Direct and Indirect SpeechThere are multiple situations when an individual requires to explain an event or activity that occurred. However, this mostly necessitates re-stating what somebody said. These kinds of instances can occur in a social setting or in official mails or conference. 
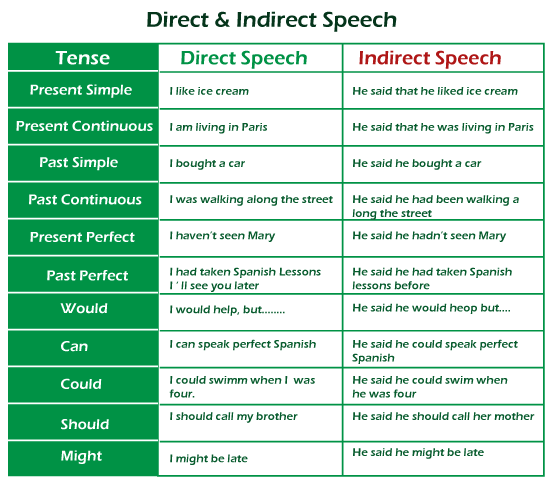
Two kinds of speech are employed to define/describe what somebody said: direct speech and indirect speech (or reported speech). Also, these depend on the kind of conversation - formal or informal. In informal conversations, indirect speech is used, and direct speech is not used until and unless the speaker uses a quote. For English learners, direct and indirect speech might be confusing. Let's define the terminology first, then learn how to speak about what someone said and how to change direct to indirect speech or vice versa. You can reply to the enquiry, "What did he say?" in two different ways: by repeating what was spoken (direct speech) by reporting what was said (indirect or reported speech). Direct SpeechThe literal words uttered are re-stated or quoted in the direct speech. Whenever we utilize direct speech in our speech or text, we place the terms spoken in-between the quotation marks ("") and make no changes to these. Through this one could be reporting something that is being said at present (for instance, a telephone dialogue) or informing somebody about a prior chat. There is no commentary or annotation in direct speaking; the statements are taken straight from one source and conveyed to another. In simple words, we take the presenter's words directly and reproduce them exactly as he or she spoke them. Examples
The direct speech is displayed in quotations in these samples, indicating that it was taken straight from the original with no changes. 
Indirect SpeechThis type of speech is when you report what somebody has said in your wording without modifying the real message or meaning of what has been stated. Indirect speech is sometimes known as the reported speech. It is also known as indirect dialogue or indirect narrative. Indirect speech, also called reported speech, occurs when we describe words or phrases in our own language. Instead of being quoted, the actual words are edited and/or interpreted. We employ phrases that refer to something that has already occurred while discussing indirect communication. To do so, we use the past tense and summarize, amend, or synthesize what has already been spoken. In order to show indirect discourse, reporting verbs are needed. The most frequent are:
The term "that" is in the bracket and can be hidden or removed from the sentence- spoken or written. Following are some instances of indirect speech :
Using the words say or 'tell. ' In Indirect speech, one must also employ the term 'tell' ('told' in the past tense) rather than the term 'say'. However, one must incorporate the object pronoun. Often the term 'say' is employed when there is no indirect object: She said that she was exhausted. Whereas always use the term 'tell' when you talk about who was being spoken to (i.e., with an indirect object) : She told me that she was exhausted. As an example:
Modifying Time ExpressionsWhenever we use reporting speech, it is often important to adjust the time phrases particularly whenever speaking about the past tense and the reference to the timing no longer implies. As an instance :
Below are some of the instances of the same :
Reporting QuestionsWhen reporting a question, the interrogative form must be converted into a positive statement, with the verb tense shifted one step back, as with ordinary reported speech. We can report two groups of inquiries: yes/no questions and inquiries that start begin a questioning term like 'what,' 'where,' 'who,' etc. When reporting a yes/no question, we use the word 'if.' As an instance : Direct speech: "Does she reside here? " Indirect speech: He asked me whether she resided here. In the above- mentioned statement, the verb 'do' is removed from the reported form of the question since it is not a query anymore, and the verb 'reside' is changed to 'resided'. For queries beginning with question terms such as 'what,' 'where,' 'when,' 'who,' and so on, we record the question but alter the interrogative type to the affirmative form. As an instance: Direct speech: Where do they stay ? Direct speech: "When are you coming ? Direct speech: "How will she come here? " Most often we employ the verb 'ask' to report an inquiry. The verb 'to ask,' like the verb 'to tell,' is usually preceded by an object pronoun. However, it is permissible to omit it. Orders and Requests ReportingWhenever you give somebody an order, you utilize the imperative form, which signifies you use only the verb and no subject. As an example :
We utilize 'tell' and the verb's infinitive to report an order. As an example :
While making the requests, you mostly use terms like 'can,' 'could,' or 'will.' As an example :
We employ the verb 'to ask' and the infinitive type of the verb to make a request. As an example :
Now that you have seen how we utilize direct and indirect communication try it for yourself. Reading a brief narrative in English language or a news update or article on the phone or laptop is a wonderful and simple approach to analyse how these are utilized since the write-ups provide numerous instances of Indirect discourse/dialogue. Rules for Transforming the Indirect Speech to Direct Speech When converting indirect speech to direct speech, the below-mentioned suggestions/advices must be adhered to :
Consider the following examples : Indirect: He asked if she was arriving at the special occasion. Indirect: The man said that he was pleased with her outcome. Speech Conversion of Direct and IndirectWhen transitioning between direct and indirect speech, there are three vital points that are essential to remember.
Changes in TenseThe tense of verbs does not significantly alter while transitioning from direct to indirect speech since if the conditions of what someone said remain the same, it may be recorded as such. As an example: "I'm feeling exhausted fatigued" (= Direct Speech ) Present Continuous She said that she is feeling fatigued (= Indirect Speech ). Present Continuous However, we frequently shift the tense when reporting on what was stated in the past. This rule is connected to back shifting, which is the practice of moving back a tense. As a result, the present will return to the past. Some modals alter as well. Here are some examples of how to use the indirect speech to direct speech : Direct Speech: I wish to see you later. Direct Speech: You have to visit us in the evening. 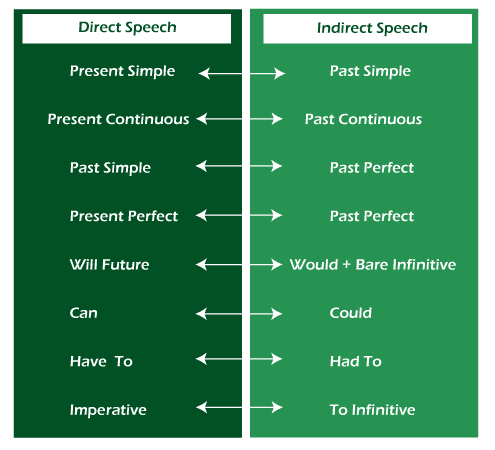
Changing PronounsPronouns in indirect speech must also be modified from what they were in the indirect speech, and the initial pronoun being adapted to match the person who made the sentence: Direct Speech: I wish to see you later. Indirect Speech: She said he wished to see me later. Direct Speech: You must reach back home in the evening. Indirect Speech: Sheena told me I must reach back home in the evening. Changing Time ExpressionsYou may also need to adjust time-related terms based on the circumstances and while you are reporting the speech. With these instances, one must believe that the discourse is being reported at a timing/period in the future. So, phrases like "yesterday" or "tomorrow" hardly make any sense in the case of an Indirect speech. Indirect Speech: She said that he had seen him the day before. Direct Speech: She said, "I saw him yesterday. " Indirect Speech: She said," He will get the novel tomorrow. " Direct Speech: She said he would get the novel the next day. ImperativesThe structure of reported speech imperatives differs from that of other reported speech sentences. The following are imperatives : Commands: Be silent ! Requests: Please shut the door. Advice: Go sit down. Suggestions: Take the exams again next week. Reported Speech Imperatives Sentence structure in this case: reporting verb (e.g. ask, tell) + noun/pronoun + to infinitive Example: He asked me to visit later. Below are a some of the instances ; Direct Speech: He said, "Keep calm. " Indirect Speech: He instructed me to keep calm. Indirect Speech: The professor asked me to close the gate. Direct Speech: The professor said, "Please close the gate. "
Next TopicDirect and Indirect Speech Rules
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










