Chemical FormulaA chemical formula is a short way to write about the atoms present in a molecule or compound, for example, an oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen atoms bonded together. We can write that one oxygen atom is bonded to another oxygen atom. But, it is a long sentence and does not seem a convenient way to provide information about the atoms bonded together in a molecule. So, to make it shorter chemical formula was introduced. For example, in the case of an oxygen molecule, the chemical formula is O2. O represents oxygen atom and 2 represents the number of oxygen atoms that are bonded together. Similarly, we use H2O for water molecule that shows one oxygen atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. 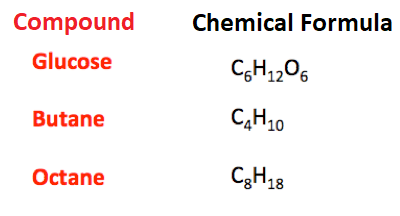
So, we can say that the chemical formula is a symbolic representation of the composition of a molecule of a compound. The symbols of atoms are used to represent the atoms and numbers are used as a subscript to represent the composition or number of atoms of an element present in the molecule or compound. So, the chemical formula indicates, the atoms of the elements present in the compound and the ratio of these elements in the compound. The chemical formula is also known as the molecular formula. It is the valency that decides that how many atoms will participate in bond formation. For example, in one molecule of water (H2O), the valency of hydrogen is 1 as it needs one electron and valency of the oxygen is 2 as it needs two electrons to complete its octet. So, one oxygen atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms to form one molecule of water. This information can be simply represented by the chemical formula H2O. The chemical formula of a molecule always remains the same as it is written by following certain rules. Let us see, what are the rules for writing the chemical formula of a molecule or compound? Rules for writing chemical formula are listed below:There are a total of three rules for writing the chemical formula. First ruleThe metal and cation are written first followed by non-metal and anion. For example, Magnesium chloride, in this magnesium is metal and chlorine is a non-metal, so, it is written as MgCl, similarly, in NaCl, metal sodium is written first and non-metal chlorine is written after it. Similarly in iron sulphide, the symbol of metal iron is written first which is followed by the symbol of non-metal sulphur such as FeS. Second ruleAccording to this rule, the valency or charge on an atom must be balanced based on the valencies of participating elements. For example, in NaCl, the charge of sodium ion is neutralized or balanced by the charge on Chlorine. Furthermore, the valencies are interchanged or cross over is applied. The valency of one element is written below another element as subscript and vice versa. The + and - signs and '1' are omitted to get the chemical formula. Third RuleThis rule tells how to write the polyatomic ions. The molecules that contain charged atoms are called polyatomic ions. As per this rule, more than one polyatomic ions should be written within the bracket. For example, OH- is a polyatomic ion with a negative charge. It is written in the bracket when it reacts with iron (Fe) to form iron hydroxide such as Fe (OH)2. The valency of iron is 2 and the valency of hydroxyl ion is 1. Iron tends to lose two electrons so it will react with two hydroxyl ions as one hydroxyl ion needs only one electron. So, its chemical formula will be Fe (OH) 2. OH is written within bracket with subscript 2 as we have two polyatomic ions in this case. So, in the case of ionic compounds that contain polyatomic ions, the formula of the polyatomic ion is written in brackets and the valencies are written below the symbol and if there is a common factor between the valencies of cation and anion, the valencies are divided by the common factor. However, if there is only one polyatomic ion, it is not written within the bracket. For example, sodium hydroxide has only one polyatomic ion. In this case, one sodium ion (Na+) reacts with one hydroxyl ion (OH-). Here, we write NaOH and do not use brackets as there is only one polyatomic ion. Let us see how we can write the chemical formula of simple compounds by using the above rules: In the case of simple molecular compounds such as binary compounds that are made of two elements, the name of the elements are written side by side and their respective valency is written below their symbols. For example, HCl, H2S, CO2, etc. The molecular compounds are formed between non-metals. See the examples below; Hydrogen ChlorideThe chemical symbol of hydrogen is H and of chlorine is Cl and the valency of both the elements is 1. Hydrogen tends to gain 1 electron to gain stability and chlorine tend to gain 1 electron to complete its octet. So, one hydrogen atom reacts with one chlorine atom, so the chemical formula of the one molecule of hydrogen chloride is HCl. See the image given below; 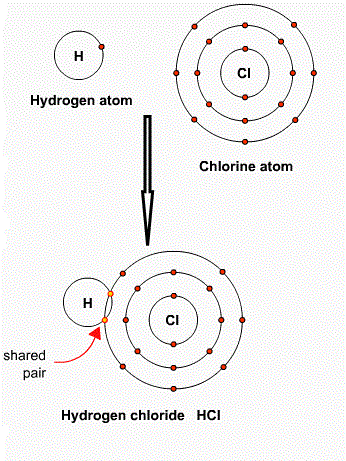
Hydrogen SulphideThe symbol of hydrogen and sulphide is H and S. The valency of hydrogen is 1 and the valency of sulphur is 2. Sulphur needs two electrons to complete its octet and hydrogen needs one electron to complete its two electrons, so, sulphur will react with two hydrogen atoms to form a molecule of hydrogen sulphide with no net charge. So, the chemical formula of this hydrogen sulphide will be H2S. See the image given below; 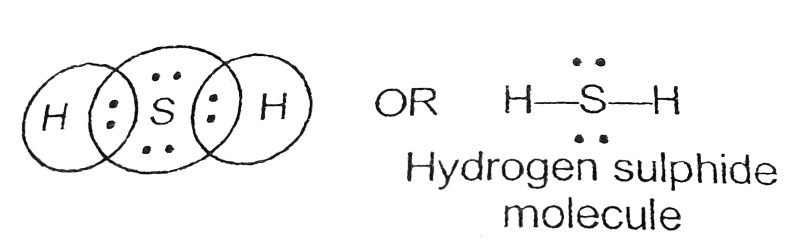
In the case of simple ionic compounds such as compounds made up of monatomic ions, the symbol of the metal atom that forms cation is written first and is followed by the symbol of the non-metal that forms anion and their valencies are written below their symbols. For example, Calcium chloride is written as CaCl2. How to write the chemical formula of complex compounds by following the above rules; i) Magnesium Chloride The chemical symbol of magnesium and chlorine are Mg and Cl respectively. The atomic number of magnesium is 12, so its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2. So, it tends to lose 2 electrons to complete its octet, so its valency is 2. 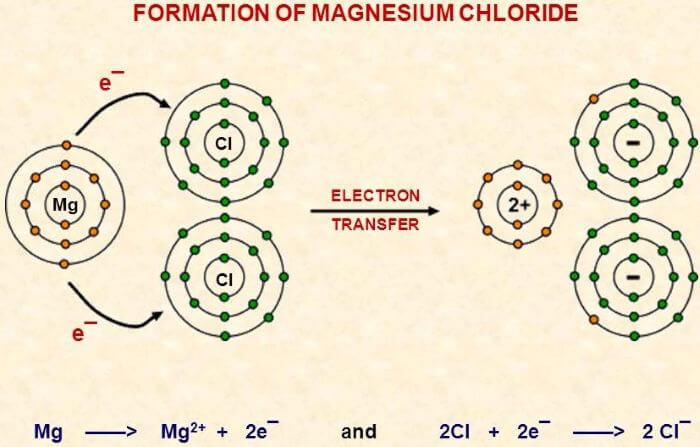
After losing 2 electrons, Mg forms an Mg2+ ion that has a 2+ charge. Whereas the atomic number of chlorine is 17 and electronic configuration is 2, 8, 7. It tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. So, it forms a Chlorine ion (Cl-) with 1- charge. As one chlorine atom needs only one electron, and Mg wants to lose 2 electrons, so two chlorine atoms will react with one magnesium atom so that both the elements could complete their octets. According to the first rule of writing chemical formula, we have written Mg first as it is a metal and chlorine is written after magnesium as chlorine is a non-metal. Now after interchanging their valencies as per the above rule, the chemical formula of this compound will be MgCl2. ii) Aluminium Oxide The chemical symbol of Aluminium and Oxygen is Al and O, respectively. The atomic number of Al is 13 so its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 3 which shows its valency is 3 so it tends to lose 3 electrons to complete its octet. The valency of oxygen is 2 as it tends to gain 2 electrons to complete 8 electrons (octet) in its valence shell. So, the bond formation will take place between 2 Al atoms and 3 O atoms to form one molecule of Aluminium Oxide as shown in the below image. According to the chemical formula rules, Al is metal and O is non-metal and after interchanging their valencies the chemical formula of Aluminium oxide will be Al2O3. 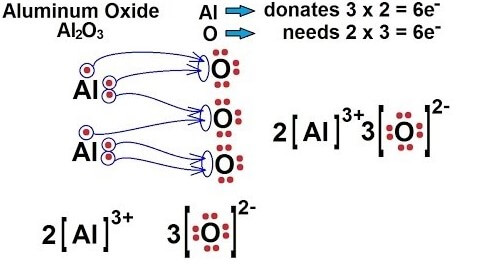
iii) Calcium Hydroxide The chemical symbol of calcium and hydroxide is Ca and OH, respectively. The valency of Ca is 2, so it has a tendency to lose 2 electrons to achieve a stable state by completing its octet. On the other hand, hydroxyl ion has a tendency to gain 1 electron. So, one calcium atom reacts with two hydroxyl ions and the chemical formula as per the rules will be Ca (OH) 2. OH is a polyatomic ion and it is more than one, so it is written within the bracket. iV) Ammonium Sulphate The chemical symbol of ammonium and Sulphate is NH4 and SO4. The valency of ammonium is 1, it tends to lose 1 electron. The valency of sulphate is 2 so it tends to gain 2 electrons. So, two ammonium ions react with one sulphate ion to form one molecule of ammonium sulphate. Both are polyatomic ions. So, according to the above rules, its chemical formula will be (NH4)2SO4. The polyatomic ion (SO4) is only one, so it is not written in brackets. The steps to write a chemical formula based on the above rules are as follows;
Let us write the chemical formula of some compounds by following the above steps; i) Chemical formula of water
ii) Chemical formula of Hydrogen sulphide
iii) Chemical formula of Carbon tetrachloride
iv) Chemical formula of Carbon dioxide
Next TopicMole Concept | What is mole
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










