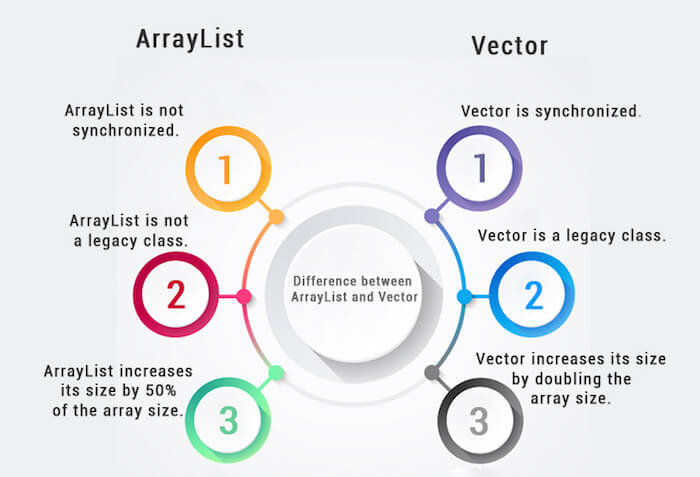
Difference between ArrayList and VectorArrayList and Vector both implements List interface and maintains insertion order. However, there are many differences between ArrayList and Vector classes that are given below.
Example of Java ArrayListLet's see a simple example where we are using ArrayList to store and traverse the elements. Test it NowOutput: Sonoo Michael James Andy Example of Java VectorLet's see a simple example of a Java Vector class that uses the Enumeration interface. Test it NowOutput: umesh irfan kumar
Next TopicJava JDBC
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










