Computer Definition In EnglishComputers are becoming a necessary component of contemporary society, permeating almost every area of our daily life. A computer is, at its most basic level, an electronic device that processes data, conducts calculations, and stores information. In order for the computer to perform its functions, a number of hardware and software components must cooperate together. The physical parts that make up a computer are known as its hardware. This includes the central processing unit (CPU), which processes data and executes instructions, the memory, which stores data and instructions that the CPU utilizes to do tasks, and the input and output devices, which enable user interaction with the computer. Keyboards, mouse, and touchscreens are examples of input devices; monitors, printers, and speakers are examples of output devices. 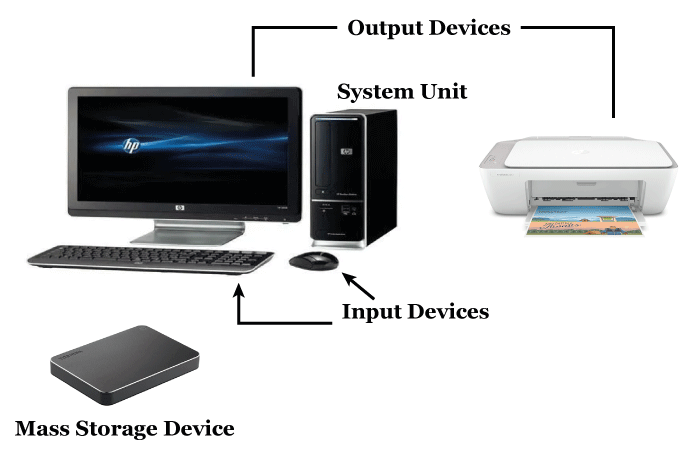
The programmes and directives that tell a computer what to do are referred to as a computer's software. This can comprise everything from the operating system, which controls the computer's resources and offers a user interface, to the programs that enable users to carry out tasks such as word processing, image editing, or web browsing. Depending on their size, use, and capabilities, computers can be divided into a number of categories. Personal computers (PCs), for instance, can be found in homes, workplaces, and educational institutions and are created for individual usage. Workstations are more powerful computers used in specialist industries like engineering or scientific research. Servers are computers that are made to offer services to other computers across a network, such as web servers that host websites or email servers that manage email conversations. The emergence of mobile computing, which refers to the use of portable devices like smartphones and tablets, has been one of the most significant advancements in computing in recent years. These gadgets offer a variety of features, including internet connectivity, camera capability, and access to a large range of applications, and are made to be very portable. The development of cloud computing, or the use of remote servers to store, manage, and analyze data, is a further significant trend in computing. This strategy may provide a number of advantages, such as increased scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, as well as improved security and dependability. History of ComputersThe history of computers dates back to the early 20th century times when humans used tools like the abacus to perform simple calculations. John W. Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert created the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), the original electronic computer, during World War II. The US military employed this enormous system to compute ballistic tables using vacuum tubes. Mauchly and Eckert created the UNIVAC, the first commercially viable computer, in response to the success of ENIAC. Scientific calculations, processing payroll, and analysis of census data were just a few of the uses for it. The first computer to employ magnetic tape for data storage was the UNIVAC. IBM dominated the computer industry in the 1960s with the IBM 360 series, which was extensively employed by businesses, organizations, and academic institutions. When it comes to applications like airline reservations, financial transactions, and scientific research, the IBM 360 mainframe computer is a potent tool that can handle massive amounts of data. The Apple I was the first personal computer created by a team of computer enthusiasts under the direction of Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in the 1970s. The Apple II, which was released after it and enjoyed financial success, helped spark the personal computer revolution. A number of new models were released by manufacturers including IBM, Compaq, and Dell during the 1980s, making personal computers more accessible and inexpensive. Computers became easier to use and more widely available with the advent of graphical user interfaces (GUIs), such as those found in Microsoft Windows and the Macintosh operating system. By allowing users to interact with one another and access information from any location in the world, the internet revolutionised computing in the 1990s. Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator, two popular web browsers, make it simple for users to search online and obtain information. With the advent of smartphones and tablets, which allowed people to access the internet and carry out functions like email and social media, mobile computing experienced a rise in the early 2000s. Parts of ComputerSome of the essential parts of a computer are discussed below: Central Processing Unit (CPU)The CPU is the computer's "brain," or central processing unit. It controls how data flows through the computer and carries out commands. The control unit and the arithmetic logic unit make up the CPU's two primary parts. In contrast to the arithmetic logic unit, which handles logical and mathematical processes, the control unit controls the data flow between the CPU and other components of the computer. Random Access Memory (RAM)Computer memory called Random Access Memory (RAM) is used to temporarily store data that the CPU is currently processing. RAM is a form of volatile memory, which means that it only retains data while the machine is turned on. Any information kept in RAM is lost when the machine is shut off. Because it enables the CPU to retrieve data rapidly and effectively, RAM is a crucial component of a computer. Hard Disk Drive (HDD)For the purpose of permanently storing data on a computer, a Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a type of storage device. In an HDD, a mechanical arm reads and writes data to spinning discs. HDDs are more expensive and have a larger data storage capacity than other storage technologies, such as Solid State Drives (SSDs), but they are slower. Solid State Drive (SSD)An alternative to hard disc drives for storage is a solid state drive (SSD), which is quicker and more dependable (HDD). SSDs do not contain any moving parts because they store data on flash memory. As a result, they outperform HDDs in terms of speed and durability. While being more expensive than HDDs, SSDs perform better and are better suited for storing operating systems and frequently used software due to their speedier performance. MotherboardThe main circuit board of a computer is called the motherboard. It gives the rest of the computer's components a platform on which to communicate. Together with the CPU socket, Memory slots, and expansion slots, the motherboard also includes other parts. Other peripherals, such the hard disc and optical drive, can be connected to it via connectors as well. Power Supply Unit (PSU)The task of transforming wall outlet AC power into computer-usable DC power falls on the Power Supply Unit (PSU). All other computer components, such as the motherboard, CPU, and other hardware, are powered by the PSU. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)A computer's graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialised processor that is used to render pictures and videos. Gaming and other graphics-intensive applications require the GPU because it handles the processing of complicated graphical data. Although some CPUs include integrated GPUs, dedicated GPUs are more powerful and performant. Optical DriveA storage device known as an optical drive employs a laser to read and write data to optical discs including CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. While being less widespread on computers, optical discs are still helpful for installing software and watching movies. Keyboard and MouseComputer input devices such as the keyboard and mouse are necessary. Text and commands are entered using the keyboard, and objects on the screen are selected and the cursor is moved using the mouse. Touchpads and touchscreens are just a couple of the several sorts of input devices that are accessible. MonitorA computer's monitor serves as its display device. It shows graphics and text produced by the CPU and GPU. Uses of ComputersToday, computers are used in almost every aspect of our lives, from simple tasks like sending emails to complex ones like running simulations and analyzing data.
Types of ComputersComputers come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and configurations, each designed to meet different needs and applications. Some of the most common types of computers are: Desktop ComputersThe most common type of computer is the desktop, which features a tower case that houses the CPU, motherboard, and power supply as well as other hardware parts. Laptop ComputersLaptop computers are built to be small and portable. They are powered by rechargeable batteries and include a built-in monitor, keyboard, touchpad, or trackball. Those who must work on the go or have a small workstation should use laptops. While having less computing power than desktop computers, laptops can nevertheless handle the majority of common tasks including word processing, online browsing, and multimedia playing. Tablet ComputersTablet computers are portable electronics primarily made for leisure and enjoyment. They are run by rechargeable batteries and have a touch screen instead of a physical keyboard. E-book reading, gaming, and surfing browsing on tablets are all fantastic. They can be used for video conferencing as well as other social media activities, and they are helpful for taking notes, drawing, and other types of sketching. All-in-One ComputersThe monitor, speakers, and other peripherals are included in all-in-one PCs, which consolidate the hardware elements of a desktop computer into a single device. Comparatively speaking, all-in-one PCs are smaller and take up less desk space. More so than conventional desktop computers, they are also simpler to set up and operate. WorkstationsWorkstations are top-of-the-line computers created for use by professionals in industries including engineering, architecture, and scholarly research. More potent gear, such as multi-core CPUs, lots of RAM, and top-tier graphics cards, are used in the construction of workstations than in desktop PCs. Workstations are used to perform computationally intensive tasks including producing 3D images, simulating intricate systems, and analyzing massive data sets. ServersComputers with the purpose of serving other devices on a network are known as servers. Website hosting, file storage, email management, and other tasks that call for a lot of processing and storage can all be done on servers. Servers can be housed on-site in a small business or organization or in a specialized data center. Compared to other computer types, servers are often more expensive and sophisticated, and they require specialist knowledge to set up and manage.
Next TopicConductance Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










