What is the full form of CBCSCBCS: Choice Based Credit SystemCBCS stands for Choice Based Credit System. This system provides an appropriate technical and learning platform for the students and teachers where the students or knowledge seekers have the flexibility to pick out their respective courses from the list of elective and soft skill courses, which will help in their overall development. 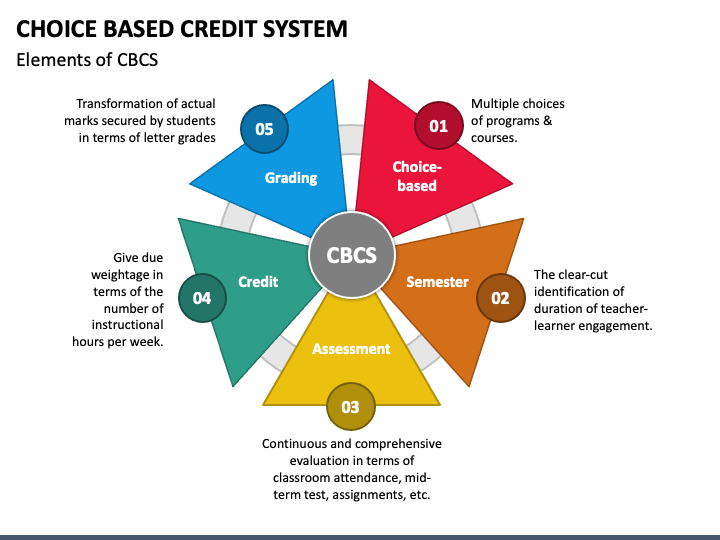
A good education is crucial for improving knowledge, fostering skills, boosting self-assurance, and improving students' lives. It gives students the tools they need to advance personally and professionally. Higher education institutions must concentrate on striking a balance between educating students and encouraging skill development by giving them the freedom to explore other subjects to guarantee the quality of their education. Choice-Based Credit System broadens students' educational horizons, providing an excellent learning platform. The CBCS method makes use of credits rather than the traditional marking scheme. Students are free to select their subjects in this course, which is focused on them. The themes may be primary or sophisticated. Importance of CBCS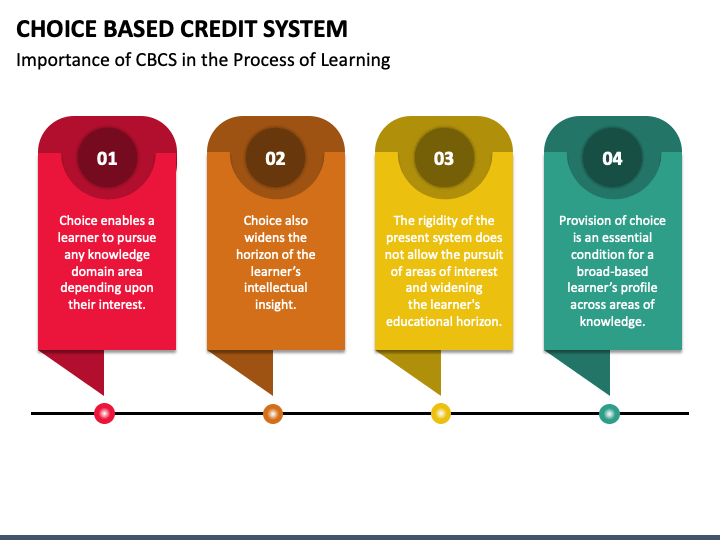
Higher education's choice-based credit system offers flexibility in curriculum planning and credit allocation depending on course difficulty and study hours. This practice enables them to pursue the subjects they choose, learn at their speed, take additional courses, and earn more credits than are necessary. The semester-wise learning and exam pattern is followed in this system. CBCS (choice-based credit system) uses a grading system; it becomes easy to calculate and evaluate students' performance with the help of this method. This system not only unlocks the track for learning but also opens the path for opportunities. This system provides ample knowledge of higher-level education to students. In this system, students get extra knowledge about their higher education, which they can't get from the standard higher education system. Advantages of CBCS (Choice-Based Credit System)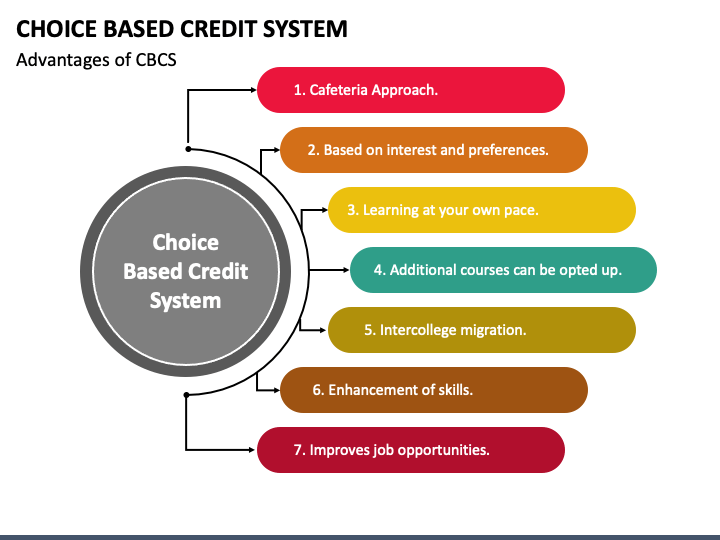
Three Types of Courses Provided by CBCS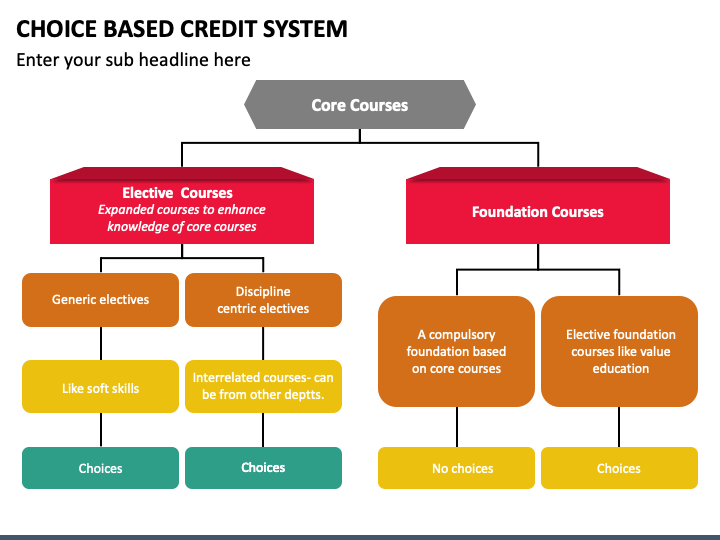
i) Core Course: A core course is one that a candidate must take as part of the application process. Discipline-specific courses (DSC) are another name for core courses. The course, which falls under this category, attempts to teach students the fundamentals of that specific topic. ii) Elective Course: The term "Elective Course" generally refers to a course that can be selected from a range of courses and that may be extremely specific, specialised, advanced, or supportive of the discipline/subject of study, provide an expanded scope, allow exposure to another subject, or develop skill. iii) Foundation Course: The Foundation Courses might be either Elective Foundation or Compulsory Foundation. Elective Foundation courses emphasise building men through education and are value-based. "Compulsory Foundation" courses are built on content that advances knowledge. All disciplines must use them. CBCS Marking SystemIn CBCS, they use a grading system instead of a percentage system. This system follows the semester system instead of the annual examination system. There are two semesters in every session. The assignment of grades is done at the end of each semester. This system is more effective than the percentage system. In CBCS, 10 points grading system is followed in which zero stands for absent or fail, and 10 points stands for outstanding. Evaluation of CBCS (Choice-Based Credit System)O Stands for outstanding A+ Stands for excellent A Stands for very good B+ Stands for good B Stands for above average C Stands for average P Stands for pass F Stands for absent or fail A student may occasionally be allowed to select fewer topics if their health prevents them from performing effectively in class. Their credits would undoubtedly suffer, but CBCS enables students to make up for the lost credits in the following semester. Students driven to think creatively, and scale new heights may find the CBCS a blessing. This technique will undoubtedly provide students access to unique professional prospects and assist them in landing their ideal jobs. The two most common grading methods are relative grading and absolute grading. The grades are issued based on a cut-off mark or percentage, and the relative grading is determined by the distribution of the numbers achieved by all learners in the classroom, which is usually normal. In absolute grading, marks are allotted based on previously defined mark intervals. Definitions of Important Words:Academic Year: An academic year is made up of two successive semesters (one odd and one even). Choice Based Credit System (CBCS): Students have an option of needed courses (core, elective or minor, or soft skill courses) under the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS). Course: A program's component commonly referred to as "papers" Not every course must have the same weight. Learning outcomes and objectives should be specified in the courses. A course's design may contain lectures, tutorials, laboratory work, fieldwork, outreach activities, project work, viva, seminars, term papers, assignments, presentations, self-study, etc., or it may utilize a combination of any of these. Credit Based Semester System (CBSS): With the help of the CBSS, students can find out how many credits they need to complete in order to be awarded a diploma, degree, or certificate. Credit Point: This term refers to the sum of a course's grade points and credits. Credit: A metric used to evaluate student work for the course. It establishes the weekly instruction requirement in terms of hours. A credit is equal to either two hours of fieldwork or practical application or an hour of weekly instruction (lecture or tutorial). The cumulative grade point average (CGPA): A student's total progress throughout all semesters is judged by their cumulative grade point average (CGPA). The cumulative grade point average (CGPA) is calculated as the ratio of a student's total credit points earned across all courses and semesters to the total credits earned across all courses and semesters. The expression has two decimal places. Grade point: Each letter grade is given a numerical weight, or "grade point," on a scale from 0 to 10. Letter Grade: It serves as a gauge of how well students performed in a particular subject. The letters O, A+, A, B+, B, C, P, and F are used to indicate grades. Program: A course of study that results in the awarding of a degree, diploma, or certificate. Semester Grade Point Average (SGPA): The semester grade point average (SGPA) is a measure of how well a semester's worth of work has performed. It is a ratio of the total course credits taken during a semester to the total credit points a student earned in all of the courses they registered for. It must have a maximum of two decimal places. Semester: There will be 90 actual teaching days, or 15 to 18 weeks, of academic work in each semester. Even semesters may run from January to June and odd semesters from July to December. A grade certificate, grade card, or transcript: It will be given to each registered student at the conclusion of each semester based on their academic performance. The grade certificate will show the course information (code, title, amount of credits, grade received), as well as the semester's SGPA and cumulative grade point average (CGPA).
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










