Difference between Exothermic Reactions and Endothermic ReactionsExothermic reactionExothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light or sound. This energy is typically released as the chemical bonds in the reactants are broken and new bonds are formed in the products. Examples of exothermic reactions include combustion, the burning of wood or fossil fuels, and the decay of radioactive materials. Endothermic reactionEndothermic reactions, on the other hand, are chemical reactions that absorb energy. This energy is typically absorbed as the chemical bonds in the reactants are broken and new bonds are formed in the products. Examples of endothermic reactions include photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, and the formation of chemical compounds such as ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). Difference between exothermic and endothermic reaction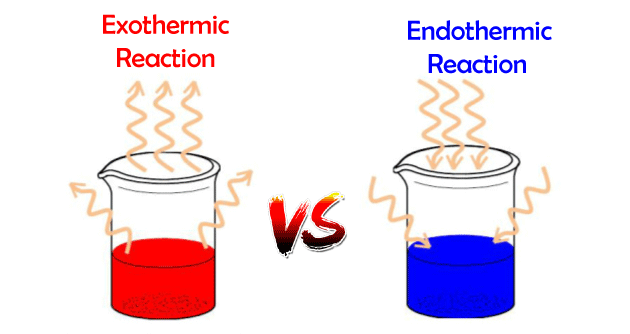
One way to distinguish between exothermic and endothermic reactions is by looking at the change in enthalpy (ΔH) of the system. Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a system, including both the internal energy and the energy required to change the volume of the system. In exothermic reactions, the enthalpy of the products is less than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in a negative change in enthalpy (ΔH < 0). This means that energy is released during the reaction. In contrast, in endothermic reactions, the enthalpy of the products is greater than the enthalpy of the reactants, resulting in a positive change in enthalpy (ΔH > 0). This means that energy is absorbed during the reaction. It is also important to note that the energy change in a reaction is not always obvious. It can be measured by calorimetry, which is the study of heat transfer and energy changes in physical and chemical processes. A calorimeter is an instrument used to measure the heat of a chemical reaction. Use of exothermic reactionsExothermic reactions have a wide range of applications in various fields. They are used in the production of heat and electricity, in the manufacturing of chemicals, in the production of fuels, in the metallurgy and many other fields. Exothermic reactions can also be used in many industrial and everyday applications. For example, exothermic reactions are used in the production of fertilizers, the refining of petroleum, and the generation of electricity in power plants. They also play a role in the human body, such as the metabolism of food in the body, the production of ATP, which is the primary energy carrier in cells, and the reactions that produce heat to maintain body temperature. In the production of fuels, exothermic reactions are used to refine crude oil into various types of fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. In the metallurgy, exothermic reactions are used in the smelting of metals and in the welding process. Use of endothermic reactionsEndothermic reactions also have many industrial and everyday applications. Endothermic reactions also have a wide range of applications in various fields. They are used in the production of cold and in the refrigeration process, in the production of certain types of fuels, in the air conditioning systems, and in many other fields. For example, in the production of cold and in the refrigeration process, endothermic reactions are used to absorb heat from the surroundings and to produce cool air. In the production of certain types of fuels, endothermic reactions are used to produce hydrogen fuel, methanol, and other types of fuels. They also play a role in the human body, such as the process of respiration, the absorption of light by chlorophyll in photosynthesis, and the formation of chemical compounds in the body. ConclusionIn summary, exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light or sound, while endothermic reactions are chemical reactions that absorb energy. The energy change in a reaction can be measured by calorimetry, and both exothermic and endothermic reactions have many industrial and everyday applications. Both exothermic and endothermic reactions have a wide range of applications in various fields, such as the production of heat and electricity, the manufacturing of chemicals, the production of fuels, the metallurgy, the refrigeration process, and the air conditioning systems. Understanding the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions is crucial for many industries and for the development of new technologies.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










