Digital India Essay
The Digital India approach is the flagship scheme of the Indian government. It is an effort to reduce the gap between the government and the public by integrating the government with its public electronically. The programme aims to render government services to the citizens electronically and reduce paper use. Apart from replacing paper, it also aims to provide high-speed internet services in the rural parts of India and connect them with the mainstream so that the benefits of the government can easily be provided to them. The government has aimed to provide broadband services to around 2.5 lakh villages across the country. Digital India also aims to disseminate digital awareness and digitally literate every country's citizen.

The coordinating ministry of the programme includes the Ministry of Electronics and Information and Technology (Meity). It is implemented by all the ministries and departments of the government, both at the centre and state levels. At the national level, it constitutes a Digital India Advisory Group chaired by Cabinet Secretary.
The vision of the Digital India Programme
1) Digital Infrastructure as Utility to Every Citizen
- The concept of the programme is to establish digital infrastructural facilities for the delivery of government services digitally.
- It aims to create a digital identity of the citizens that will be unique to every citizen for their whole life and that can be easily authenticable.
- Ensuring easy access to Common Service Centres and safe Cyber spaces for the public.
2) Governance and Services on Demand
- To integrate different ministries and departments for better coordination in the delivery of services by the government.
- Make all government services available to the public through online platforms.
- To move citizens towards online and cashless financial transactions.
- To transform government services digitally for ease of doing business in the country.
- Ensuring availability of every citizen on the Cloud.
3) Digital Empowerment of citizens
- By making every citizen digitally literate, primarily rural people.
- By making available digital services in vernacular languages.
- By ensuring the universal accessibility of all digital resources.
The 9 Key Pillars of Digital India
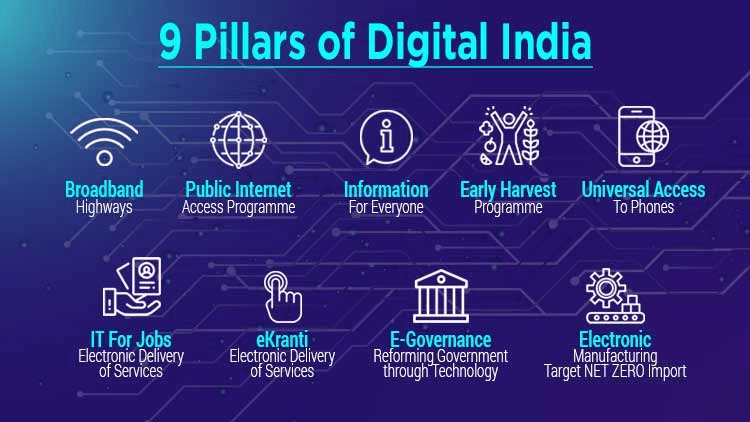
The Indian government focuses on nine pillars to achieve the objectives of the Digital India Programme. They are:
1) Broadband Highways
Under this, there are three sub-components-
- Broadband for All Rural
Its target is to cover 2,50,000 Gram Panchayats with broadband connection by December 2016. The outlay of the project is estimated to be around 32,000 cr., and the Department of Technology is its nodal department.
- Broadband for All Urban
Under this, Virtual Network Operators will deliver services, and communication infrastructures will be compulsory in new urban buildings.
- National Information Infrastructure
In this, cloud data centres of central government and states will be integrated with SWAN, NKN, NOFN, and NOPN networks. It will help connect 100, 50, 20, and 5 government offices/ service centres at state, district, block, and panchayat levels.
2) Universal Access to Phone Connectivity
It focuses on increasing mobile connectivity more inclusively by covering around 42,300 villages; still, untouched by this service.
Department of Telecommunication will be the nodal agency of the mission, and the deadline to complete this task is between FY 2014-2018.
3) Public Internet Access Initiative
It has two sub-components:
- Common Service Centres-
Common Service Centres (CSCs) are the points that benefit citizens by providing various government services online. Under this, it aimed to increase the number of CSCs from 1,35,000 to 2,50,000 with the motive of one CSC at each Gram Panchayat.
The Deity will be responsible for the implementation of the initiative.
- Enable Post Offices to be multi-service centres
The government has targeted to develop 1,50,000 Post Offices into multi-service centres, and the Department of Posts will act as the nodal agency for this mission.
4) e-Governance: Reforming Government through Technology
It is the program to re-engineer the government working manner using IT. It involves shifting from manual to digital databases so that all government processes can be digitized.
Guiding Principles for the transformation are:
- Online repositories for the documents like educational certificates, voter IDs, driving licenses, etc., should be made mandatory to ease citizens from submitting their documents in hard copy.
- System for online application and its tracking should be made.
- Government services should be integrated with their respective platform, like UIDAI, UPI, etc., to disseminate services efficiently.
- A proper automatic Public Grievance Redressal system should be established for the public's complaints.
5) e-Kranti - Electronic Delivery of services
Transforming e-Governance for Transforming Governance is the vision of e-Kranti. It aims to make all government services available to the country's citizens electronically via an integrated system. It will help deliver services more transparent, efficient, and reliable. Through this, the government is working to provide all the benefits possible with the help of technology.
A total of 44 Mission Mode Projects have been sanctioned under the mission, out of that 10 of them are recently announced under the mission, like Technology for Education= e-Education Technology for Health= e-Health Technology for Farmers, Technology for Security, Technology for Financial Inclusion, Technology for Justice, Technology for Planning, Technology for Cyber Security, etc.
6) Information for All
The vision behind this initiative is to provide information about every work and decision of the government in real-time through online platforms.
To serve the same purpose, "MyGov." was launched, allowing public engagement in certain things' decision-making and providing real-time information. It channelizes the communication link between the public and the government.
The establishment of Open data platforms will be encouraged to make the public data more accessible easily.
7) Electronics Manufacturing
Complete digitization can be attained only with adequate availability of electronics. Due to this, Electronic manufacturing has been made one of the pillars of the mission. For achieving electronics adequacy, the focus should be on the following points:
- Net Zero Import should be prioritized by boosting domestic manufacturing of electronics.
- There should be a focus on aspects related to manufacturing that are required to increase production, like taxation, incentives to manufacturers, Incubation, Skill development, etc.
- Strengthening existing electronics manufacturing units to increase domestic production.
8) IT for Jobs
The Digital India program will help increase employment and create new employment opportunities. It will create jobs in the IT industry for both skilled and semi-skilled labour.
- Under this, IT job training will be provided to 1 cr?students of rural areas and towns over five years.
- To increase the penetration of ICT in the northeastern region, BPOs will be established in each northeastern district.
- Telecom Service Provider will train 5 lakh rural working people to make them digitally literate.
9) Early Harvest Programme
EHP includes projects that can be implemented relatively within a short period, and the effects of their implementation can be seen shortly. It has projects like:
- IT Platforms for Messages
- Government Greetings to be e- Greetings
- Biometric Attendance
- Wi-fi in all Universities
- Secure E-mail within the Government
- Standardized Government E-mail Design
- Public Wi-fi Hotspots
- School Books to be e-Books
- SMS-based weather information, disaster alerts
- National Portal for Lost and Found Children
These projects have eased the life of the citizens; it has helped in rendering services digitally, from sending messages to making online attendance, providing students and the public with Wi-fi facilities and making available textbooks online, and providing SMS-based weather forecasts to farmers and other related stakeholders.
Initiatives and products which are digitizing India under the Digital India program are categorized as: -
1) Communication sector
- Bharat Net
- BSNL Next Generation Network
- BSNL Wi-fi Services
2) Digital India Product
- Digi Locker
- National Scholarship portal
- e-Hospital/ ORS
- e-Sign
- Digitize India Platform
- BHIM UPI services

3) Applications and Portals
- Digital India Portal and App.
- MyGov App and MyGov.in Portal
- Swachh Bharat Mission App
4) Digital India Policies
- National Centre for Flexible Electronics
- Centre of Excellence for IoT
- e- Governance Policy
- Electronics Development Fund Policy (EDF Policy)
5) Digital Products of Indian Railways
- e- Ticketing
- SMS service
- e- Catering
- Online PNR status information
6) Other services
- Online Cab services
- Online Food Delivery
- Online Bus Ticket booking
- Mobile recharge facilities
Effects of the Digital India Programme
The Digital India mission is one such initiative that has brought changes in the life of an ordinary individuals. Every person uses the services offered under the Digital India initiative daily. It has impacted every sector of the economy.
Effects on Technology
Digital India is the result of the advancement of technology. It has opened the scope of growth of technology in the country by normalizing the use of technology in day-to-day life. It is helping India shift from a labour-intensive economy to a technology-driven one. It has created the demand for the advancement of technological infrastructure.
Effects on Economy
Digital India has made India a leading country in online transactions with the help of UPI. It has supported the growth of macroeconomic factors like GDP, employment, etc.
Effects on Social Sector
Social Sectors such as healthcare and education have evolved significantly with Digital India's help. Education has shifted from physical space to online platforms; some have become significant unicorns like Byju's and PhysicsWala. In the healthcare sector, the government started e-Sanjeevani, an Online OPD facility. All these became possible just because of the online revolution, which drastically increased the services' reach.
Effects on Agriculture
Linking farmers with digital services was challenging, but the government worked seamlessly to make farmers comfortable with the technology. Digital India eased the life of the farmers by providing real-time weather forecasts and crop-related information directly from experts in the respective field.
Effects on the Banking sector
Digitization has revolutionized the banking sector. It has reduced the workload of the bankers with digital India products and policies; various banking operations can now be done online. Every bank provides the services of e-banking.
E-Banking is a relief for both customers as well as banking staff. Now, customers are not required to visit the bank for tasks such as depositing and withdrawing money, getting bank statements, etc. Bankers are relieved from the work pressure due to the presence of many customers every time.
Challenges of Digital India
- A Large number of the Digitally illiterate population
The biggest challenge of the mission is to provide digital literacy to the public irrespective of their educational background. Executing a literacy and awareness campaign on such a large scale is a humongous task.
Digital literacy is mainly required to be disseminated in the rural parts of the country.
- Connecting Rural and Remote areas
The Digital India program target will only be achieved when it has penetration in rural and remote areas. These areas pose different challenges like acceptance by the public, terrain, climate, etc., which can prove to be a hurdle in connectivity.
- Coordination issues between Central and State Governments
The Digital India programme is a central sector scheme, and for the plan's successful implementation, it is vital to have good coordination between central and state governments. Some conditions can prove to be a problem with the scheme's implementation.
- Cyber Crime
The more people will move to online platforms and become digital, the threat of cybercrime will rise simultaneously. People are moving towards online platforms for services like banking, document storage, etc., and their data can be in danger. Government should have a robust solution to safeguard people from such fraud for the successful execution of the scheme.
- Establishing Faith in Technology
Various people still don't fully believe in technology, especially in money-related matters. They still prefer to go to the bank for transfer, withdrawal, or deposit of a large amount of money, and it is because they are scared of the failure of technology and not aware of where to go in such situations.
Therefore, to establish faith in technology, the government will have to do a dual task: create awareness campaigns to burst myths about technology and encourage them to use it. Secondly, the government should make a body to hear the grievances and address the problems of the public in case of such technological failures and frauds.
- Costly Implementation
Transforming India into a digital economy requires immense infrastructure development like fibre optics, IT infrastructures, data centres, etc. For such infrastructural development, a large amount of financial investment is needed. The arrangement of funds for the programme is one of the significant challenges for the Indian government. The government has earmarked a total financial outlay of Rs. 1,13,000 Cr. for the scheme.
- Net Neutrality
Net neutrality is one of the critical aspects of making this scheme effective. In our country, there is not 100% net neutrality. In India, people don't have so much money to have subscriptions and access to everything; as a result, they cannot use many services, raising the need for net neutrality.
Net neutrality will provide real meaning to digital India, where all the services of different platforms will be open to the public and can be accessed without any extra charge.
Institutional Framework and Management structure of Digital India Programme
Digital India is the dream project of the Indian government. It has been prepared with utmost care and devotion. The institutional and management structure includes key ministers and noted departments of the concerned ministries, including the Prime Minister, in its implementation structure.
Constituents of Digital India scheme management structure
- Monitoring Committee on Digital India
This committee works under the chairmanship of the Prime Minister of India. This committee includes representatives from various concerned ministries/ departments. The committee's main task is to monitor the execution of the Digital India Programme at regular intervals.
- Digital India Advisory Group
The Minister of Communications and IT is the group's chairman, along with other members from related ministries of state/UT governments and some from different line ministries. It provides the necessary insights and advice on policies and strategic steps to the Monitoring Committee on Digital India for the successful implementation of the scheme.
- Apex Committee
The head of this committee is the Cabinet secretary of the Government of India. It executes and monitors the accurate implementation of the policies and strategies advised by the Advisory Group. It forms the coordination and integrates different government initiatives related to Digital India, as per need.
- Expenditure Finance Committee (EFC)/ Committee on Non-Plan Expenditure (CNE)
This committee is responsible for the financial approvals for the projects under Digital India Programme. It also fixes the financial terms and conditions of participation by the states. This committee is headed by Secretary (Expenditure).
- Council of Mission Leaders on Digital India
This council works as a platform for sharing the previous and new initiatives related to e-Gov under Digital India Mission. It will also present various ICT projects and initiatives of Deity to other governments and departments. The council is headed by the Secretary (DeitY).
- At the State level, the State Committee on Digital India is headed by the state's Chief minister.
After that, there is the State/UT Apex Committee on Digital India under the chairmanship of the Chief Secretaries of the states.
Opportunities for Digital India Programme
- It is an initiative to transform the country with IT. It aims to make every citizen of the country a user of core digital services by providing them with good digital literacy.
- It will increase the reach of high-speed internet to the villages, and for that, around 7 lakh Km of broadband cable is being installed to connect 2.5 lakh villages to the internet.
- Digital India provides the opportunity to transform; with the internet's reach, the villages' schools can access smart classrooms.
- It has removed the Indians from the counter. Services like e-ticketing, e-commerce, e- Catering, e-healthcare, etc., are now available online. In earlier times, people had to stand in queue for hours for such tasks. It has made life easy, and anyone can use these services from their home.
- It facilitates faceless work in offices which has helped curb corruption, and the process has become more efficient and effective.
The Future of Digital India
Digital India is a campaign that can boost India's GDP growth and be a pioneering factor in attaining the mark of a $5 trillion economy by 2025. It will transform the image of India of being outdated and help in shifting from only an agriculture-based economy to an IT-based economy. This mission will uplift the intellectual and social quotient of the individual. It will improve the country's citizens with an increase in their literacy level.
Digital India will lead to a decrease in the cases of corruption and other offences like money laundering, tax evasion, etc. It will help in the faster resolution of pending cases in the system.
It will change the education system, where students can get an education and learn skills from anywhere. It will make education relatively less costly, reducing the need for extensive infrastructure.

It will reduce the gap between the government and the citizens of the country and will make the government more accountable. Through digitization, people will get the platform to question, and the government will hear them. Consequently, it will be a tool for the empowerment of the ordinary person.
|





 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










