Buffer Definition
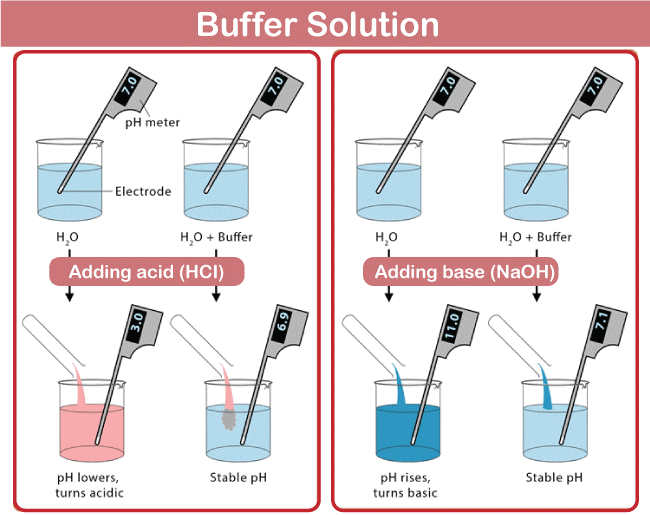
Buffer is a term used to describe a solution that helps to maintain a certain pH level. It is widely used in industrial, medical, and scientific applications. Buffer solutions are used in a wide range of applications, such as buffer solutions used in biological and chemical research, wastewater treatment, food preservation, and biochemical engineering. In chemistry, buffer solutions contain a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. The acid and base in a buffer solution react to neutralize any added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution. The ratio of the acid and base concentrations determines the pH of a buffer solution.
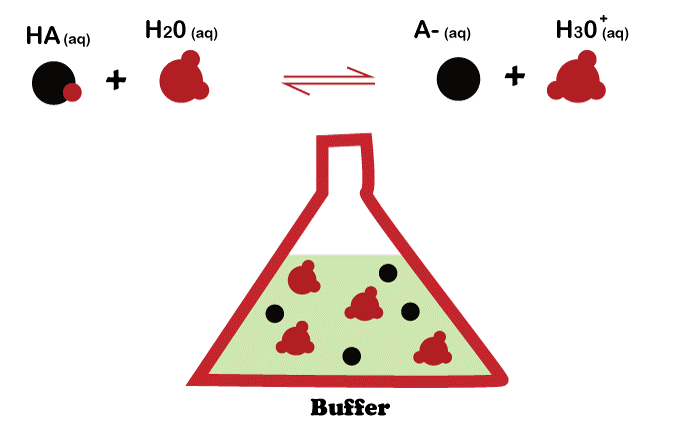
Components in Buffer Solution
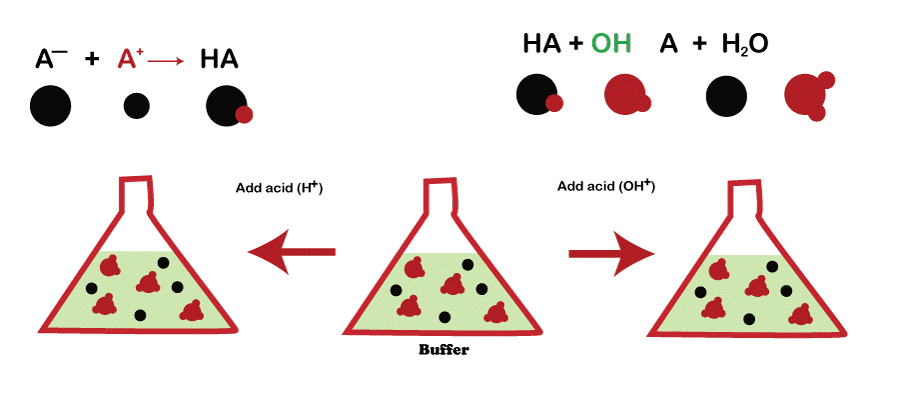
A buffer solution comprises a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa. The acid and base concentrations of the buffer solution must be in such a ratio that the pH of the solution is maintained when an acid or base is added to it. A buffer solution's pH is maintained when an acid or base is introduced by the buffer solution's reaction with the added acid or base to neutralize it. The acid-base solution is the most prevalent form of buffer solution. Buffer is made up of a conjugate base of mild acid. The buffer solution responds when an acid is introduced, neutralizing the added acid and preserving the pH of the mixture.
On the other hand, when a base is introduced to a buffer solution, the weak base interacts with the new base to neutralize it and keep the solution's pH constant. The pH of a fluid can also be stabilized using buffer solutions.
Applications of Buffer Solution
- The pH of a fluid can also be stabilized using buffer solutions. The carbonate buffer made up of a mild acid (carbonic acid) and its conjugate base, is the most frequently used buffer solution. (Bicarbonate). The bicarbonate interacts with the acid introduced to the carbonate buffer, neutralizing and preserving the solution's P.H. In contrast, when a base is incorporated into the carbonate buffer, the carbonic acid interacts with the base, reducing it and preserving the solution's pH.
- Buffer solutions such as intravenous, dialysis, and red cell lysates are also used in medical applications. In medical applications, a buffer solution is used to maintain the pH of a solution at the desired level. For example, in intravenous solutions, the buffer solution is used to maintain the pH of the solution at the desired level so that the body can absorb the solution more efficiently. Similarly, in dialysis solutions, a buffer solution is used to maintain the pH of the dialysis fluid at the desired level so that the cells and tissues being dialyzed are not damaged.
- Buffer solutions are also used in biological and chemical research. Buffer solutions are used to maintain the pH of a solution at the desired level so that the reactions can proceed at the desired rate. For example, in biochemical engineering, buffer solutions are used to maintain the pH of the reaction mixture at the desired level so that the enzymes used in the reaction can function properly.
We can say that, buffer solutions are frequently used in numerous uses, including those in industry, medicine, and science. A weak acid and its corresponding base, or vice versa, make up buffer solutions that keep a solution's pH at the desired level. The pH of a fluid can also be stabilized using buffer solutions. Buffer solutions are used in medical uses to keep the solution's pH at the intended level so the body can absorb it more effectively. In biological and chemical research, buffer solutions are used to maintain the pH of the reaction mixture at the desired level so that the enzymes used in the reaction can function properly.
What is the Importance of Buffer?
- Buffers reduce the impact of contaminants and other substances on the system by absorbing and trapping them.
- Buffers help to reduce the risk of corrosion in industrial systems by providing a protective layer around metal components.
- Buffers help reduce the effects of changes in temperature on a system by providing a stable environment in which reactions can occur.
- Buffers can also act as catalysts, speeding up reactions and helping to make them more efficient.
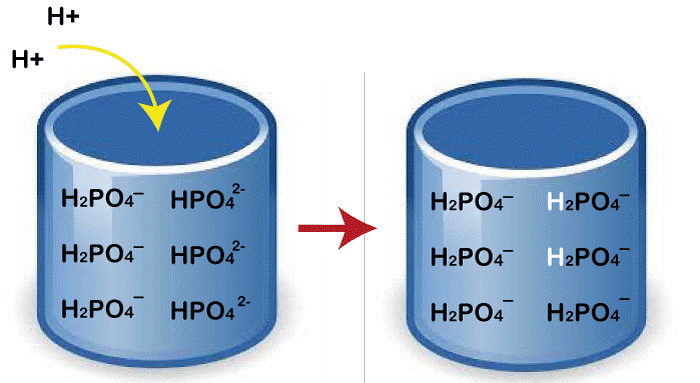
Advantages and Disadvantages of Buffer
Buffer solutions are aqueous solutions composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base (or a weak base and its conjugate acid). These solutions are designed to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
Advantages
- Buffer solutions are used to maintain a constant pH in a solution. This is especially useful in biochemical processes, where the pH of the solution must be kept within a certain range for optimal results.
- Buffer solutions are also beneficial in that they can help protect delicate proteins and enzymes from the harsh environment of a basic or acidic solution.
- Buffer solutions are also used to reduce the effects of temperature changes. By maintaining a constant pH, buffer solutions can help prevent the denaturation of proteins and other macromolecules.
- Buffer solutions are used in many industries, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Disadvantages
- Buffer solutions require a precise balance of acid and base to be effective. If the ratio of acid and base is incorrect, the buffer solution may not be able to resist pH changes.
- Buffer solutions can be expensive to prepare and maintain.
- Buffer solutions are only sometimes appropriate for use in certain applications. For example, they may not be suitable for use in very high or low pH solutions.
- Buffer solutions may interfere with certain biochemical processes, such as the activity of enzymes.
Buffer solutions provide many advantages, such as maintaining a constant pH and protecting delicate proteins from denaturation. However, buffer solutions may only be suitable for some applications and can be expensive to prepare and maintain.
Use Cases of Buffer Solution
- A buffer solution is a kind of solution that aids in keeping the pH level in a system consistent. It consists of either a weak base or its corresponding acid or vice versa. This type of solution is commonly used in many industries, such as food production, medical science, and environmental engineering.
- Buffer solutions are employed in the food industry to preserve the pH of prepared food items. For example, acidic fruit juices are usually buffered to a neutral pH before packaging to prevent spoilage or changes in taste or texture. Furthermore, these solutions control the pH of water used in food preparation, which helps preserve the freshness and flavour of the food.
- In medical science, buffer solutions are used in diagnostic tests and treatments to stabilize various biological systems. For instance, they are used to calibrate pH meters, which measure the acidity of body fluids such as blood or urine. They are also used to adjust the pH of medications to ensure they are effective and aid in diagnosing diseases affected by pH levels, such as diabetes and kidney disease.
- In environmental engineering, buffer solutions reduce the acidity of wastewater, soil, and groundwater. This helps to protect the environment from the effects of acid rain and industrial pollutants, which can cause long-term damage to vegetation, wildlife, and aquatic ecosystems.
- Buffer solutions are also used in aquaculture to regulate the pH of the water in fish tanks, ponds, and other aquatic systems. This helps to keep fish and other aquatic organisms healthy and helps to prevent the spread of disease.
- Overall, buffer solutions are used in various industries to maintain a consistent pH level and protect the environment from the harmful effects of acid rain and industrial pollutants. They are also used to regulate the pH of medications, food products, and aquatic systems, which helps ensure these items' safety and effectiveness.
What are the Alternatives to Buffer Solution?
- Buffer solutions are mixtures of weak acids or bases with their conjugate salts used to maintain a particular pH in a solution. Buffers are widely used in many biochemical and industrial processes, such as in producing beer, wine, and cheese and in many laboratory experiments. While buffer solutions are extremely useful, several alternatives can be used to maintain a particular pH in a solution.
- A common alternative to buffer solutions is using a pH indicator, a chemical compound that changes colour when the pH of a solution is changed. For instance, phenolphthalein is a typical sign that turns pink when the pH rises above eight from being white. P.H. indicators can be used to measure the pH of a solution and show if the pH varies over time. For example, methyl orange turns crimson when the pH surpasses 4.5.
- Acid-base titrations are another alternative to buffering solutions. To measure the amount of acid or base contained in a solution, titrations entail adding a base or an acid. The titration's limit, typically when the fluid's pH equals 7, is established using an indicator. Titrations can quantify the concentrations of other substances and the quantity of acid or base contained in a solution.
- A weak acid or base can also be used as an alternative to Buffer solutions. Acetic acid is a weak acid frequently used to keep a solution's pH within a certain range. Weak bases like ammonia can be used to increase the pH of a solution, while acetic acid can be used to reduce the pH. The amount of acid or base required to maintain a particular pH will depend on the concentration of the acid or base and the desired pH.
- Finally, salts can be used as an alternative to Buffer solutions. Salts can be used to raise the pH of a solution, as they are composed of anions and cations that can react with acids or bases. For example, sodium bicarbonate is commonly used to raise the pH of a solution, as it reacts with acids to form carbon dioxide and water.
Buffer solutions are frequently employed to preserve a specific pH in a solution. However, there are several alternatives to buffer solutions, such as using pH indicators, acid-base titrations, weak acids or bases, and salts. Each alternative has advantages and disadvantages and can be used in different applications.
Types of Buffer Solution
When a tiny quantity of an acid or base is added, a buffer solution defies pH changes. Buffer solutions are used in various applications, including chemical analysis, industrial processes, food production, and medical treatments. Buffer solutions are composed of a mixture of weak acids and bases, also known as conjugate pairs. The weak acid and base are in equilibrium with each other, and their concentrations determine the pH of the solution. The interaction between an acid and a base when a tiny quantity of an acid or base is introduced to the solution aids in keeping the ph. There are two major types of buffer solutions.
- Initial Buffer Options: A mild acid and its conjugate base are mixed in these mixtures. Examples of primary buffer solutions include acetic acid and sodium acetate, boric acid and sodium borate, and citric acid and sodium citrate. These solutions effectively resist changes in pH over a range of approximately 2-3 pH units
- Secondary Buffer Solutions: These solutions contain a mixture of two weak acids or two weak bases. Examples of secondary buffer solutions include phosphate buffer and carbonate buffer. These solutions effectively resist changes in pH over a range of approximately 3-5 pH units.
Buffer solutions can also be further classified into three categories based on their composition:
- Monoprotic Buffers: These solutions contain one acid and its conjugate base or one base and its conjugate acid.
- Diprotic Buffers: These solutions contain two acids and their conjugate bases or two bases and their conjugate acids.
- Triprotic Buffers: These solutions contain three or three conjugate acids and their conjugate bases.
In addition to these categories, buffer solutions can be classified according to their pH range. Buffers can be divided into two main types:
- Acidic Buffers: These solutions have a pH range of approximately 2-6. Examples of acidic buffers include acetic acid/sodium acetate and boric acid/sodium borate.
- Alkaline Buffers: These solutions have a pH range of approximately 7-11. Examples of alkaline buffers include carbonate buffer and phosphate buffer.
Conclusion
Buffer solutions are important in many areas of science and industry. They are used in chemical analysis, such as titrations and pH measurements, and industrial processes, such as wastewater treatment. Buffers are also used in food production, such as cheese and wine, and in medical treatments, such as dialysis and intravenous solutions.
Buffer solutions are a powerful tool for maintaining a stable pH in various applications. By mixing weak acids and bases, buffer solutions can resist changes in pH when small amounts of acids or bases are added. As a result, buffer solutions are used in many areas of science and industry, from chemical analysis to food production and medical treatments.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now











