Difference between URL and Domain NameThe World Wide Web (WWW) is a collection of resources, including files, web pages, and websites. These resources are accessible via the internet. Every web resources have its unique URL. It is a collection of characters that defines the location of a web page or website. The URL primarily contains the protocol used to access the website, the domain name, and the web page name. As a result, the domain name is part of the URL. The domain name is a unique or specific name that is utilized to identify the website. Domain names are typically easier for humans to remember than IP addresses. In this article, you will learn about the difference between the Domain Name and a URL. But before discussing the differences, you must know about the Domain Name and URL What is a URL?URL is an abbreviation for "Uniform Resource Locator". It offers the location of the resource on the internet. When users want to access a website, they enter it in the search box at the top of the browser. The web address is another name for the URL. The URL must be unique because it must refer to a specific website or webpage. Typically, the URL is categorized into three parts. The first part determines which protocol to use. The domain name is identified in the second part. The final part refers to the web page's name. Let's take an example to understand it effectively. Example: https://www.javatpoint.com/computer-network-tutorial 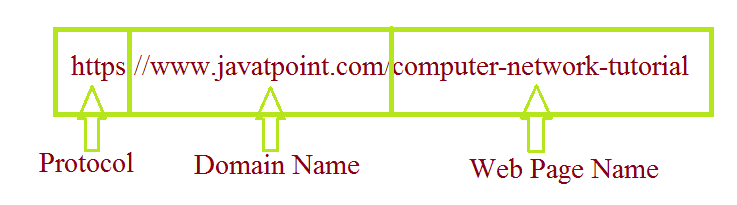
In this example, HTTP is an abbreviation for "Hyper Text Transfer Protocol". It is a collection of rules for communicating between the browser and the computer system so that they may understand each other. The www represents the World Wide Web. It refers to the web resources that may be accessible through the internet. The next section is the domain name which is "javatpoint.com". It is a specific type of name that belongs to a registered owner. It directs visitors to the website's home page. Finally, the remainder of this URL links to a particular web page on that website. What is a Domain Name?The domain name was created to simplify IP addresses and make them more human-friendly. The IP address is a logical address that is allocated to each computer system connected to a computer network. It basically identifies the computer's position on the internet and aids in routing information. For instance, an IP address is 166.58.48.34. These are difficult to remember and difficult to pronounce. The Domain Name System (DNS) converts a domain name into the IP address with which the computer system wishes to interact. When a user enters the domain name into a browser, the browser searches for and identifies the proper IP address and then sends the website associated with that IP address. DNS is divided into two parts: abstract and concrete. The abstract defines the name syntax and rules for naming authority, and the concrete describes the utilization of a distributed computing system that maps names to addresses. A delimiter character also separates domain suffixes. Individual domain portions may represent users or groups, but these parts are referred to as labels. A domain is also a suffix of a label in a domain name. Let's take an example to understand it very effectively. Example: javatpoint.com In this example, the lowest level of the domain is javatpoint.com, and the top-level domain is com. Key Differences between the URL and Domain Name
There are various key differences between the URL and Domain Name. Some main differences between the URL and Domain Name are as follows:
Head-to-head comparison between URL and Domain NameHere, you will learn the head-to-head comparisons between the URL and Domain Name. The main differences between URL and Domain Name are as follows:
ConclusionURL and domain names are similar entities, but they differ in some ways. The URL is the whole internet address of a webpage. Still, the domain name is simply the name of the organization/individual entity and top-level internet domains like edu, gov, com, etc. The domain name is the abbreviated version, whereas the URL contains more information.
Next TopicDifference between
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










