CSS SpecificityWhen more than one conflicting rules of CSS indicates the same element, then the browser will follow some rules for determining the particular one. Specificity is the way which helps the browsers to decide which property value is most relevant for the element. It determines which style declaration is applied to an element. Before going in deep about specificity, let's discuss some points about it:
Specificity hierarchyEach selector has a place in the hierarchy. There are mainly four categories that define the selector's specificity level: Inline styles: It is directly attached to the element which is to be styled. For example: <p style="color: red;">. It has the highest priority. IDs: It is a unique identifier for the elements of a page that has the second-highest priority. For example: #para. Classes, attributes, and pseudo-classes: It includes classes, attributes, and pseudo-classes (like :focus, :hover, etc.). Elements and pseudo-elements: It includes the name of elements (div, h1) and pseudo-elements (like :after and :before). They have the lowest priority. 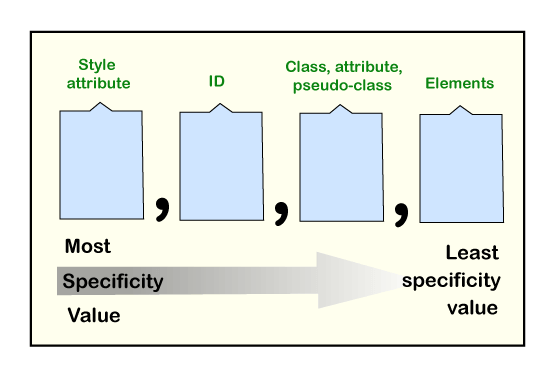
Specificity rulesSpecificity is the weight, which is applied to the CSS declaration. It is determined by the number of every selector type in the matching selector. Let's see the calculation of specificity. The specificity rules are discussed below, along with an example. The specificity of ID selectors is higher than attribute selectorsLet us try to understand it with an example. ExampleIn this example, we are going to use the id selector with the background-color property. Test it NowIn equal specificity, the latest rule will countIn the external stylesheet, if the same rule is applied twice, then the latest (or last) rule will be applied. ExampleIn this example, the specificity of the name of elements is same. In this case, the latest specified element name will be considered. Test it NowThe specificity of class selector is greater than the element selectorsA class selector (.nav, .high, etc.) is highly specific than element selectors (like div, h1, p, etc.) ExampleTest it Now
Next TopicCSS text-indent
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










