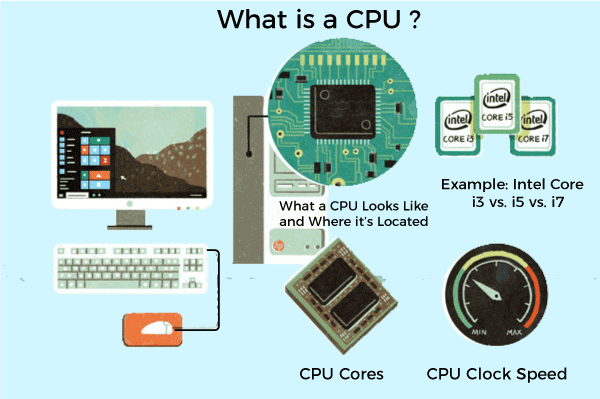
CPU - Central processing Unit

CPU is the abbreviated form of Central processing unit. It is also known as the central processor or the primary or main processor. Sometimes it is also referred as the processor. An electronic circuit known as a central processing unit (CPU), main processor, or simply processor executes instructions contained in a computer programme.
Using the guidance in the programme, the CPU carries on basic arithmetic and logic functions as well as regulating / managing and I/O operations.
As opposed to external components, which primarily includes the main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialised processors such as graphics processing units (GPUs).
However, CPUs' primary task has remained almost the same and has not changed over time, despite changes in their appearance, layout, design, and execution. A central processing unit typically includes an ALU that usually is involved in performing arithmetic and logic tasks or processors, processor after registering the supply inputs to the ALU and stores the results of ALU operations. The main processor also includes a control unit that arranges or adapts the fetching (from memory) and execution or implementation of instructions by guiding the coordinated operations or of ALU, registers, and other essential attributes, etc.
Integrated circuit microprocessors (IC microprocessors) are used to enforce most contemporary Central processing units. Along with this, one or more central processing units are implemented on a single metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) IC chip are used.
Multi-core processors are microprocessor chips with several processors.
It is possible to multithread the physical processor cores to generate extra virtual or logical processors.
An integrated circuit or IC usually comprises of processing units that may also consist of memory, a peripheral interface, and other essential aspects of the computer, such as integrated devices, known as microcontrollers or system on chip(SoC). There is no central processing unit in array processors, which are multi-processors that work in parallel with no single unit. Virtual processing units are a form of virtual computing and an abstraction of dynamically collated computational resources.
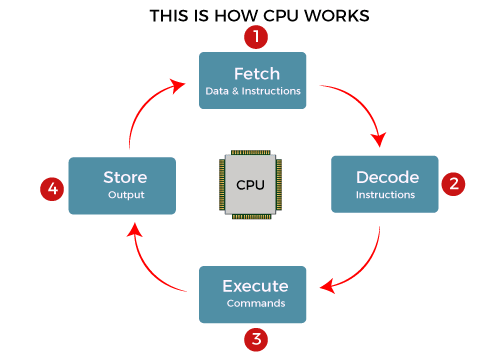
The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is responsible for executing all commands received from the computer's hardware and software.
The central processing unit (CPU) is often regarded to as the computer's brain.
While this may be true, it's probably more apt to call software "brains" and the CPU "supercomputers." A CPU is great at math, but without software, it wouldn't be able to do much else.Input from a peripheral (keyboard, mouse, printer, etc.) or computer programme is the CPU's primary function.
It then outputs relevant data to your monitor or computer screen or conducts the peripheral's requested task, as appropriate.
Central Processing Unit's - History and Evolution
Computers have become a part of our everyday lives, but the first computer was developed in 1946 at the University of Pennsylvania!
- Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer or ENIAC was the processo
- Alan Turing and John von Neumann presented the reprogramming feature that is so widely utilised nowadays. A modern computer's architecture is based on von Neumann's design.
- Microprocessors have come a long way since Intel's 4004 - the first microprocessor ever developed.
- We'll take a look at what's happened so far.
- In the early 1970s, Ted Hoff and others at Intel came up with the idea for the first Processor, which was then produced by the company.
- Intel's 4004 processor was the company's first processor.

1971 - Intel 4004
- Designed by Intel's Federico Faggin and Ted Hoff and Busicom's Masatoshi Shima, it went on sale on November 15, 1971. "
- 2300 transistors with pMOS technology were used in the device.
- There were a total of 46 instructions.
- The intended clock speed was 1 MHz, but it was only achieved at 740 kHz.
- As the world's first microprocessor, it powered the Busicom 141-PF calculator, which is still in use today.
1972 - Intel 8008
- Introduced in August 1972, it is also known as MCS-8.
- CTC's Victor Poor and Harry Pyle worked on it, as did Intel's Ted Hoff, Faggin, Stanley Mazor, and Hal Feeney.
- There were 3500 transistors in it.
- But it was slower than the 4004.
- This computer had a clock speed of 0.5 MHz and a total number of 48 instructions.
Micral and SCELBI were the first personal computers to use it.
1974 - Intel 8080
- Intel 8080 was introduced in 1974.
- Faggin, Mazor, and Masatoshi Shima created it in April 1974.
- The clock speed was increased to 2 MHz, and it used 6000 transistors and nMOS technology. »
- Most notable was the separation of the address (16 bit) and data (8 bit) buses, which was a major advancement.
- It also had 256 input/output ports.
- The MITS Altair 8800 and IMSAI 8080 both used it.
- Similarly, the main processor in Space Invaders (an arcade video game) was the 8080 microprocessor.
1974 - Motorola 6800
- The Motorola processor had no I/O ports.
- I/Os were memory-mapped.
- In addition, the instruction set contained 72 instructions at a clock speed of just 2 MHz
- HCF (Halt and Catch Fire) opcode was used for the first time, preventing the processor from responding to any interrupts until it was reset.
- Motorola introduced HCF, a self-testing feature, for the first time.
1977 - Intel 8085
- The processor was also used as a microcontroller, operating on a +5V supply, unlike the other processors formed so far.
- Von Neumann architecture was used for the first time.
- "It was constructed with nMOS technology and 6500 transistors."
- There were 256 instructions in the instruction set.
- In NASA and ESA space explorations, the radiation-hardened version was employed.
1978 - Intel 8086
- The clock speed was designed to be 10MHz.
- Bruce Ravenel was part of the architecture development team, which included Stephen P. Morse.
- Jim McKevitt, John Bayliss, and William Pohlman designed Logic, with William Pohlman serving as the project manager.
- Mycron 2000 was the first microcomputer to use it.
1979 - Intel 8088
- HMOS-based 8088 was launched on July 1st.
- PLCC (plastic leaded chip carrier) package was available as well as a 40-pin DIP package. »
- There was only 8-bits of data in the path, however.
- 10 MHz was the intended frequency.
- 8088 was the basis for the original IBM PC.
1987 - SPARC
- It's a Sun Microsystems processor.
- It had a 40 MHz clock speed.
- 8 million transistors and 256 I/O pins were used to build it.
- According to the TOP500 list, Fujitsu's K Computer is ranked number one among the world's 500 fastest supercomputers.
- It was based on the SPARC architecture.
1991 - Am386
- There was a striking similarity between this AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) processor and Intel x86 processors.
- In terms of clock speed, the processor was a competitor to Intel's.
- Many manufacturers chose AMD's floating point unit because of its excellent performance.
1993 - Pentium Processor
- P5 was the first Pentium processor.
- Two models were available: 510-pin version and 567-pin
- 1 million transistors were used in its construction.
- At the time, this 32-bit processor was the most advanced processor available.
- There were two instructions that could be executed at the same time in this superscalar x86 microarchitecture, speeding up computation.

1995 - Pentium Pro
- Pentium II was the first Pentium processor.
- It was packaged in a ceramic multi-chip module (MCM) with 387 pins, which was a first for the industry.
- In addition to its dual processor configuration, it has a 200 MHz clock speed.
- In order to build this processor, approximately 5.5 million transistors were used.
- MMX instructions were not included.
- This processor was utilised in ASCI Red, which had teraFLOP (one trillion floating-point operations per second) performance or results.
1997- Pentium II
- The Pentium II processor family was introduced on May 7 and offered a wide range of processors.
- With each new model, the clock speed was steadily increased to 450 MHz.
- A slot or socket module was used instead of the traditional processor.
- Because of this, computer manufacturers were able to fit it into a small space.
- Under this umbrella, a number of processors were introduced: Some of these were Klamath;
- Deschutes; Pentium II overdrive; Tonga, etc.
- It had a heatsink/fan combination that could be removed, which helped with heat dissipation.
1999-Pentium III
- It was introduced on February 26th.
- The SSE instruction was added to the previous model to speed up floating-point calculations.
- Like Pentium II, this processor was released in two versions: Celeron (low-end version) and Xeon (high-end version) (High-end version).
- The following processors are included in this family: Katmai; Coppermine; Coppermine T and Tualatin.
- PSN (Processor Serial Number) was introduced in the production process that formed the processor's unique identity.
1999 - Athlon
- Athlon was announced by AMD on June 23.
- A clock speed of 800 MHz was achieved by using 37 million transistors.
- It came in a 453-pin PGA (Pin Grid Array) package.
- It was faster than Intel's Pentium III, which made Athlon a legitimate competitor. »
- That made it the first processor to reach the 1 gigahertz speed mark in history.
- Enhanced 3DNow! was first launched, which sped up by 2-4 times.
2000-Pentium IV
- Pentium IV was Intel's new single-core processor, with clock speeds ranging from 1.3 GHz to 3.08 GHz.
- When it came to packaging, the 423-pin processor was available in both OLGA and PPGA (Plastic Pin Grid Array) formats.
- The processors that fall under this category include; Willamette; Northwood; Pentium 4-M; Mobile Pentium etc
- Processors in this family were the first to use the NetBurst architecture.
2003-Pentium -M
- This was an Intel single-core mobile processor.
- It was designed with a clock speed is 2.26 GHz.
- There are two processors in this family: Banias; Dothan.
- TDP of 24.5 watts and clock speed of 1.7GHz for Banias
- DOTHAN: Die of 90 nanometers and 2.16 gigahertz, with 21-watt TDP.
- It was used for the first time in the Intel Carmel notebook, Centrino-brand.
2006-Core 2
- E6320 is another name for Intel Core 2 brand, which was launched on July 27, 2006. It had clock speed of upto 3.5 GHz .
- Single-core, dual-core, and quad-core processors were introduced under this family.
- The processor is no longer available for purchase.
- The desktop processors under this brand include:
- The Conroe XE; Allendale; Wolfdale
- We have Allendale XE, Wolfdale XE, and more.
- This brand's laptop processors include:
- Merom XE; Penryn; Merom
- As well as Merom-L and Penryn XE
- Using a slower clock speed, the processor was able to conserve battery power.
Latest Technology- CPU
Since the launch of the 4004 microprocessor, the technology has advanced significantly.
A smaller chip, faster clocks, and larger caches have all resulted in a smaller chip and faster clocks.
Products based on Intel's microarchitecture were introduced in 2011.
It has been able to produce dies with a 32-nanometer thickness.
Included is Intel Quick sync, which is a hardware-based video encoding and decoding solution from Intel.
Interconnecting the different parts of the processor is also made easier with an improved 256-bit/cycle ring bus connect.
- This processor has a transistor count of 2,27 billion.
- The designed clock speed is 3.6 GHz.
- Cougar Point Chipset motherboards in the 67-series were recalled by Intel due to a hardware issue.
- The following series are part of this family:Intel Pentium: Celeron: Core i3: Core i5: Core i7: Core i7 Extreme: It has the vPro feature that has the ability to delete data from a hard drive via 3G signals or Ethernet or Internet.
Ivy Bridge
It was announced in 2011 that Intel would be releasing a 22-nanometer die processor called Ivy Bridge, but it was only released on April 29, 2012.
The use of 3D (tri-gate) transistors allows for a smaller die.
In comparison to 2D transistors, 3D transistors reduce power consumption by nearly 50%.
PCI Express is also supported, as is DirectX 11, which improves the graphics.
3.80 GHz is the clock speed of the processor.
According to reports, they have a temperature 20oC higher than Sandy Bridge.
Under this family, there are the following desktop models:
i3, i5, and i7 Processors
Mobile that fall under this category include: i3, i5, and i7 Core Processors
It is one of the tick version of sandy bridge.
Latest - Fifth Generation CPU or Central Processing Units
- The fifth generation Central Processing Unit is based on Artificial Intelligence.
- A still-under-development Central Processing Unit.
- The use of voice recognition is an example of a current application.
- By the way, it's still being worked on right now.
- AI aims to create an intelligent device that can respond to natural language input and can learn on its own.
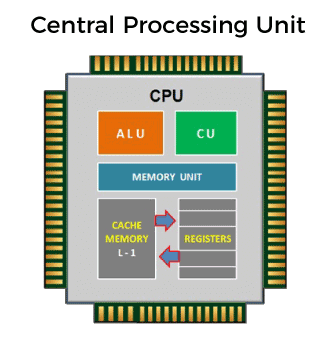
Three major sections make up the Central Processing Unit: Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, and Memory. It takes both of these sections to work together to complete the necessary micro-operations.
Arithmetic/Logic Unit(ALU)
Math and Logic Unit performs calculations on a computer.
This part of the computer performs all addition, multiplication, and comparison operations.
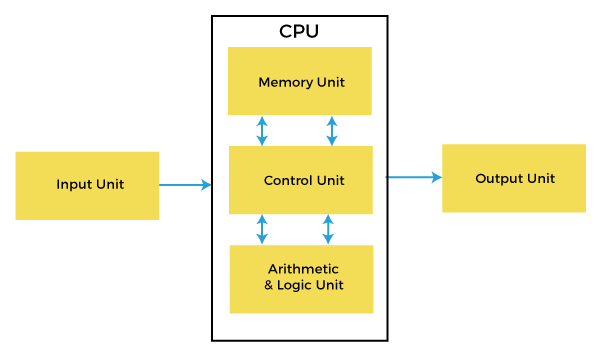
Unit of control
Instructions are sent to memory, which decodes them before they are executed by the control unit.
The arithmetic/Logic Unit will be called upon as needed.
Hence a computer cannot function without the Central Processing Unit.
|











 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










