Cloud computing DefinitionWe can now deliver numerous services over the Internet with the help of cloud computing. Instead of storing files locally or on a single hard disc, you can use cloud-based storage to save them remotely. As long as a device has internet access, it can access the information and program necessary to carry them out. For individuals and companies, cloud computing is a popular choice due to several factors, including cost-effectiveness. Cloud computing technology has made data storage even easier in the twentieth century. 
Major LessonsCloud computing delivers a wide range of services through the Internet. People requiring extra storage capacity and businesses looking for a dependable off-site data backup solution are increasingly interested in cloud storage. Using cloud-based storage, we can swiftly recover files from a remote database. Private services are hosted on a network and are only accessible to certain clients, whereas we can provide both public and private services online for a fee. The relevance of cloud security in IT has increased. Familiarity with Cloud ComputingThanks to companies that provide cloud services, users can store data and apps on remote servers and access information via the Internet. The user can access it remotely because they are not required to be at a specific location. You can process data with cloud computing without using a computer or bringing around bulky equipment. Your data, work, and applications will be accessible from any device that can connect to the Internet once the Internet becomes the Cloud. Additionally, the job is sent to big computer clusters far away in cyberspace. Clouds can be both public and private. A hybrid option combines elements of public and private services. Internet-based public cloud service companies offer their services in exchange for money. On the other hand, access to personal cloud services is restricted to a small group of users. Types of Cloud ServicesRegardless of the service type, cloud computing services provide users with several benefits, including Backup, archiving, and information retrieval for email building and assessing streaming audio and video apps while performing data analysis distribution of software on demand. Cloud computing is used by many industries, including huge enterprises, small businesses, non-profit organizations, governmental institutions, and even individual consumers. 
Cloud computing is not a stand-alone technology, much like a chip or a phone. Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) make up the system's three main components (PaaS). Software is licensed to users under the software-as-a-service (SaaS) paradigm. Licenses are typically made accessible on-demand or under a pay-as-you-go system. The Microsoft Office 365 suite includes a similar technique. Customers can use an on-demand, outsourced service instead of completely purchasing software and servers. Using the IaaS method, operating systems, servers, and storage can all be made accessible over IP-based connectivity as a component of an on-demand service. Well-known examples of IaaS platforms are Microsoft Azure and IBM Cloud. Platform-as-a-Service is the most challenging of the three cloud computing layers (PaaS). PaaS and SaaS are quite similar, with PaaS being the primary difference. Advantages of Cloud ComputingCloud-based software, which can be accessed on any device via a browser or native apps, has advantages for businesses in all sectors. Users can effortlessly transfer files and settings between devices. Only recently has cloud computing been used for file access. Thanks to cloud computing, people can access their email and store files using services like Dropbox and Google Drive from any computer. Users can back up their music, data, and photos using cloud computing services, ensuring they always have access in the event of a hard disc disaster. Additionally, huge corporations can save a tonne of money with this method. Businesses had to invest in costly information management infrastructure, technology purchases, building, and maintenance before the Cloud was a practical substitute. People can use the cloud architecture to reduce the storage they need on their computers or laptops. Since software companies may now sell their products online rather than through more conventional, tangible channels like discs or flash drives, customers can upgrade software more quickly. 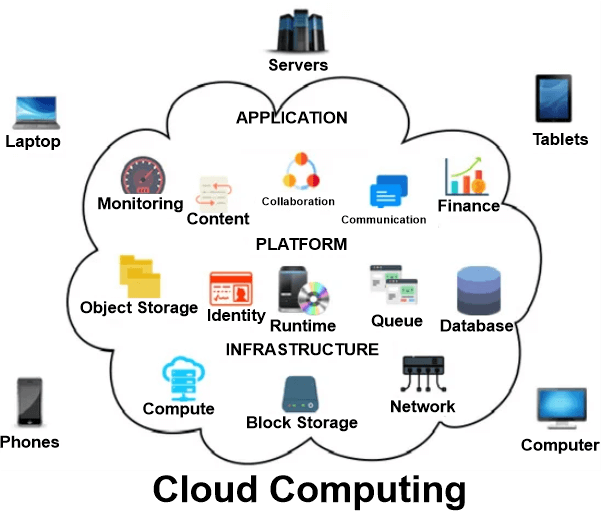
For instance, customers of Adobe can use the programs that are a component of its Creative Cloud by subscribing online. Users can now obtain updated versions and software fixes by using cloud computing. In terms of private financial and medical details, security has always been a primary concern with the Cloud. The problem still exists today, even though regulations require cloud computing firms to strengthen their compliance and security measures. It is encrypted to secure sensitive information; nevertheless, the data is lost if the encryption key is lost. Cloud computing firms' servers are vulnerable to internal problems, power outages, and natural calamities. The impact of cloud computing on the world is twofold. A blackout in California might immobilize users in New York. If something causes the Maine-based supplier of a Texas-based company to crash, the Texas company could lose its data. On the other hand, because so many people may access and modify data through a single gateway, unintentional errors could propagate across the system. Enterprises can use the Corporate World Cloud computing in various ways. While some clients choose a hybrid approach, maintaining parts of their apps and data on private servers and some in the Cloud, other clients keep everything in-house. When it comes to providing services, the following are the top businesses in the business computer sector:
With a pay-as-you-go, outsourced business model, Amazon Web Services is entirely accessible to the general public. After registering on the platform, you can sign up for apps and extra services. Microsoft Azure customers can store data on their servers, and the Alibaba Group includes Alibaba Cloud. What Is a Cloud Computing Example?Businesses and consumers use a variety of cloud computing apps nowadays. Websites that stream audio and video are an example of a cloud service because the actual media files are kept elsewhere. Utilizing data storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive, or Box is an additional option. What Are the Most Popular Models of Cloud Computing?Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), platforms as a Service (PaaS), and software as a Service are the three primary categories of cloud computing services (SaaS).
Cloud Computing SecurityCloud security refers to protecting digital assets and data stored on cloud-based services. They are using services like firewalls, security tokens, VPNs, and data encryption, among others, as well as the two-factor authentication (2FA) and two-factor encryption standards. Value DeclarationAdvocates for Cloud computing claim that public and hybrid clouds can help organizations avoid or lower initial IT infrastructure expenses. Additionally, supporters argue that cloud computing enables IT teams to more quickly adjust resources to meet fluctuating and unpredictable demand more by offering burst computing capability and high computing power at specific times of peak demand and that it helps businesses get their applications up and running more quickly with improved manageability and less maintenance. MarketAccording to IDC, the present $706 billion level of global spending on cloud computing services will have climbed to $1.3 trillion by 2025. In 2022, more than $1.3 trillion in commercial IT expenditure will be impacted by the shift to the Cloud, and by 2025, that amount will have increased to around $1.8 trillion. 
According to a McKinsey & Company analysis, Fortune 500 companies will have access to more than $1 trillion in run-rate EBITDA in 2030 as a result of cloud cost-optimization levers and value-oriented business use cases, contrary to Gartner's prediction that end-user spending on public cloud services will reach $600 billion by 2023. Types of Cloud ComputingThere are numerous varieties of clouds, and each one is distinct. Public CloudPublic clouds offer their services on servers and storage connected to the Internet. Independent businesses manage the infrastructure, software, and hardware management and maintain these. Customers use accounts that are virtually universally accessible to pay for services. Private CloudThe term "private cloud" describes cloud infrastructure that is solely maintained or hosted for a single company, either internally or by a third party. The firm needs to re-evaluate its decisions on resource allocation because virtualizing the business environment for a private cloud project requires a lot of work. Although there are few architectural distinctions between public- and personal cloud services, security issues become much more pressing when numerous clients share resources (such as apps, storage, and other resources). Private clouds are only accessible to a small number of clients, typically just one company or organization. The company's data center could host the cloud computing service. The decision of businesses and organizations to choose a public cloud or on-premises solution is influenced by several criteria, including the functionality of the answers, cost, integrational and organizational aspects, and safety and security. Numerous private cloud computing services are available on a private network. Hybrid CloudHybrid cloud storage is another option. For instance, a company might utilize a private cloud application to hold confidential client information while connecting that application to a public cloud software provider that offers business intelligence tools. Through the integration of externally accessible public cloud services, this hybrid cloud example increases the ability of the corporation to supply a particular business function. The adoption of hybrid clouds is influenced by various elements, including an organization's application needs, data security, compliance requirements, and required levels of data control.Hybrid clouds, as their name implies, include both public and private services. This style of architecture increases the user's options while enhancing their infrastructure and security. Another example of a hybrid cloud is when IT companies take computing resources from the public Cloud to handle urgent capacity needs that the private Cloud cannot control. Hybrid clouds can use Cloud bursting with the capability to scale between clouds. Under the conditions of cloud bursting, an application continues to function in a private cloud or data center until the need for processing power increases. At this point, it "bursts" into a public cloud. The fact that a business only has to pay for more computer resources when needed is a key advantage of cloud bursting and a hybrid cloud strategy. Multi-CloudMultiple cloud components often communicate with one another using a loosely coupled method like a messaging queue in cloud architecture, the software systems architecture involved in cloud computing delivery. When applied to this and other mechanisms, elastic provision implies intelligence in tight or loose coupling. ArchitectureData centers can create internal IT architectures that can manage typical workloads and utilize cloud resources from public or private clouds when processing demand spikes by using cloud bursting. A hybrid cloud built on various hardware is called a "cross-platform hybrid cloud." Usually, a cross-platform hybrid cloud is powered by many CPU architectures, such as x86-64 and ARM. Users may expand and deploy applications transparently without being aware of the variety of hardware available in the Cloud. The development of ARM-based system-on-chip for server-class computing has led to the emergence of this type of Cloud. 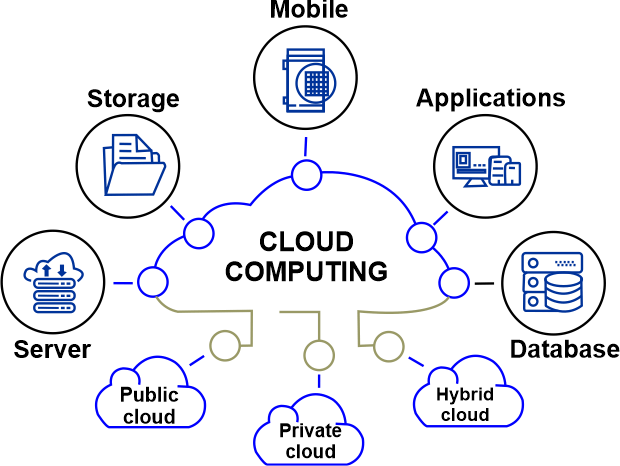
In essence, hybrid cloud infrastructure works to get rid of the constraints that come with private cloud networking's multi-access relay features. The benefits of virtualized interface models include increased runtime flexibility and adaptive memory processing. ConclusionThe high-level issues of commercialization, standardization, and governance in cloud computing systems' conception, development, deployment, and upkeep are addressed methodically. The system, software, web, performance, information technology engineering, security, platform, risk, and quality engineering are a few diverse fields contributing to this multidisciplinary approach.
Next TopicComputer Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










