CSS right propertyThis CSS property specifies the right offset for the horizontal positioned elements and does not affect the non-positioned elements. It is one of the four offset properties that are left, top, and bottom. When both left and right properties are defined, the right value has a preference if the container is right-to-left, and the left value has preference if the container is left-to-right. The effect of this property depends on how the corresponding element is positioned, i.e., the value of the position property. The right property does not affect when the position property is set to the value static. The effects of this property on positioned elements other than the value static are listed as follows:
SyntaxProperty ValuesThe values of this property are defined as follows: auto: This is the default value. It allows the browser to calculate the right edge position. length: This value defines the position of the right property in px, cm, pt, etc. It allows negative values. percentage: This value defines the position of the right property in percentage (%). It is calculated to the width of the element's containing block. It also allows negative values. initial: It sets the property to its default value. inherit: It inherits the property from its parent element. ExampleIn this example, there are four absolutely positioned (i.e., position: absolute;) div elements. We are applying the right property to them. The div elements with right: initial; and right: auto; will overlap because of having default values and similar dimensions. Test it NowOutput 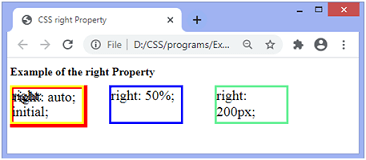
ExampleIn this example, there are four relatively positioned (i.e., position: relative;) div elements. We are applying CSS right property on them. Here, we are using the negative values of the length and percentage on two div elements. Test it NowOutput 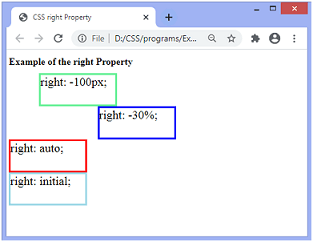
Next TopicCSS bottom property
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










