firms. The report may be used as a prediction for several years because it is updated often during the year, either monthly or quarterly. 3. Cash BudgetA cash flow budget estimates how much money a firm will bring in or spend over a given time period. Businesses create their cash budgets by making assumptions about their production and sales forecasts, forecasting their payables and receivables, and more. The data in this Budget can assist the company in determining if the company has sufficient access to cash to cover operational costs, whether the money is being spent wisely, and if a company is on pace to turn a profit. 4. Financial BudgetThis Budget is used by businesses to determine how much money they will require, when, and for what purposes. It takes into account your company's assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity?the crucial parts of a balance sheet that give you a broad sense of how healthy your company is. 5. Labor BudgetA labour budget is crucial for every firm that intends to hire personnel to carry out its objectives. It assists you in identifying the workforce you will need to reach your objectives so you can schedule the payroll for each employee. It assists you in allocating costs for seasonal workers in addition to organizing the regular workforce. 6. Static BudgetThis Budget, as its name implies, is an estimation of the income and spending that will remain constant throughout the year. Regardless of whether sales grow or decrease, the Budget's line items can be utilized as benchmarks. Nonprofit organizations, educational institutions, and governmental organizations that have been given a certain amount to use for their operations in each area often develop static budgets. Advantages and Disadvantages of Budget
Advantages of BudgetsBudgets have advantages for the company, as well as for its management and other employees: 1. The Budget facilitates planning - Once company objectives are established and codified through a budget, it can be assured that the other business strategies are equally realizable. It also aids in making judgments about the output of various commodities and services and ensures that everything is accessible when it is needed. 2. The Budget facilitates communication and coordination - A firm adopts a budget that enables its many departments and divisions to collaborate in order to achieve a common goal. It aids in keeping discipline throughout and guarantees that each department contributes in some way to the achievement of the objective. Once established, the Budget assists in resolving any predicted issues and clearing up any potential areas of uncertainty. 3. The Budget aids in decision-making - Since a business can plan ahead and think ahead with the aid of a budget, they are able to choose not only the type of goods and services to be provided to customers, but also the purchases that will be made, which may aid in pricing manipulation. 4. The Budget may be utilized for monitoring and controlling ? The most significant advantage of budget preparation is assisting management in having budgetary control to track and evaluate real outcomes. This also aids in adjusting different measures to change the company's operations as time goes on, or potentially changing the Budget if it becomes unrealistic. 5. The Budget may be used to regulate and motivate - A budget frequently functions as a motivational element since it gives managers and other staff members preset targets. When the specified goals are met, the majority of firms proclaim various forms of bonuses and promotions for their personnel, which benefits both the business and its employees. Disadvantages of BudgetsThere are many advantages to having a budget and exercising fiscal management, but there are also some drawbacks, which are detailed below: 1. The benefits should outweigh the expense of creating a budget - The process of creating a budget may be very complicated, and some firms, particularly small ones, may find it to be excessively time- and resource-intensive for just modest returns. But in the modern day, most lending institutions, including banks, frequently demand budgets as a component of the business plan to move on with their lending or investment choices. In these situations, the value of creating the Budget must typically outweigh its expense. 2. Budgets need to be more accurate - Budgets deal with future forecasts and predictions based on data from the past and present. As a result, there is a high probability that the results will be off. With the improper information conveyed, a corporation that is heavily dependent on finances may find it challenging to succeed. Therefore, great caution must be exercised while estimating different facts and numbers. Budgetary control is used to compare the Budget to what occurred; if the Budget proves unrealistic, it may need to be adjusted. 3. The Budget may demotivate - Employees at the ground level who lack management powers or who do not participate in the agreement and establishment of a budget may feel that it is being pushed upon them, and this may act as a demotivating factor. Since failure to meet the goal might result in difficulties for the employee, threats may be made instead of encouragement to the workforce. 4. Budgets may result in dysfunctional management - Employees in one business unit may outperform their planned goals, which might cause issues in other parts of the organization. As an illustration, the sales department may have trouble selling the production department's surplus output. Budgets must be created at realistic levels and connected and coordinated across all departments with the appropriate information in order to prevent such dysfunctional management. 5. Budgets may be set at too low levels - Budgets prepared by individuals may be set at low achievable rates since a budget that is too simple to achieve will not be beneficial to the business and may even result in lower output levels and higher costs than they were before the Budget was established. Budgets should ensure the optimal use of the available resources. Components of Budget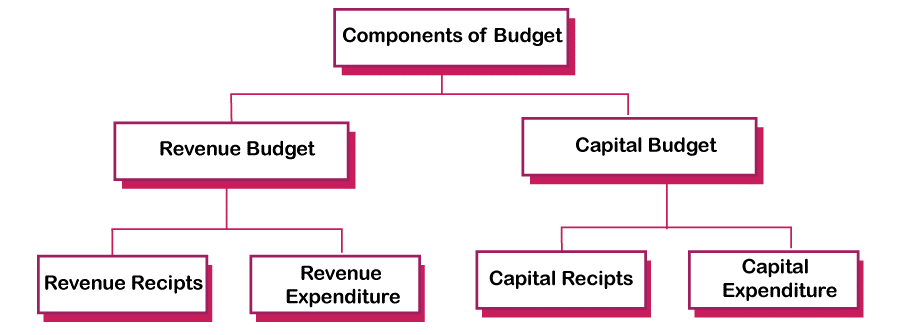
The Budget is divided into two categories: Budget Expenditure, which includes Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure, and Budget Receipts, which includes Revenue Receipts and Capital Receipts. 1) Budget Receipt: During the government's fiscal year, they estimated financial revenues from all sources. Budget revenues are divided into the following categories:
2) Budget Expenditure: The projected cost for the government's fiscal year. The government's spending is categorized as follows:
Budget Deficit and Its Classification
A budget deficit or budget deficit is when the government's budgeted expenses exceed its budgeted income. In India, there are three significant categories of budget deficits: primary, fiscal, and revenue. 1. Revenue Deficit: A revenue deficit is one in which government spending exceeds government revenue. It suggests that they should engage in disinvestment and raise their borrowing to keep up with demand. 2. Fiscal Deficit: The amount of total spending that exceeds the amount of total receipts, excluding borrowing. It represents government borrowings, which cause national debt, credibility erosion, inflation, and crowding out. 3. Primary Deficit: The gap between the government's interest payments and its fiscal deficit is known as the primary deficit. It demonstrates a country's lack of fiscal restraint. Balanced and Unbalanced Budget1. Balanced Budget: This term describes a scenario where government revenue and government spending are equal. It shows how stable the government's finances are. 2. Unbalanced Budget: This refers to a budget where the government's revenue and expenses are different. It denotes either a surplus or a deficit in the Budget: a. Budget Surplus: A budget surplus occurs when the government's spending is less than its receipts. It lowers inflation overall in the economy. b. Deficit Budget: A deficit budget is one in which the government's revenue is lower than its expenditures. It is suggested during a slowdown in the economy. Essential Elements for A Successful Budget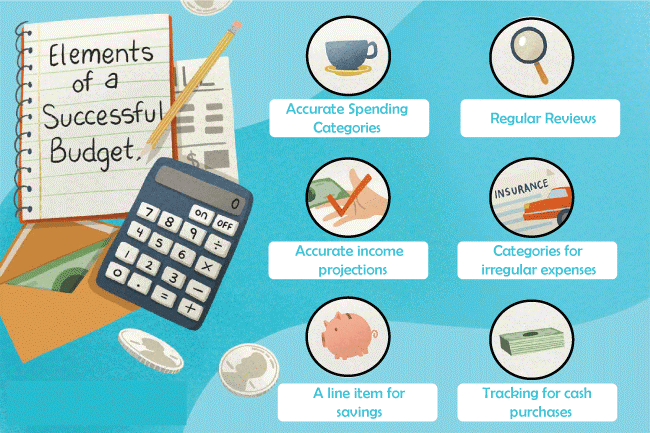
The following crucial components are necessary for a budget plan to succeed in a company: (a) Accurate Business Activity Forecasting: Forecasting is crucial in creating a budget. It serves as both the foundation and a key component in creating an appropriate budget. (b) Coordinating Business Activities: Since each Budget has implications for the others in different ways, budgeting must combine all of the separate budgets into a comprehensive plan. Budgets for people, purchasing, manufacturing, and sales must all be coordinated. (c) Communicating the Budgets: Individual budgets must be communicated to the various organizational units for a comprehensive budgeting program to be successful. The fundamental idea is that creating a budget is only useful if the intended recipient is aware of it. Managers are not accountable for the Budget until it is presented to them clearly and authoritatively. (d) Cooperation and Acceptance: Effective budgeting also necessitates that plans be welcomed by those who will be carrying them out. The entire organization should actively participate in the budgeting process. ConclusionAn essential tool for managing both incoming and outgoing financial flows is budget planning and preparation. Planning will maintain guidelines for the distribution of money and how they should be used. In the event that there is any doubt regarding where and how the money was spent, organization via budget planning is a terrific approach to go back to previously recorded transactions. Funders will be given the opportunity to stage plans more effectively in the future by keeping track of this information. The plan will also enable you to determine whether the amount of a certain payout needs to be examined and revised in order to better meet the demands of the companies.
Next TopicBuffer Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










