Configuring Kali LinuxOnce we boot Kali Linux, we will have Kali's main menu that is organized by theme with the various types of tasks and activities that are relevant for the penetration tester and other security professionals as 0073hown in Figure below. 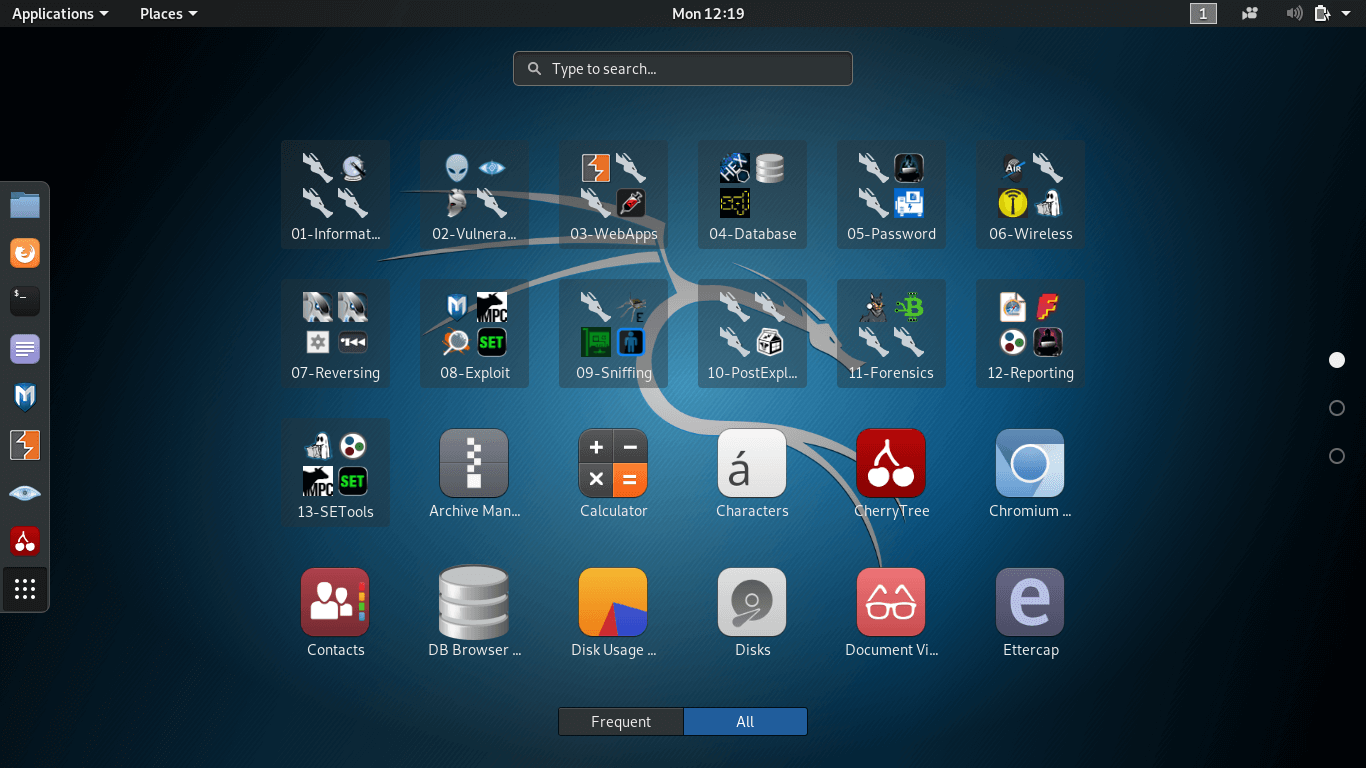
The task and activities are:
Kali Linux configurationHow to configure Network in Kali Linux 1. On the Desktop with NetworkManager: In Kali Linux, the NetworkManager is already installed and can be configured through GNOME's control center or through the top-right menu on Desktop as shown in Figure below. 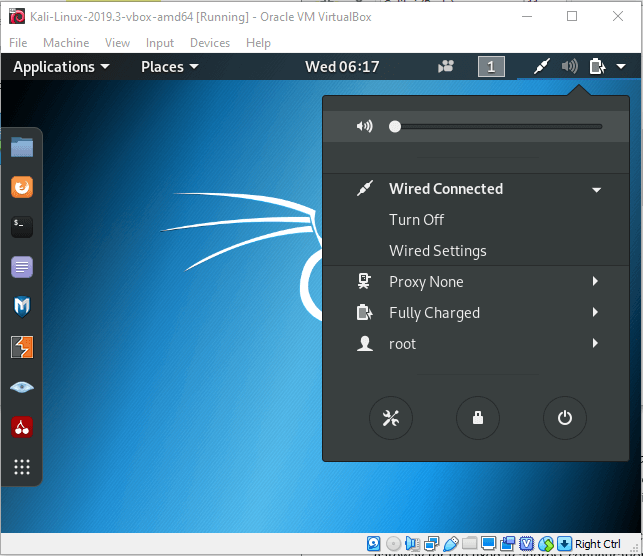
2. On the Command-line with "ifupdown" command: When we want to configure the network settings without using the graphical desktop, we can use the command-line with the already-installed package i.e., ifupdown. It has Ifup and Ifdown tool. The network device can be removed at any time with the ifdown network device. And can modify and back up the network using the ifup network device. And for wireless interfaces, we need the wpasupplicant package, which is included in Kali by default. The most commonly used options are WPA-SSID (defines the name of the wireless network to join) and WPA-PSK (defines the key protecting the network). Note: You must provide more details such as IP address, the network, and the IP of the gateway for the fixed IP address configuration.3. On the Command-line with "systemd-networkd" command: The ifupdown approach is a legacy tool used by Debian but still used as the default for server and other minimal installations. The new tool is introduced in the Kali for Network Configuration, which is systemd-networkd. It's integration with the init system makes it an attractive choice. You can configure these by placing the network files into the /etc/systemd/network/directory. How to update Kali LinuxStep 1: We need to configure Kali Linux Repositories. /etc/apt/sources.list file must contain the following official Kali repositories: Step 2: Updating Kali Linux by first updating the package list. Open terminal and enter: Step 3: After updating the package list, update kept back packages Step 4: Uninstall those packages that are no longer required.
Next TopicKali Linux Commands
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










