Difference between Inspiration and Expiration
Inspiration
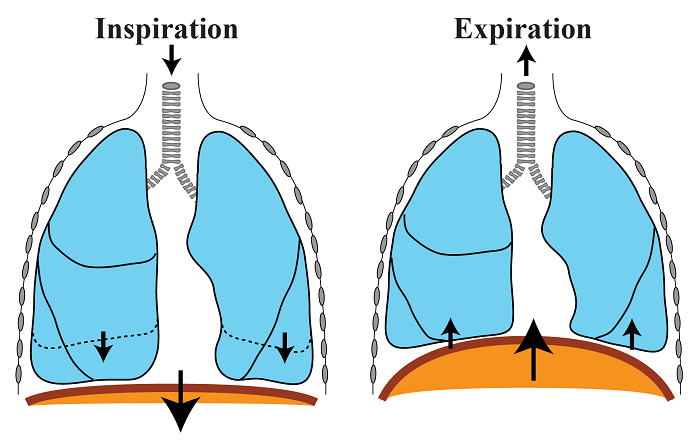
The process of inhaling oxygen-rich air is known as inspiration.
The diaphragm becomes flat and the ribs are forced upwards and outwards during inspiration, increasing the capacity of the lungs.
Expiration
Expiration is the process of exhaling air that is high in carbon dioxide.
The diaphragm relaxes and rises during expiration, while the ribs move inward and downward. Lung volume decreases as a result of this.
Difference between inspiration and expiration
| Part of the respiratory system |
Inspiration |
Expiration |
| Diaphragm |
Contracts and flattens downwards |
Relaxes and moves upwards |
| External intercostal muscles |
Muscles contract |
Muscles relax |
| Internal intercostal muscles |
Muscles relax |
Contracts |
| Rib cage and sternum |
Move upwards and outwards |
Move downwards and inwards |
| Thoracic cavity |
Increases |
Decreases |
| Air pressure |
Decrease inside thorax and lungs |
Increase inside thorax and lungs |
| Air movement |
Extreme air pressure drives air into the lungs at low pressure |
Air forced out of lungs by thorax compression and elastic recoil of lungs |
Breathing Process Mechanism
The two stages of breathing are inspiration and expiration, where air enters the lungs during inspiration and leaves during expiration. The air is driven into and out of the lungs by establishing a differential pressure between the lungs and the environment.
These breathing systems include two different ways of breathing in the lungs. As given below:
- Inspiration
- Expiration
Inspiration
- Inspiration plays a role in breathing.
- Air is being moved from the environment to the human body's lungs during the inhaling process.
- The pharynx is the first organ where air leaves the nasal chamber nose, and it is followed by the bronchitis air pipe. The air then enters the tiny air sacs known as alveoli.
- To help oxygenate the blood, the alveoli facilitate air movement to the heart.
- If the pressure inside the lungs is lower than the pressure outside, inspiration may happen.
- The diaphragm in the body contracts during this inspiration period and travels across to the lungs.
- Diaphragmatic contraction, which increases in the thoracic chamber's volume along the anteroposterior axis, starts the inspiration process.
- The sternum and ribs are raised when external muscles contract, increasing the capacity of the dorsoventral thoracic chamber.
- The pulmonary volume also rises as a result of the total increase in the thoracic volume.
- When the pulmonary volume is increased, the intra-pulmonary pressure falls until it equals or falls below atmospheric pressure, causing air from the outside to push its way into the lungs, which is the inspiration.
Expiration
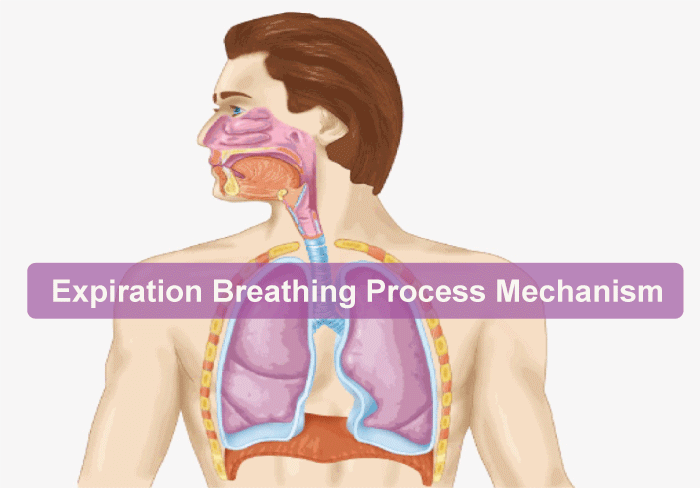
- Air is moved from the lungs to the outside during exhalation.
- Expiration is transferring air from the lungs to the outer atmosphere.
- The complete inspiration process is reversed, from the lungs to the nose.
- Alveoli in the lungs' respiratory tract release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during expiration.
- Expiration occurs when the intrapulmonary pressure exceeds the ambient pressure.
- Such gradients are produced with assistance from the diaphragm, and a particular group of muscles called the external and internal intercostal muscles between the ribs.
- When the diaphragm and sternum muscles are relaxed, the thoracic volume and, consequently, the pulmonary volume are decreased.
- Air is expelled from the lungs due to the intrapulmonary pressure rising slightly above atmospheric pressure.
- With the help of more abdominal muscles, we can strengthen both inspiration and expiration.
- A healthy person per minute takes 12-16 breaths per day. A spirometer may be used to evaluate breathing motions, which aids in physically assessing pulmonary function.
Inspiration and Expiration: Commonly Asked Questions
Question 1: What is the crucial component that causes inspiration and expiration?
Answer: The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract during inspiration. As the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, expiration occurs. The pressure and total amount of air inside the lungs change depending on whether the muscles around them are contracted or relaxed.
Question 2: What is the duration of inspiration and expiration?
Answer: Normal breathing typically looks like this while at rest: about 1 to 1.5 seconds, take a breath in (inhalation). A 1.5 to 2-second exhale (breathing out). A natural pause of one to two seconds with practically no breathing.
Question 3: Should inspiration last longer than expiration?
Answer: Breathing causes the expulsion of air from the lungs. Usually, there is a 1:3 ratio between inspiration and expiry time. When expiration happens passively, it takes longer than inspiration.
Question 4: What is the relationship between inspiration and expiration?
Answer: The diaphragm and intercostal muscles constrict during inspiration, allowing air to enter the lungs. The inspiration muscles relax, forcing gases to exit the lungs during expiration.
Question 5: What regulates the act of both inspiration and expiration?
Answer: The medulla oblongata, a region of the metencephalon, contains the respiratory center. Both inspiration and expiration are controlled by this center, which also controls the depth and speed of breathing.
| 




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










