Concept of SamplingSampling is done only on an independent variable. For example, if we digitize x-axis in sampling. Sampling is divided into two parts:
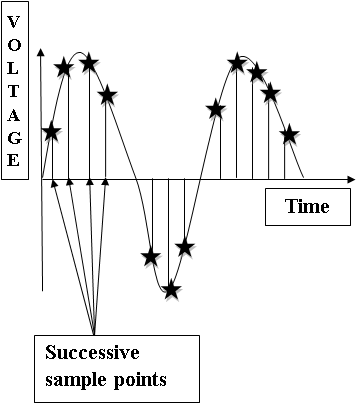
There are variations in the sampled signal which is due to noise. To reduce the noise more samples are taken which means more data or pixel which result in a better image with less noise present in it. In an image, pixel is the smallest element which is represented in the form of a matrix. In sampling, the number of samples taken in X-axis is continuous and refers to a number of pixels in that image. 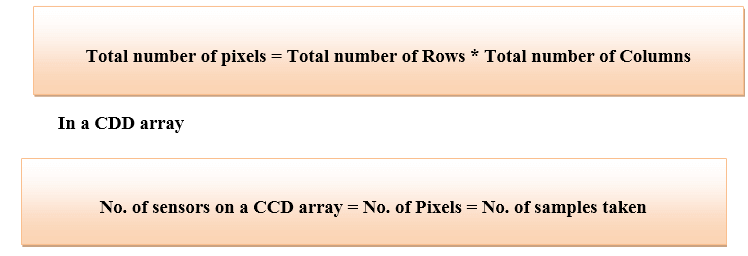
OversamplingAs we have seen above, there are two types of sampling, up-sampling, and down-sampling. Up-sampling is also known as oversampling. In an image, oversampling means using a high-resolution image sensor as compare to camera output image resolution. One of the oversampling applications in image processing is known as zooming. ZoomingIncreasing pixel quantity is known as Zooming. When we zoom in an image, more detail can be seen. Increasing the number of pixels is done using oversampling. Zooming has two steps:
Another, way to zoom an image is by zooming optically using the motor movement of the lens, and then the image is captured. Optical Zoom vs. digital Zoom
Zooming methodsThere are three types of methods used in zooming; they are as follows:
Pixel replicationPixel replication is also known as Nearest neighbor interpolation. In this method, a copy is produced of the neighboring pixels. This algorithm works the same as zooming. Working:In this method, new pixels are generated from the originally given pixel. Each pixel is copied from its neighboring pixel n time row and column-wise, and we get a zoomed image. For example, we have 2 row and 2 columns of an image. And we zoom the image twice. 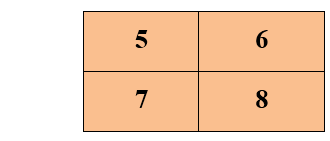
ROW WISE ZOOMING:When an image is zoom row-wise, it copies the pixels from row to the new cell 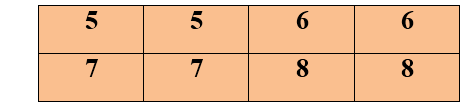
COLUMN SIZE ZOOMING:Next step is to copy the pixel column-wise to the new adjacent column. 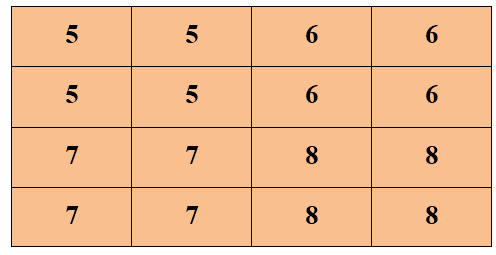
As we can see that the original image was having2 rows and 2 columns, but after zooming the image, it is converted into 4 rows and 4 columns. 
AdvantagesIt is very simple, and we have to copy the pixels. DisadvantagesWhen we zoom an image, the output is very blurry. As a result, we have a full blurred image. Zero order holdIt is another method of zooming. Zero order hold is also known as zoom in twice, as it can only be zoomed twice. WorkingIn this method, two adjacent elements are taken from the row, then elements are added, and the result is divided by two. The result is placed in between the elements. For example: We have 2 rows and 2 columns of an image and we zoom in the image twice.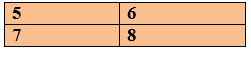
Row Wise Zooming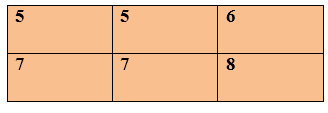
When an image is zooming in row-wise, then rows are added (5+6) =11 and then it is divided by 2. We will get 5.5 approximate to 5 and the operation is performed in the second row. Column Wise Zooming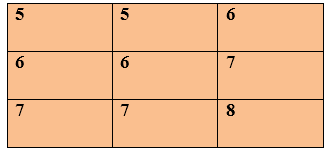
When an image is zoomed column-wise, then columns are added (5+7) = 12 and then it is divided by 2. We will get 6, and this operation is performed in all the columns. As we can see that the original image was having 2 rows and 2 columns but after zooming, the image it is converted into 3 rows and 3 columns. 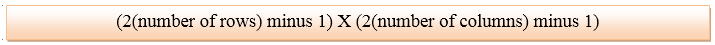
It is very simple and it does not create a blurry picture. DisadvantageIt works on the power of 2. Reasons behind Twice ZoomingAs we have seen in the above example, we have an image of 2 rows and 2 columns. If we want to zoom in an image 7 or 9 times then it cannot be done. It can only zoom in the power of 2 i.e 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, etc. K-Times zoomingK-Times Zooming is the perfect zooming algorithm. In this algorithm, k stands for the zooming factor. Following are the steps to get a zoomed image which are used in both row and column:
For example: We have 2 rows and 3 columns of an image. And we have to zoom in the image thrice. 
In this case, the zooming factor (k) is 3. So, the number of values to be inserted is k-1 = 3-1 = 2. Row Wise ZoomingLet's take 1st two adjacent pixels. i.e. 2 and 3. Now, subtract 3 from 2. Note: We have calculated two values because we have to insert k-1 values.Now, repeat the above steps for the next two pixels. 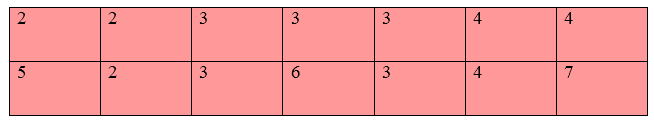
Column Wise ZoomingIn column wise zooming, the same steps are performed as done in row-wise zooming. 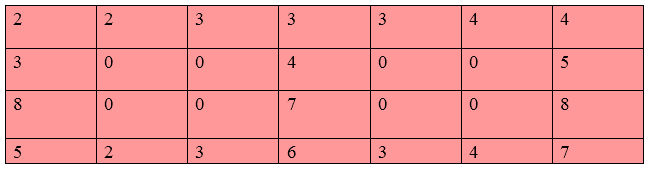
As, we can see that the original image was having 2 rows and 3 columns but after zooming, the image it is converted into 4 rows and 7 columns. 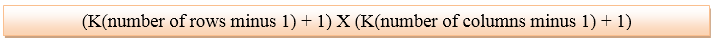
AdvantagesIt can be zoomed to any factor, thrice or four times or even more. DisadvantagesCost of computation is increased due to the additional step in the end.
Next TopicPixels, Dots and Lines per Inch
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










