Commercial Bank DefinitionBankA bank is a financial organization with the legal right to accept money and provide loans. Banks may provide financial operations, including safe deposit lockers, currency exchange, and investment management. Many different sorts of banks are accessible, including retail, commercial or corporate, and financial companies. 
In most countries, banks are governed by the ruling party or central bank. The four categories into which banks are divided are:
Regional Rural Banks (RRB), Foreign Banks, Public Sector Banks, and Private Sector Banks are additional types of Commercial Banks. A country's economy depends on commercial banks. By accepting money from customers and lending it to others, they provide end users with vital banking services and contribute to market capital and liquidity growth. Commercial BankA commercial bank is a type of financial organization that handles all transactions involving the withdrawal and deposit of funds for the common people, offering loans for investments and other similar tasks. These banks are profit-making organizations that operate solely for financial gain. 
Lending and borrowing are the two main aspects of a commercial bank. The bank accepts deposits and distributes funds to various projects to earn interest (profit). The borrowing rate is the interest rate that a bank charges depositors, whereas the lending rate is the rate at which a bank gives credit. History of Commercial Banks in IndiaCommercial banks are particularly significant in India because they aid in economic growth and offer important data on financial operations. The advancement of India has long been boosted by its banks, which provide cost-effective financial facilities to a huge proportion of individuals and fulfill the short- and medium-term credit requirements of numerous organizations, especially medium-sized and small businesses. According to the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) Act of 1934, all significant banks are classified as commercial enterprises. Other banking models in the bank category include Small Finance, cooperative, and Payments Banks. The remaining ownership types of the banks are the private sector, regional or rural, public sector, and foreign banks. Importance of Commercial BanksEconomic activity depends heavily on commercial banks. They help build capital and liquidity in the market and offer consumers an important service. Commercial banks maintain liquidity by lending out the money that their clients deposit in their accounts. Commercial banks create credit, increasing consumer spending, employment, and other key indicators such as manufacturing. Thus, a central bank in their nation or region sets strict regulations on commercial banks. For example, commercial institutions are bound to reserve requirements set by central banks. This signifies that banks must reserve a certain portion of the consumer deposits they receive at the central bank if there is a sudden rise in withdrawals from the public. The Function of Commercial Bank
There are two basic categories into which commercial banks can divide their functions. 
Primary functions
Secondary functions
Role of commercial banksThe banking sector controls an entire nation's economy. A commercial bank performs the following roles:
Types of Commercial BanksThere are four basic types of commercial banks: 
1. Private bank: It is a subtype of the commercial bank where private individuals or businesses own most of the share capital. The entire private bank is listed as a company with limited liability. For example, Housing Development Financing Corporation (HDFC) Bank, Yes Bank, Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) Bank, and more banks. 2. Public bank: This type of bank is nationalized, and the government owns a sizable portion. For example, Bank of Baroda, Punjab National Bank, Corporation Bank, Dena Bank, and State Bank of India (SBI). 3. Foreign banks: These banks were founded in foreign nations and had branches worldwide. For example, American Express Bank, Citibank, Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC), Standard & Chartered Bank, and others. 4. Regional Rural Banks: These banks are scheduled commercial banks with the primary goal of lending money to economically deprived society groups, such as agricultural laborers, small business owners, and marginal farmers. They typically function at the regional level in the various states of India and could also have branches in particular urban regions. RRBs also perform the following other crucial duties:
Commercial Bank ExamplesBelow are some examples of commercial banks in India:
Commercial Banking CareersA commercial banker might work with any or all of the abovementioned services and products, or they may choose to focus on one particular field. Several more job titles are:
Banking: Retail vs. Commercial
Depository banks include both commercial and retail banking. Commercial finance organizations provide services to both people and enterprises. Yet, only the general public can use the services offered by retail banks. 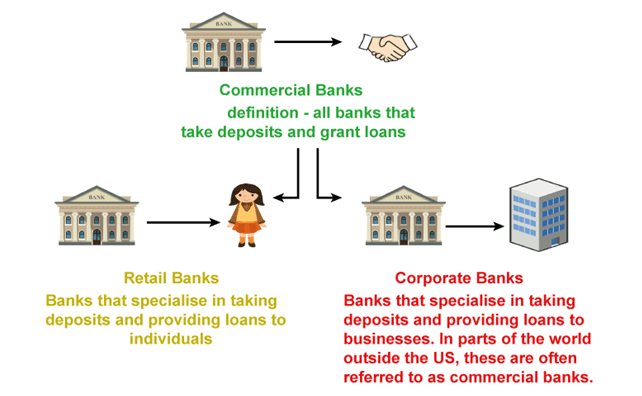
Commercial finance is a sizable industry that serves small and medium-sized businesses, while retail banking serves the general public. Commercial institutions provide services such as trade financing, corporate loans, cash flow management, treasury management facilities, agency services, and overdraft facilities in addition to their basic duties. Retail banks, in contrast, provide services including mortgage loans, saving and checking accounts, cash credit, debit and credit cards.
Next TopicCommunity Health Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










