WHAT IS COMMERCE

Simply put, commerce is the establishment of a large-scale exchange of goods and services into money or monetary value between economic agents, i.e. producers and consumers. It includes all activities that directly or indirectly affect the exchange process. It works on the principle that whatever is produced must be consumed. In short, commerce creates a continuous and efficient supply and demand for goods and services in the economy. A point should be noticed here that "commerce is a subset of business not a synonym for it".
Characteristics
Some of the most important characteristics of commerce are as follows:
- Commerce makes a bridge between the producers and consumers of goods and services.
- It helps in the exchange of goods and services in the economy for sufficient consideration.
- Commerce covers all the services which are given by various organizations to make a free flow of goods and services in the market.
- It eliminates all barriers that affect the process of exchange. These barriers are related to the person, time, place, risk, knowledge, finance, etc.
- Commercial activities take place with the earnings of profits.
- Commerce tends to create utility in the economy.
Importance of Commerce
Commerce plays an important role in the life of an individual as well as in the economy of a country. It also helps in the development of the companies. Commerce is important in the following ways:
- Commerce satisfies the increasing human wants.
- It connects producers to consumers.
- It improves the standard of living by providing various products and services to society.
- It helps in the distribution and movement of goods and services in the domestic as well as international markets.
- Commerce creates employment opportunities in the economy.
- It increases national income and wealth and also helps a country in earning foreign exchange.
- It promotes the growth of industrial development.
- It expands aids to trade and modernizes them.
- It encourages international trade and helps in the import and export of goods and services.
- Import of skilled labor and export of raw materials helps in the development of underdeveloped countries. This can also be possible only because of commerce.
Types of Commerce
As per the market segmentation, there are six types of business models or commerce, which include the following:
1. Business-to-Business (B2B)
In this type of commerce, goods and services are sold from one business firm to another. In this case, the buying firm can resell the goods or services to the consumer or the end-user. Producers and wholesalers are the best examples of B2B commerce.
2. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
In B2C or direct-to-consumer commerce, the goods or services are sold by a firm directly to the end-user, i.e., final consumers. It removes the interference of middlemen which reduces the prices of goods and services. Some examples of this model of commerce are WalMart, Target, REI, Gap, etc.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C commerce refers to a market environment in which goods or services are purchased by a consumer from another consumer with the help of a third-party business or platform to make the transaction. This third party is known as a middleman or broker. Examples of C2C commerce are eBay and Craigslist.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
C2B is that type of commerce in which a consumer prepares the products or services to sell them to the companies. Blogging, YouTube reviewing, photography, graphic designing, etc. are some examples of C2B commerce. Online shopping companies such as Flipkart, Amazon, etc. also allow the website's owners to sell their products on their site by connecting with them.
5. Business-to-Administration (B2A)
B2A is also called Business-to-Government (B2G), refers to the transactions between the companies and government or administration agencies. Accela, a software company is an example of such a model of commerce that serves government software solutions and many other services.
6. Consumer-to-Administration (C2A)
In C2A commerce, the transactions take place between individuals and government administration. This model is helpful for the consumers to ask queries directly from their local public authorities. These queries can be related to taxes, health, payment of tuition fees for higher education, etc.
Classification
Commerce can be classified into two different categories which include the following:
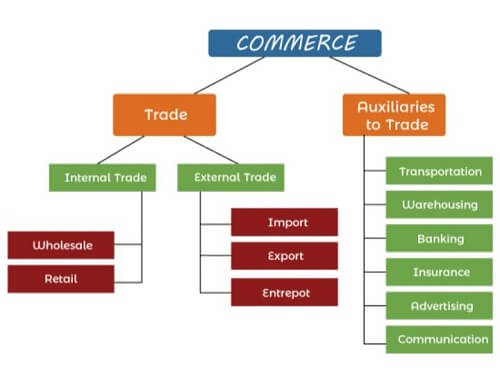
1. Trade
The process of transfer or exchange of goods and services for mutual benefit is known as trade. The person who plays the role of a middleman between the producer and the consumer is called a trader. Trade is further classified into two parts:
-
Internal Trade
It refers to the buying and selling of goods and services within the geographical boundaries of a nation. In this type of trade, the payment is made by using the country's legal currency or through the banking system of the country. Internal trade has two types:
- Wholesale: In this type of internal trade, the goods are purchased in bulk from the producer and then sold to many retailers.
- Retail: In this type of internal trade, the goods are bought from the wholesaler by the retailer and then resold to the consumers in small quantities as per their demand.
-
External Trade
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services from and to other countries. External trade takes place beyond the geographical boundaries of a country. External trade has three types:
- Import: When goods and services are bought from another country then it is known as an import.
- Export: When goods and services are sold to another country then it is known as an export.
- Entrepot: It refers to re-exporting the goods. In simpler words, when a country imports the goods not for domestic consumption but for reselling to another country then it is known as an entrepot.
2. Auxiliaries to Trade
It includes all those activities which support the easy flow of trading. These auxiliaries remove all the hindrances that arise while trading. They include the following:
-
Transportation
Transportation eliminates the hindrance of place by supplying or sending the goods from their place of manufacturing to the place of consumption. As we know, the goods are manufactured in one place but are demanded at various locations. To solve this problem, the transportation activities are proved to be helpful.
-
Warehousing
Warehousing removes the hindrance of time and storage. Various goods are produced in a particular season but are demanded throughout the year for daily uses like cotton, sugar, juice, etc. Other than this, there are some goods which are demanded in a particular season only such as woolen clothes, cotton clothes, umbrellas, etc. Hence, warehousing provides proper storage and safety to these goods for future trading.
-
Banking
The banking sector helps in eliminating the hindrance of finance by providing financial support to the organization or enterprise. As we know, there is a time gap between the production and consumption of goods which means there will be a gap between the investment and receiving the payments of funds. In such a case, the banks help the entrepreneur in raising funds so that the production activities of the firm will not be affected.
-
Insurance
Insurance is helpful in removing the hindrance of fear or risk of loss during transporting goods from one place to another. It also reduces the risk of loss of goods by theft or fire.
-
Advertising
Advertising removes the hindrance of information/knowledge in the market by informing the customers and making them aware of the goods and services provided by the producers. The seller can use various channels like radio, internet, television, newspaper, etc. to advertise their products.
-
Communication
The goods and services offered by the sellers are needed to be communicated among the buyers as well as buyers should also convey their needs to the sellers by way of orders. This need of both the buyers and sellers can be transferred by the way of communication.
Subjects Related to Commerce
The major subjects that are included in commerce are as under:
1. Accountancy
Accountancy refers to the practice of recording, allocating, and outlining the day-to-day transactions for a business. Various sub-fields of accounting are as follows:
- Financial Accounting
- Cost Accounting
- Management Accounting
- Tax Accounting
- Social Responsibility Accounting

2. Business Studies
Business refers to the process of making money by producing or buying and selling goods and services with the main aim of earning profits. The study of such a process is known as Business Studies. However, Business Studies is much more than this definition. It includes the fields of finance, accountancy, marketing, management, etc. It helps the individual in understanding how a business can be set up and operated effectively and efficiently.

3. Economics
Economics refers to the study of optimal utilization of limited or scarce resources at the micro as well as macro level. It helps in understanding the market conditions which is further beneficial for an individual or an organization to organize resources and coordinate with each other so that the possible outcome can be estimated. The two types of economics are:
-
Microeconomics: It is a subject matter that deals with the economic problems related to the small or microeconomic units, i.e., an individual consumer, producer, firm, market, etc.

- Macroeconomics: It is a subject matter that deals with the economic problems related to the macro units or economy as a whole, i.e., at the national or international level.
Best Courses for Commerce Students
There are lots of courses that a commerce student can opt for. These courses are:
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Bachelor of Laws (LLB)
- Cost and Management Accountant (CMA)
- Chartered Accountancy (CA)
- Company Secretary (CS)
- Bachelor of Economics (BE)
- Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA)
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
- Journalism and Mass Communication
Career Options for Commerce Students
Some of the top career options available for commerce students are as follows:
- Chartered Accountant,
- Investment Banker,
- Cost Accountant,
- Actuaries,
- Financial Planner,
- Financial Manager,
- Financial Analyst,
- Economist,
- Banking,
- Company Secretary,
- Insurance Agent,
- Stock Broker,
- Management Accounting, etc.
|




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now











