What is the Full Form of CSSDCSSD: Central Sterile Supply DepartmentCSSD stands for Central Sterile Supply Department. There has been increased interest in planning sterilizations during the past few years. A hospital's central sterile supply department (CSSD) is a service division that manages the distribution of sterile supplies to all hospital departments. According to Bhattacharjee's description, it can be summarized as the hospital service that provides sterile supplies to all departments, including general wards, OPDs, and specialist units. To prevent hospital-acquired infections (HAI), CSSD aims to supply all hospital departments with equipment guaranteed to be sterile and ready for use in patient care. 
The CSSD should be a separate department with receiving, cleaning, packing, disinfecting, and sterilizing facilities. Instruments should be distributed and stored according to established methods. Correct design, adequate equipment, skilled workers, and good workflow are critical components of this area. The term CSSD was first used by the American College of Surgeons in 1928, marking the beginning of CSSD history. In the United Kingdom, Regular CSSD was developed in 1955 by the Cambridge Military Hospital. In India, the first CSSD was established in 1965 by Safdarjung Hospital in New Delhi. The central sterile services department (CSSD), also referred to as the sterile processing department (SPD), sterile processing, central supply department (CSD), or central supply, is an integrated area in hospitals and other healthcare facilities that performs sterilization and other actions on medical consumables, equipment, and supplies for later use by healthcare professionals in the operating room of the hospital as well as for other uses like aseptic procedures which includes catheterization, wound care, and other aseptic procedures. The CSSD is essential for improving patient safety and lowering hospital surgical infection rates. It is crucial to ensure that surgical equipment is properly disinfected from an infection control standpoint. If surgical equipment is microbially contaminated, there is a higher chance that the surgical wound will become contaminated and infected as a result. As a result, one of the fundamental and effective ways to prevent surgical site infection is to sterilize surgical tools (SSI) properly. Numerous hospital departments depend on the CSSD's services. The task of sterilizing and preparing medical and surgical supplies and equipment for use in patient care falls within the purview of the Sterile Supply Department. Maintaining consistently high standards for sterilization procedures and product quality is crucial because all goods are now pre-infected, cleaned, packed, and sterilized in one department. Efficient processing is crucial for effectiveness, economy, and patient safety, given the growth in the quantity and variety of surgical procedures and medical devices. We could improve patient and employee safety by implementing cutting-edge technologies and procedures. 
We must overcome significant obstacles to copy or replicate best practices in the sterilization process. We should set up systems to support and guarantee the proper handling of surgical tools during and after the operation. Digital tools supporting CSSD procedures make managing and documenting data easy. Digital technologies also make it possible to update data instantly and communicate information more effectively. With the help of these solutions, CSSD employees may make fewer mistakes, experience less pressure, and adhere to policies and rules more easily. A high standard in the CSSD, the "backbone" of sterile practice in any hospital, is maintained by upgrading the quality management with the most recent advancements. The department's goals are to provide sterilized material from a central location, department where sterilizing procedures are carried out in controlled environments, helping to lower the frequency of hospital infections. BackgroundCleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing reusable medical equipment are often the functions of a sterile services department. Reusable medical equipment, or RME, can include any medical device, including IV pumps, crash carts, and surgical instruments made of stainless steel. RME is divided into three classes of data categories which are non-critical, semi-critical, and critical, each requiring a certain amount of reprocessing. Non-critical devices like IV poles and pumps need to be disinfected at least to an intermediate degree, which can be done using the majority of hospital disinfectants. Semi-critical goods, which typically include endoscopes like those used in colonoscopies, are anticipated to come into touch with an intact mucous membrane. These goods require high-level disinfectants like hydrogen peroxide plasma, peracetic acid, or glutaraldehyde solution. Sterilization is necessary for critical things, such as equipment inserted into a patient's bloodstream or a sterile body portion. Use of Sterilization TechniquesThe primary task is sterilization, which eliminates all living things from an item of the cleanest services divisions. In a separate decontamination chamber, the items that they will sterilize must first be cleaned, and they must then examine them for efficacy, cleanliness, and damage. There are various sterilization techniques, and the choice of which to use depends on various criteria, including operational costs, potential worker dangers, effectiveness, timing, and the nature of the materials to be sterilized. 
Steam sterilization is one of the most affordable and simple techniques used in the US. Instrument trays and packages are put in a steam-filled room with a temperature of 250-270 °F (121-132 °C), which effectively destroys all microorganisms. Ethylene oxide (ETO) gas can also be used to sterilize things. This procedure, developed by the US military in the 1950s, is used on objects that cannot withstand extremely high temperatures sterilization with steam. They developed alternative approaches in the 1990s since ETO sterilization is dangerous to employees and takes much longer than steam sterilization. Today, the most popular sterilization technique at low temperatures is hydrogen peroxide plasma, which poses almost no risk to the workers and requires fewer cycles than ETO sterilization. Depending on the institution, a hospital's sterile storage policy may be an event or time-related. If the policy is event-related, the package is considered sterile until an incident that endangers its sterility occurs (e.g., opened, dropped the package, high humidity conditions, etc). If the healthcare facility's policy is time-related, an expiration date is added to the package before supplying it to the end user as a sterile product. The sealed package must be returned to the supplier if it was broken or opened by a health worker along the supply route CSSD to re-sterilize. The most important sterilization stage is decontamination, which starts with point-of-use cleaning in the operating room. A gadget's sterilization will only occur if it is cleaned properly. Cleaning procedures must follow the manufacturer's instructions for use (IFUs). Each thing processed must adhere to these. Having a well-operating decontamination area depends on several things, including the following:
Technician for Sterile ProcessingSurgical instruments and other medical supplies are cleaned and sterilized by sterile processing technicians so they can be safely distributed and used on new patients. The medical facility's special department typically houses all of this work including the following job titles:
DivisionsDecontamination, assembly and sterile processing, sterile storage, and distribution are the four main divisions into which sterile processing departments are normally organized.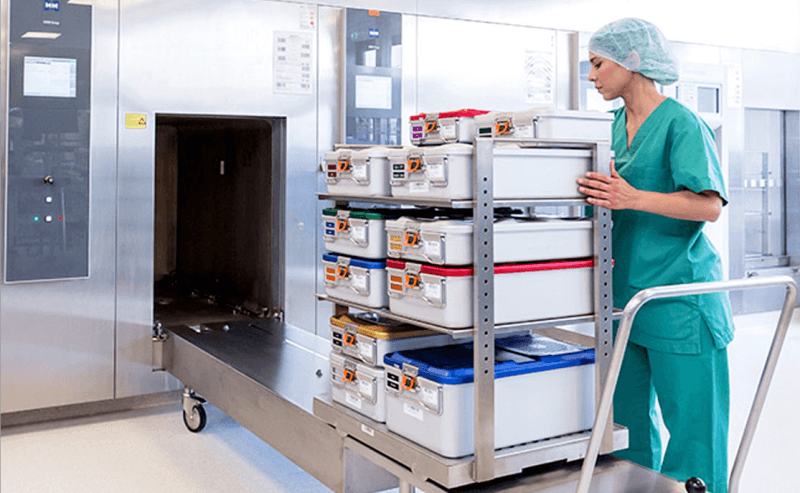 
Decontamination
Storage and Sterilization
Distribution
Goals of CSSD
Process in CSSD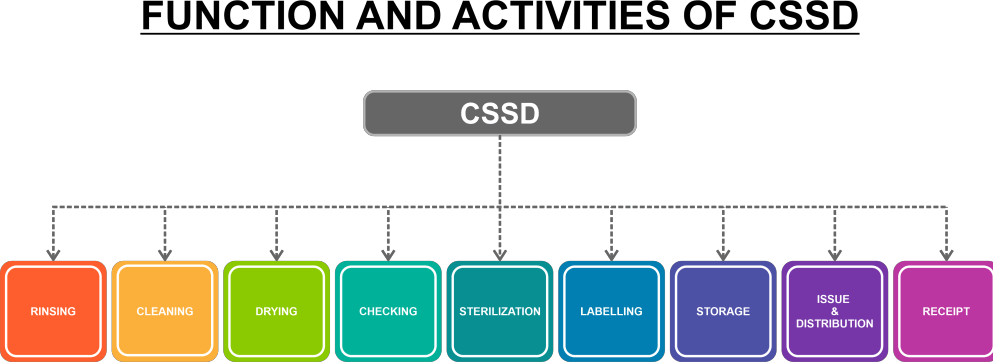
ReceivingA CSSD assistant receives non-sterile materials from various hospital departments, examines them, and keeps track of their state. After receiving the instruments, they are separated and checked for damage. The instruments are sent for repair or discarded as necessary if they are damaged. CleaningThis function involves cleaning used instruments and procedure sets (such as cut-down sets, tracheostomy sets, lumber puncture sets, sterna puncture sets, aspiration sets, catheterization sets, suturing sets, dressing sets, etc.) using either a manual cleaning process or an ultrasonic cleaning system.
Workflow in CSSDArea for Assembly and PackagingAfter washing and drying, all the instruments are put together and sealed either manually or by a machine. All of the packs have labels and autoclave indicator tapes attached. 
A Field for AutoclavingIn this area, many types of sterilizing devices are used, three gravity displacement autoclaves and two vacuum-assisted autoclaves. The packs are put into the autoclave machine, which runs for 30 minutes at the prescribed temperature and pressure (121 c and 20 psi, respectively). After the packs have been sterilized, the sterilizing units are shut off, and the autoclave indicators are examined to ensure that the packs have been sufficiently sterilized. If necessary, the sterilization procedure is then repeated. If a material successfully kills 99.99% of bacterial spores, it is declared sterile. We must repeat the entire process if the sterile packs are torn, opened, damp, etc. Packs that have been sterilized sufficiently are kept in the sterile storage area. Sterile Storage AreaSterilized things are stored here, and some items we can't distribute on the same day are held in an ultraviolet storage cabinet. Issuing WindowAfter entering the relevant issuing register, all sterile supplies and other things are distributed to the departments involved from a separate window. CSSD's Monitoring Protocol
Keeping Records
Maintenance of EquipmentEquipment upkeep is carried out following AMC and warranty. The logbook or register is where all the information is kept. Recall Procedure
Performance ReviewBased on pertinent records and statistical indices about quality, productivity, material consumption, etc., performance evaluation is conducted. Internal quality audits are routinely performed monthly to evaluate the system's effectiveness, and performance records and on-site inspections are used. The comments obtained from such evaluations are noted and used to enhance quality-related actions in the future.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










