Data Labelling in Machine LearningData labeling is the way of identifying the raw data and adding suitable labels or tags to that data to specify what this data is about, which allows ML models to make an accurate prediction. In this topic, we will understand in detail Data Labelling, including the importance of data labeling in Machine Learning, different approaches, how data labeling works, etc. However, before starting, let's first understand what the labels are and how these are different from features in Machine Learning. 
Labels and Features in Machine LearningLabels in Machine LearningLabels are also known as tags, which are used to give an identification to a piece of data and tell some information about that element. Labels are also referred to as the final output for a prediction. For example, as in the below image, we have labels such as a cat and dog, etc. For audio, labels could be the words that are said. This set of labels lets the ML model learn the dataset, as when we train a model with supervised techniques, we provide the model with a labeled dataset. With this labeled training dataset, the ML model easily predicts the accurate result when given the test dataset. 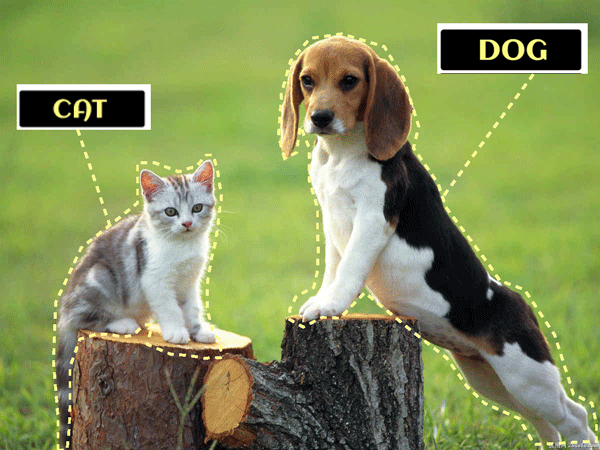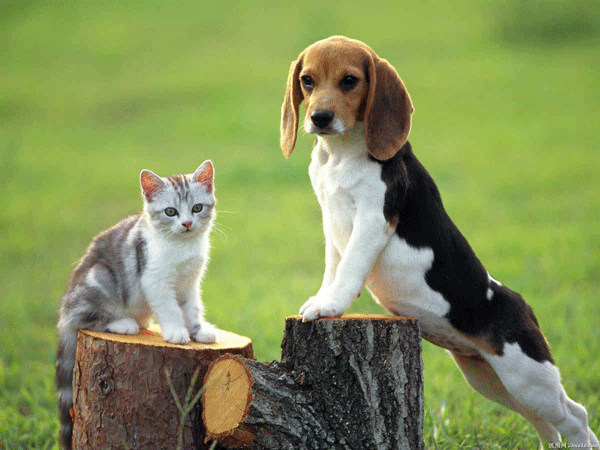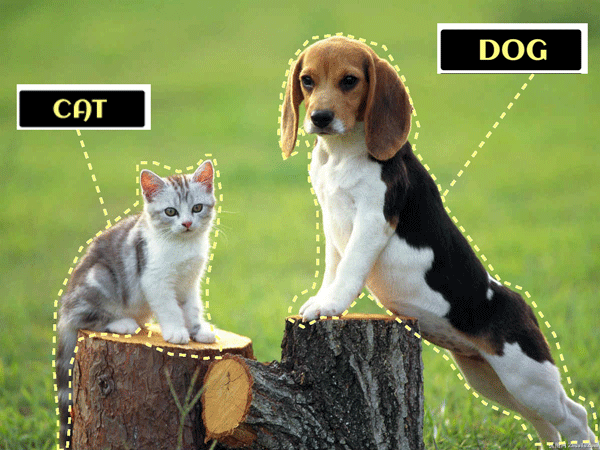
Features in Machine LearningFeatures are the individual independent variables that work as input for the ML system. For an ML dataset, a column can be understood as a feature. ML models use these features to make predictions. Further, we can also get the new features from the old features using feature engineering methods. We can understand the difference between both of them with a simple example of an image dataset of animals. So, height, weight, color, etc., are the features. Whereas it is a cat or dog, these are the labels. Now let's understand the main topic, i.e., Data Labelling What is Data Labelling?If we input a vast amount of raw data to a Machine Learning model and expect it to learn from it, then it is not enough. As it will give an abrupt result, so it is necessary to pre-process the data, and one of the parts of the pre-processing data stage is Data Labelling. In the data labeling process, we provide some identification to raw data (that may include an image, audio, text) and add some tags to it. These tags tell which class of object the data belongs to, which helps the ML model learn from this data and make the most accurate prediction. Hence, we can define it as, "Data labelling is a process of adding some meaning to different types of datasets, so that it can be properly used to train a Machine Learning Model. Data labelling is also called as Data Annotation (however, there is minor difference between both of them)." Data Labelling is required in the case of Supervised Learning, as in supervised learning techniques, we input the labeled data set into the model. Labeled Data vs. Unlabelled DataIn data labeling, data is labeled, but in machine learning, both labeled and unlabelled data are used. So, what is the difference between them?
Note: Semi-supervised learning uses combined data, i.e., labeled and unlabelled data, to train the model, which reduces the difficulties of getting labeled data.How does Data Labelling Work?Nowadays, most machine learning models use supervised learning techniques that map the input variable to an output variable and make predictions. For supervised learning, we need the labeled dataset to train the model so that it can make accurate predictions. The Data labeling begins with a process of "Human-in-the-loop" or HITL participation, where humans are asked to make a judgment for the given unlabelled data. For example, a human labeler may be asked to tag an image dataset, where "does the image contain a cat" is true. 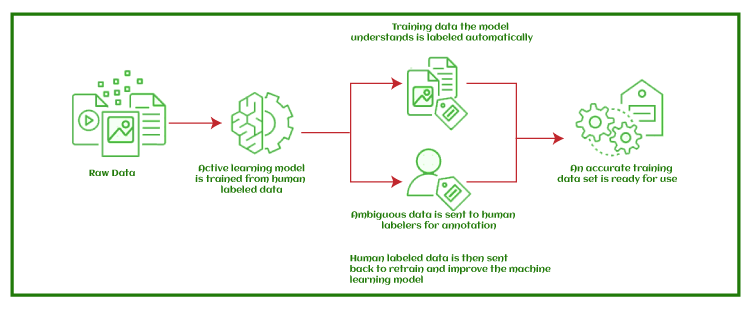
With these human-provided labels, an ML model learns from the data and underlying patterns, which is known as the Model training process, and the trained model then can be used to make a prediction with new data/test data. Approaches to Data LabellingData labeling is an important step while building the high-performance Machine Learning Model. Although the process of data labeling appears easy and simple, it is a bit critical to implement. Therefore, in order to use data labeling techniques, companies should consider multiple factors to find the best approach to labeling. Some common data labeling approaches are given as follows:
Benefits and Challenges of Data LabellingBeing an important concept of machine learning, data labeling has different benefits at the same time and also has some challenges. It can make an accurate prediction but is also a costly approach. Below are some benefits and challenges of Data labeling: Benefits
ChallengesData labeling has various challenges, and some of the most common challenges are:
Use Cases of Data LabellingAs data labeling is one of the important concepts of machine learning, it has various use cases. Some of them are given below:
Best Practices for Data LabellingThere are various techniques that help in improving the efficiency and accuracy of data labeling. Some of these techniques are as follows: Active LearningThe active Learning technique makes the data labeling more efficient by identifying the most appropriate dataset to be labeled by humans using different ML algorithms and Semi-supervised learning. Active Learning approaches include:
Transfer LearningUsing transfer learning, one or more pre-trained models from one dataset are applied to another. This can also include multi-task learning, in which tasks are learned back-to-back. Label AuditingThe label auditing technique is used to verify the accuracy of labels and update them as per requirement. ConsensusThis technique calculates the rate of agreement between different labelers, either human or machine, on the given dataset. This is calculated as the sum of aggreging labels to the total number of labels per asset. Intuitive and streamlined task interfacesIt minimizes cognitive load and context switching for human labelers. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










