Cylinder DefinitionA cylinder is a type of component that belongs to the mechanical field and is used in numerous applications. Let us talk a bit about the structure of the cylinder- Cylinders are essentials with tubes with a piston that moves inside them. They are applied in the appliances to convert energy from one form to another. These days, cylinders are almost used in everything- from car engines to industrial machinery; they are everywhere and are specially designed for a wide range of modern technologies. In this article, we will explore everything related to the cylinders- from the history of cylinders, their construction and operation, and how they are used in different applications. We will also look at the different types of cylinders that exist and what materials are used to build their unique structure. History of CylindersThe history of cylinders can be traced back to the Greeks era. The Greeks used cylinders to construct pumps and other machinery; Archimedes was the first ever recorded person who used a cylinder to lift the water in the third century. The cylinders came in demand after the industrial revolution that took place in the 18th and 19th century, which made the cylinders widely used in the industry. The cylinders played a huge role during this century, and here is why- The steam engine was developed in this era, and the steam engines completely relied on cylinders to convert thermal energy into mechanical energy. Not only this but by the mid-19th century, cylinders were being used in almost everything from locomotives to the textile industry; they were found almost everywhere. Their use continued to grow throughout the 20th century. Basic Construction and Operation of The CylinderA cylinder is a tube-like structure that has a piston present inside it. The piston is made out of metal and is specially designed to fit snugly inside the cylinder. There is a seal present that covers the gas or liquid present between the piston and the cylinder walls to prevent any leakages. How does a cylinder work- the cylinder works when a force is applied to the piston. The piston moves inside the cylinder, which eventually creates pressure that can be used to do the work. The pressure is created by the movement of gas or liquid inside the cylinder, which is often compressed or expanded as the piston moves. Note: It is important to remove the cylinder's seal to make it function. Please do not remove the seal by using sharp objects, as it can lead to a hole that may lead to gas leakage.Construction Of the CylinderCylinders are designed specifically to perform certain functions. They can be designed to operate in various ways, and it completely depends on their intended application. Here is an example: specific cylinders are designed to produce linear motions, while others are designed to rotate. In contrast, certain cylinders are designed to operate at high temperatures or pressures, while others are designed to operate at low-pressure temperatures. Applications of CylinderFrom industrial machinery to transportation, cylinders are used in a wide range of applications. Here is the list of the most common applications that function with the help of a cylinder: Car EnginesIn car engines, the role of the cylinder is to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Most of the engines have 4 to 6 cylinders, although some cars with high-performance engines have as many as 12 cylinders to function properly. Hydraulic SystemIn this system, the main purpose of the cylinder is to convert fluid pressure into mechanical force. Hydraulic cylinders are used in many appliances like construction equipment, and they are also used in aerospace applications. Pneumatic SystemsFor Pneumatic systems, specific cylinders are used as they rely completely on compressed air to create a mechanical force. Pneumatic Cylinders are used in many appliances like manufacturing equipment and medical devices. Industrial MachineryTextile mills, printing presses, and assembly lines are the most common industries that use industrial-based cylinders. TransportationThe transportation industry also has a wide range of requirements for cylinders. In the transportation industry, cylinders are used in Aircraft, ships, and in trains as well. Let us have a look at the purpose of cylinders in the applications mentioned above- a. Aircraft- in aircraft, the cylinders are used to operate the landing gear. b. Ships- in ships, cylinders are used to control valves and pumps. Types of CylindersThere are several different types of cylinders, and each cylinder is designed to solve a specific purpose. Here is a list of some of the most common types of cylinders: 1. Single Acting CylinderSingle Acting cylinders are specially designed to produce a force with only one direction. These cylinders typically rely on a spring or other mechanism to return the piston to its original position after the occurrence of the movement. 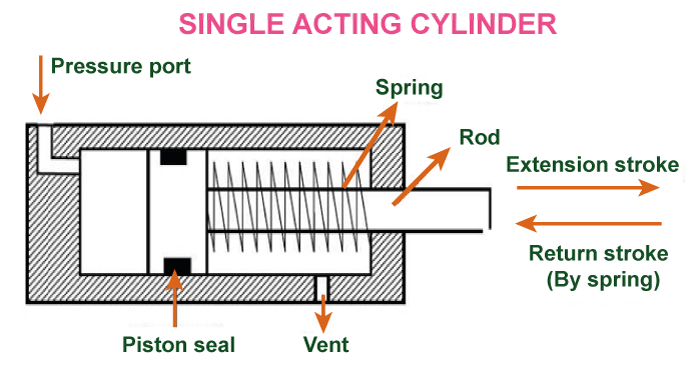
Single-acting cylinders are hydraulic devices that use pressurized fluid or air to move a piston in a single direction, either in an extending position or in a retracting position. Single-acting cylinders are used in applications where the force required to extend the cylinder is greater than the force required to retract the cylinder. These types of cylinders are small and simple in design than the other double-acting counterparts; because of this, these cylinders are more cost-effective and are also easier to maintain. As these cylinders move only in One Direction, they generally are unsuitable for certain applications whereby direction movement is required to make the appliance work properly. Single-acting cylinders are generally used in manufacturing and transportation industries to make lifting, pushing, and pulling heavy loads easy. Double Acting CylindersDouble Acting Cylinders are specifically designed to produce force in both directions. Ports are at both ends of the cylinder, allowing fluid to enter and exit from either side. Because of this feature, it makes them ideal for applications where precise control is required; it is specially used in heavy machinery. 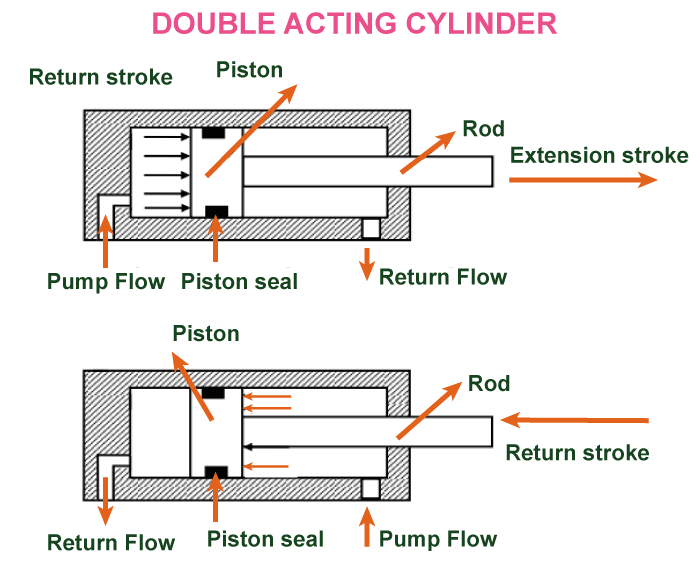
A double-acting cylinder is a type of hydraulic cylinder that is capable of providing power in both directions of movement. A double-acting cylinder consists of a piston that divides the cylinder into two equal chambers. The two chambers are connected to separate ports that allow fluid or gas flow to either side of the piston, causing it to move in the desired direction that is specifically required for the appliance. The industry uses the double-acting cylinder, especially in mobile equipment appliances, because of its versatility and efficiency. The reason behind the use of double-acting cylinders in mobile equipment applications is that it allows for a greater range of motion and control over the movement of machinery as compared to the single-acting cylinder full storm. Secondly, it can also provide power in both directions as it is more energy efficient than the single-acting cylinder, which only provides power in one direction and requires a return mechanism. The double-acting cylinders are commonly found in industrial presses and agricultural machinery. These are used in mobile equipment, such as excavators, back hosts, and dump trucks, where they provide the necessary force to move heavy loads. Overall, the double-acting cylinder is a reliable and efficient component that is required in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. It has the ability to provide power in both directions, which eventually makes it easier for the appliances to perform their function well and also it is an essential tool in a wide range of industries as it helps in increasing productivity and overall efficiency full stop Telescopic CylindersTelescopic cylinders are specially designed to provide a long stroke in a packed or compact space. Here is the design of the cylinder- the cylinder consists of multiple cylinders, and each cylinder has a miny cylinder present inside it. Because of this design, the cylinders can provide a greater stroke than would be possible with a single cylinder that too of the same length. 
Telescopic cylinders are also known as multi-stage cylinders or telescoping cylinders. These cylinders are hydraulic or pneumatic accumulators consisting of a series of nested tubes or stages, and each of these can extend and retract independently of the others. Telescopic cylinders are generally used in industrial applications where a large stroke length is required, but this space is limited. All these cylinders are made up of a base stage which is fixed to the machinery, and a series of smallest stages that are fixed inside each other. When the force of pressurized fluid is applied to the stage base, it causes each of the smallest stage to extend in certain sequence a lot longer stroke. On the other hand, when the fluid is released, the stages come back to their original position. The telescopic cylinders have one big advantage, which is their compact design. Due to their compact design, the long stroke strength can take place without taking up much space. These cylinders are commonly used in applications like dumbstruck, dump trucks, cranes, and other heavy equipment requiring a long stroke in a limited or confined space. Secondly, telescopic cylinders can be customized according to the load capacity and the space that is present in the appliance. One of the major disadvantages we can find in telescopic cylinders is that they can be more complex and expensive than the single state cylinder and require more maintenance due to the additional seals and moving paths attached according to the appliance. Secondly, they may be more flexible than single-stage cylinders, which can lead to increased wear and tear over a period of time. Overall telescopic cylinders are versatile and useful for industrial applications requiring a long stroke length in a confined space. It is essential to note that careful consideration should be given to their specific advantages and disadvantages to determine if they are the best choice for your appliance. Rotary CylindersThese amazing cylinders are specially designed to produce rotary motion rather than the linear motion which is found in standard cylinders. Rotary Cylinders are specifically used in applications where components need to be rotated to function well. The best example of rotary cylinders is conveyor systems. 
Rotary cylinders are mechanical devices used to convert fluid power into linear motion or, in the Rotary motion first term, these cylinders are commonly used in industrial applications requiring precise and powerful actuation. The structure of the Rotary cylinder consists of a piston or a rotator that rotates inside the cylinder. The piston or agitator is connected to a shaft that is attached to the load, which eventually converts the Rotary motion of the piston into a linear motion of the load. Compressed air hydraulic fluids or other sustainable fluids power these cylinders. Rotary cylinders are commonly used in manufacturing processes like assembly lines, packaging, and material handling. These cylinders can also be found in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. Not only this, but they are also found in robotics and other automated systems. Rotary cylinders are known for their precise control over motion. They are also highly reliable and have a long service life full. They require minimal maintenance and are easy to install and operate. Overall, Rotary cylinders are mechanical devices used in various industrial applications, from automotive to robotics. We can find them in almost every field. They provide process and powerful activation and are highly reliable, and also serve a long life. Rodless cylindersRodless cylinders are the most unique and creative cylinders; they are designed to provide a linear motion that too without using a piston rod. These cylinders generally use a magnetically-coupled piston that moves inside a stationary cylinder. The rodless cylinder is a type of dynamic activator that operates without a piston rod extending out of the cylinder. This cylinder body itself acts as a piston in the presence of an internal piston that moves along the length of the cylinder. Due to their design, the cylinder allows for a longer stroke length than the traditional piston-cylinder system, making it idle for applications where space is defined.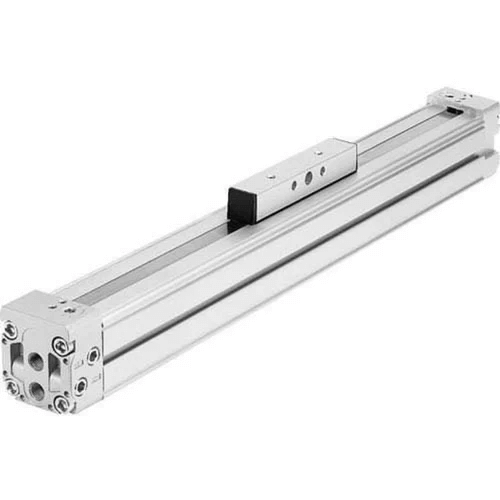 
One of the major advantages of using a rodless cylinder is that it can offer a more compact design as compared to the traditional cylinder, as there is no need to accommodate the extended piston rod. Secondly, this cylinder is less prone to damage as no external components can be bent or broken. Thirdly the advantage that rodless cylinder serve is their versatility. These cylinders can be used in a wide range of applications like material handling, automation, and robotics. These cylinders are particularly useful in situations where there is a requirement for precise and smooth linear motions like pick and place operations. However, these cylinders also have certain limitations. They can be more expensive as compared to traditional cylinders, and their internal piston design can make them more difficult to maintain. Secondly, they may require additional support or a guiding mechanism to prevent twisting or bending while operating according to the appliance. Overall, rodless cylinders offer a unique solution for pneumatic actuation in an application where the space is defined or concise and require a precise linear motion. Material and Manufacturing MethodsCylinders can be made of various sought of materials. The material that must be used to make a cylinder completely depends on the appliance it has to fix. The most common materials used to make a cylinder are- steel, aluminum, and composite materials. On the other hand, the manufacturing method will completely depend on the cylinder's size and complexity, which will completely depend upon the appliance's size and requirement. The cylinders that are supposed to be small and compact in size can be easily produced by using machinery processes like turning and milling. Whereas large and complex cylinders may be produced by casting or forging. ConclusionCylinders are a modern yet common component that are used in a huge amount to make modern technologies function properly and effectively. Cylinders are designed to convert energy from one form to another and are used in almost all appliances, from hydraulic and pneumatic systems to industrial machinery and transportation; you will indeed find different sought of cylinders almost everywhere. To summarize in the above article we have discussed the different types of cylinders present in the industry and how they are perfect for a certain appliance and also for the special needs of the appliance. Each cylinder is designed for a specific application. It can be made from a wide range of materials by using different manufacturing methods, which completely depend on the cylinder's size and purpose. As we can see, technology is expanding every second, and there are high chances that we are likely to see new types of cylinders getting developed in the industry to solve more and more problems faced in appliances, not only this but with the use and advancement of technology, the cylinders will be able to become more useful. They will also be able to expand their versatility.
Next TopicData Structure Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










