What is the full form of CCU1. CCU: Critical care unitCCU stands for Critical care unit. The critical care unit (CCU) offers specialized, 24-hour care for patients with significant medical disorders. Although knowing that you or your loved one has to be admitted to the CCU might be upsetting, you can find solace in knowing that this is the ideal location for patients to get the specialized care they require. Patients in the CCU are closely watched by professionally trained specialists who monitor each patient's vital signs around the clock. Their medical staff can respond quickly to any irregularities or warning signals to ensure the patient receives the required care. 
Description of CCUA critical care unit is sometimes referred to by the abbreviation CCU. When used in this manner, intensive care and critical care have identical meanings and provide the same kind of care. The terms CCU and ICU are equivalent in this context. A CCU is a more specialized unit known as a cardiac or coronary care unit at other institutions. Let's examine the care given in this kind of unit in more detail. Why Are Patients Shifted To CCU?The CCU is for patients who need continual, severe care, although it may not be as bad as it seems. After a lengthy surgical procedure, many patients travel to the CCU so that their vital signs may be constantly monitored in case there are any issues. Other cases include those who need breathing help, have severe head injuries, have high blood pressure, or are in danger of having a cardiac attack. Our CCU team comprises the following medical professionals since CCU patients can need their treatment.
We are aware of the hardships patients, and their families may be experiencing at this time. Our team is committed to giving patients the top-notch treatment they require to recover safely since they know their grave obligation. 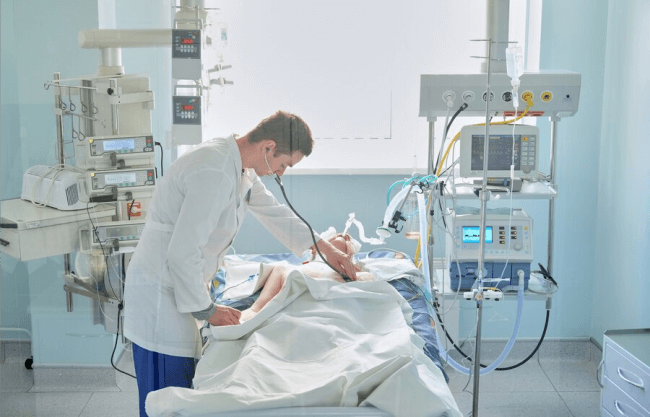
Visitation Policy At CCUFor the CCU, we have an open visitor policy. Although visitors can make patients feel more at ease, it is advised that you keep your visits brief so that the patient has enough time to sleep. It's crucial to remember that the patients in this unit require a lot of rest. Additionally, remember that other patients are attempting to relax, so speaking quietly is appreciated. What Fundamental Distinctions Exist Between An ICU And CCU?Critical care units and intensive care units are the same. Both focus on monitoring and caring for patients requiring round-the-clock care. A separate cardiac care unit may or may not be present in ICU hospitals. Patients with heart issues are the primary focus of a cardiac care unit, whereas patients with various diseases that threaten their lives are cared for in an ICU. 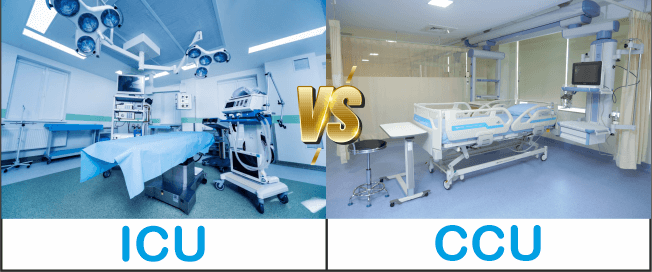
People with severe conditions are treated in intensive, critical, and cardiac care units, which all employ comparable monitoring and treatment technology. Typically, these units' medical gear consists of:
2. Coronary Care Unit or Cardiac Care UnitHeart attacks, unstable angina, cardiac dysrhythmia, and (in fact) several other cardiac disorders that require continual monitoring and care are treated in a hospital ward known as a coronary care unit (CCU), sometimes known as a cardiac care unit (CCU). 
CCUs offer intense treatment to those with serious heart problems, whether referred to as coronary, cardiac, or cardiovascular care. Larger hospitals and those that often do cardiac surgery are more likely to have CCUs. The CCU employs physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals who have received significant training in cardiac conditions. In addition, they have training in systemic intensive care. This is because patients in CCU frequently suffer from additional serious consequences. The CCU often has a relatively small patient-to-healthcare provider ratio. CharacteristicsThe provision of telemetry, or the ongoing electrocardiographic monitoring of the heart rhythm, is the primary component of coronary care. Allowing for early intervention with medication, cardioversion, or defibrillation, improves the prognosis. Patients with unstable angina or myocardial infarction frequently have arrhythmias. They are frequently hospitalized in the coronary care unit as a result. A particular indication is typically required for other indications, such as atrial fibrillation, while some indications, such as heart block, need admission to a coronary care unit. UtilizationCardiac disorders were among the 18 ailments and treatments in the United States in 2011, with a high ICU utilization rate (ICU utilization in more than 40% of stays). Local VariationsIntensive care units (ICU) with a special focus on the care of critically ill cardiac patients make up the majority of coronary care units in the United States. These facilities often offer cardiothoracic surgery regularly. Invasive monitoring techniques like pulmonary artery catheters and supporting techniques like mechanical ventilation and intra-aortic balloon pumps are frequently used (IABP). Acute Cardiac CareAcute care units for critically sick patients and intermediate care units for patients who are not critically ill coexist at some hospitals, such as Johns Hopkins. The degree of care offered in acute coronary care units (ACCUs), sometimes known as "critical coronary care units" (CCUs), is comparable to that of intensive care. Acute myocardial infarction patients, cardiogenic shock patients, and post-operative "open-heart" patients frequently stay here. Urgent Coronary CareSubacute coronary care units (SCC), sometimes called progressive care units (PCUs), intermediate coronary care units (ICUs), or step-down units, provide some level of treatment between the critical care unit and the main hospital floor. These devices are frequently used to treat patients who need cardiac telemetry, such as those with unstable angina. HistoryImplications of cardiovascular disease happened in 1960's. When it became obvious that close supervision by highly trained staff, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and medicinal procedures may reduce the mortality from coronary heart disease, they developed coronary care units in the 1960s. Desmond Julian established the first CCU at the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh in 1964 and gave the British Thoracic Society the first description of a CCU in 1961. Early CCUs were also established in Sydney, Toronto, Philadelphia, Kansas City, etc. Hughes Day, who also originated the name, opened the first coronary care unit in the US at Bethany Medical Center in Kansas City. The first "crash carts" were created at Bethany Medical Center. The results of individuals observed in a coronary care setting were consistently better, according to studies published in 1967. In 1953, DF Beck successfully revived a doctor who had suffered a myocardial infarction, and he also invented the open-chest defibrillation technique. 
In addition to highlighting the efficiency of a combination of mouth-to-mouth, sternal compression, and closed chest defibrillation in restoring heart activity in ventricular fibrillation patients, Kouwenhoven and colleagues at Johns Hopkins launched external defibrillation in Boston in 1956. Mason Sones made the first diagnostic angiography in 1958 by accidentally injecting dye into the coronary artery rather than the entire bloodstream, which was previously thought to be lethal. The interest in intensive care for myocardial infarction increased due to these improvements. Two hundred fifty patients with acute MIs were the subject of a 1967 report by Thomas Killip and John Kimball that detailed how CCUs had much higher survival rates than other facilities. This, along with additional reports, caused a rise in cardiac care facilities. These days, catheterization units are widespread in big cities. Understanding a Cardiac Care Unit/Coronary Care UnitThe leading cause of death worldwide, according to the World Health Organization Trusted Source, is heart disease. As a result, some hospitals establish a designated treatment area just for patients with cardiac issues. Other AbbreviationsVarious more CCU versions include Cardiovascular, coronary, or critical care unit (CICU or CVICU), CCCU(Critical Cardiovascular, Coronary Unit), Intensive Cardiovascular Care Unit which is also known as the Cardiovascular Unit, Recovery unit for cardiac, coronary, or cardiovascular surgery. 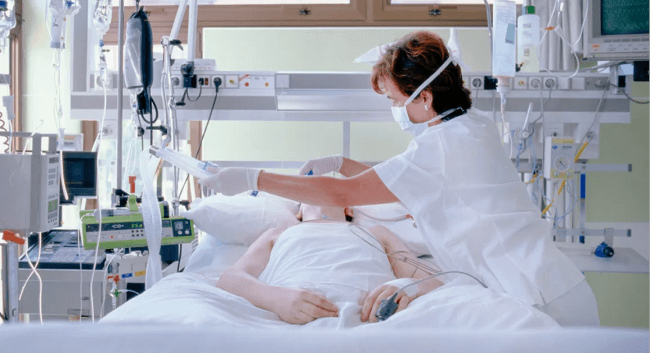
Which Medical Conditions Are Treated In A Cardiac Care Unit?A cardiac care unit may be your best option for treatment if you have experienced a heart attack or require constant observation following heart failure. Examples of cardiac conditions include arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, unstable angina, or a heart infection. They are recuperating following a cardiac operation. The medical staff at a cardiac care unit also handles problems that may often develop in cardiac patients, including:
Patients in the CCU frequently have concurrent acute or chronic diseases, making their care more difficult and extending their hospital stays. ConclusionWhen referring to a particular hospital unit, the term CCU might represent one of two things. We may refer to a critical care unit at various institutions. An intensive care unit is equivalent to this. Intensive Care unit (ICU), where patients with a range of serious ailments receive the best treatment possible from skilled medical professionals. A CCU stands for a cardiac care unit at other hospitals. This is a dedicated facility for patients recovering from heart surgery or those with significant cardiac diseases. The medical staff in this facility will be well trained in cardiac care. You will be moved to a standard hospital room to finish your treatment after you no longer require 24-hour critical or specialist cardiac care.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










