Ecology DefinitionThe subjects of human science, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere are all included in an ecology branch of study. Ecology is the study of living things, their habitats, and the relationships between those living things. Numerous layers are researched, including organisms, populations, communities, biosphere, and ecosystems. 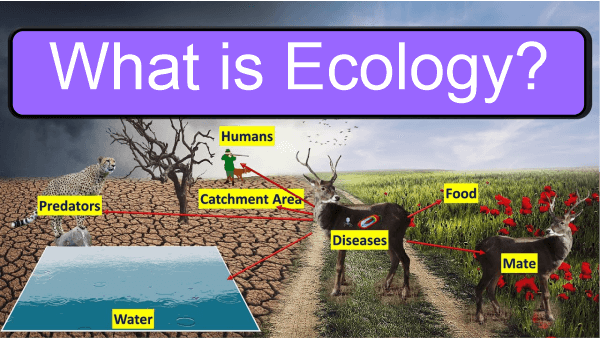
Getting a better knowledge of the life processes, habitats, interactions, and biodiversity of organisms is the primary goal of an ecologist. Let's study the idea of ecology and take a closer look at the ecological details that are given here. Biological and Abiotic Factors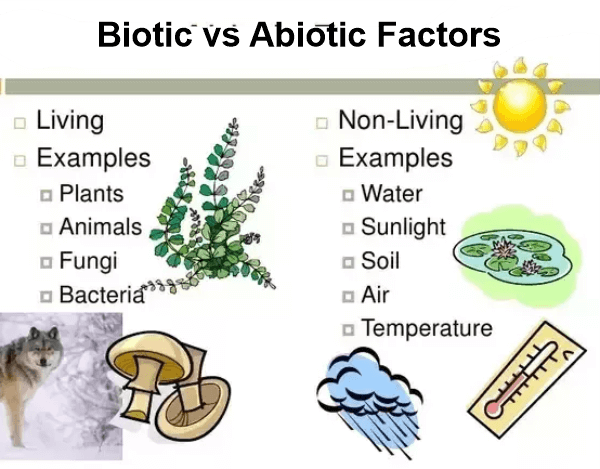
Ecology's main objective is to comprehend how living things' biotic and abiotic components are distributed in their surroundings. Biologic and abiotic factors comprise living and non-living things and how they interact with one another and the environment. Biotic ComponentsLiving things make up an ecosystem's biotic components. A few examples of biotic components include creatures like birds, animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. Abiotic ComponentsThe ecosystem's non-living chemical and physical elements are called abiotic components. The hydrosphere, lithosphere, or atmosphere may include these elements. Only a few examples include sunlight, soil, air, moisture, minerals, and other abiotic components. On the other hand, abiotic components are composed of inanimate elements like sunlight, water, and topography. Biologic components are made up of living organisms. Ecological CategoriesEcology may be broken down into several categories. The many ecological types are listed below: 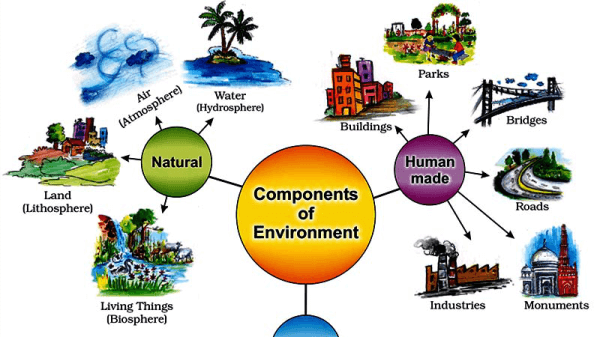
Worldwide EcologyIt focuses on how the world's ecosystems, land, atmosphere, and oceans interact. It helps comprehend global relationships and their impact on the world. Geographic EcologyIt is concerned with the transfer of energy, materials, organisms, and other ecosystem products. Landscape ecology draws attention to human activities impact on the landscape's features and purposes. Ecology of EcosystemsThe entire ecosystem is examined, encompassing both living and non-living elements and their interactions with other parts of the ecosystem. This area of research looks at how ecosystems interact and operate. Ecological CommunityIt focuses on how living things interact with one another to alter community structure. Two or more populations of various species localized in one area make up an ecological community. The Ecology of the Population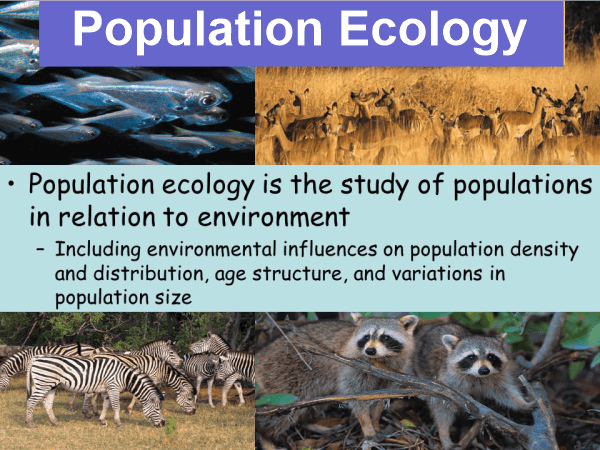
The number of organisms in a population and factors that influence and modify their genetic makeup are discussed. Ecologists are interested in population growth, variations in size, and other population-related interactions. A population in biology is a group of people belonging to the same species present in one location simultaneously. The major causes that raise the population are births and immigration, whereas the main factors that reduce the population are deaths and emigration. The distribution and density of populations are investigated by population ecology. Population density refers to the number of individuals in a given volume or region. It aids in assessing if a certain species is endangered, needs to have its population under control, or needs its resources restored. Biological EcologyBiologic ecology studies how an organism responds to environmental pressures through its behavior, morphology, physiology, etc. It looks at the relationships between certain species and biotic and abiotic components. Ecologists investigate how organisms respond to their surroundings' living and non-living components. Certain species are associated with certain morphological, behavioral, and physiological adaptations. Molecular EcologyEcology investigates the production of proteins and how they affect living things and their surroundings. The molecular level is where this takes place. DNA creates the proteins that interact with the environment and one another. Several cultivated species are the result of these interactions. The Importance of Ecology
The following examples show how important ecology is: Preserving the environment Ecology helps us understand how human activities affect the ecosystem. It makes clear to everyone the extent of our ecological damage. A lack of ecological understanding leads to the deterioration of the ecosystem and the land. A few species have also become extinct or are in danger due to it. Examples include mammoths, white sharks, and dinosaurs. We can thus protect living things from harm and danger by having a thorough awareness of the environment. Allocating Resources Ecology enables us to understand which resources are essential for the existence of various creatures. A lack of ecological understanding has caused these resources to be scarce and underutilized, increasing competition. Energy Conservation For their development and expansion, all living things need energy. Energy sources, including light, food, and radiation, should be used up more due to a lack of ecological understanding, which would lead to depletion. By minimizing the excessive use of energy resources, comprehensive knowledge of ecological demands aids in conserving energy for future applications. Eco-Friendliness The ecosystem encourages species to cooperate and adopt behaviors that protect the ecology of life. Ecology Examples: Here are a few examples of ecology: Human Ecology The interaction between people and the environment is the main topic. It draws attention to the damaging effects humans have on the environment and teaches us how to improve ourselves for the good of everybody, including the environment. Construction niche It focuses on investigating how living things modify their surroundings for the advantage of both themselves and other creatures. For example, termites build a 6-foot mound while feeding and protecting their colony. Questions and AnswersQuestion 1. Describe ecology. Answer: The interaction of living organisms with one another and their environment is the focus of ecology research. Question 2. What various ecological levels are there? Answer: Organisms, communities, populations, and ecosystems are a few of the numerous ecological levels. Question 3. What various ecological kinds are there? Answer: One of the many types of ecology is molecular ecology. Other categories include ecosystem ecology, landscape ecology, population ecology, community ecology, and global ecology. Question 4. What connections exist between ecology and evolution? Answer: Ecology is important in the development of new species and the modification of already existing ones. One of the several elements that affect evolutionary change is natural selection. Question 5. Who invented the term "ecology"? Answer: Ecology was developed, according to German naturalist Ernst Haeckel. However, biology, geology, and evolution are other sciences that have influenced ecology. Question 6. What is habitat ecology? Answer: Habitat ecology refers to the unique naturalistic way, characterized by physical and biological characteristics, in which a particular species of an organism lives. Question 7. Describe a niche. Answer: An ecosystem known as a "basic niche" allows organisms to survive, reproduce, and use biotic and abiotic resources without interfering with other species.
Next TopicElectricity Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










