What is the full form of ECT
ECT: Electroconvulsive Therapy
ECT stands for Electroconvulsive Therapy. It is a therapy in which mental disorders are treated using electric current. In this therapy, electric current is used to produce brief convulsions in patients. Due to the involvement of electric current, it is also referred to as shock treatment.
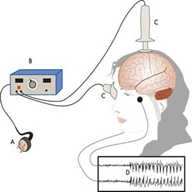
ECT was first used in 1938. It is mainly used to treat severe depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. It is also recommended for people who have symptoms like delusions and hallucinations or when other treatments and medicines are not working.
In this therapy, before applying the electric current, the patient is put in a sleepy state through anesthesia and medicines are given to relax the muscles. Then electrodes are placed on the skull to apply the therapy, which may last up to 8 seconds. It produces a short seizure in the brain. Immediately following the therapy, the patient may temporarily experience nausea, headache, jaw pain and short-term memory loss, etc. The frequency of this treatment may vary from person to person, depending on the nature of the illness and an improvement after each session. On average, patients undergo 6-12 sessions of ECT.
Types of ECT
ECT is basically of two types: Unilateral and Bilateral.
- In unilateral ECT, one electrode is placed on the top (vertex) of the head, and another is placed on the right side of the skull.
- In bilateral ECT, electrodes are placed on both sides of the head.
Why is it done?
The severe symptoms of a number of mental health problems can be significantly and quickly improved by electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). In order to treat:
- Severe depression, especially when coupled with psychosis, the urge to end one's life, or an inability to eat.
- Depression that is treatment-resistant is extreme depression that doesn't go better with drugs or other therapies.
- Bipolar disorder is characterized by severe mania, a condition of high exhilaration, agitation, or hyperactivity. Impaired decision-making, reckless or impulsive conduct, drug misuse, and psychosis are other indications of mania.
- Lack of movement, rapid or odd motions, absence of speech, and other symptoms are characteristics of catatonia. It has links to schizophrenia and a few other mental conditions. Catatonia can occasionally be brought on by a medical condition.
- Aggression and agitation in dementia patients can be difficult to treat and have a detrimental impact on quality of life.
- When other types of therapy have failed, or drugs are not tolerated, ECT may be a viable therapeutic option.
Sometimes ECT is applied:
- When using drugs during pregnancy is prohibited because they might damage the growing fetus
- When elderly folks can't handle the adverse effects of medication
- When it comes to those who favour ECT over medicine
- When has ECT been effective in the past
Risks
While being mostly risk-free, ECT may have some dangers and side effects:
- Confusion: After therapy, you can have disorientation that lasts for a short while to a long time. There's a chance you have no idea where you are or why you're there. In rare cases, confusion may last for a few days or longer. Older folks typically exhibit confusion more overtly.
- Loss of memory: Some patients have problems recalling incidents that happened just prior to therapy, in the days, weeks, or months prior to treatment, or, very infrequently, from years past. Retrograde amnesia is the medical term for this disorder. Moreover, you could have problems remembering what happened throughout the weeks of your therapy. When therapy is finished, most people's memory issues normally go better within a few months.
- Adverse physical repercussions: Some persons report nausea, headaches, jaw discomfort, or muscular aches the days before an ECT session. Often, medicine can be used to address them.
- Healthcare issues: There is a chance of medical issues with every sort of medical operation, especially one that uses an anaesthetic. Heart rate and blood pressure rise during ECT, and in rare circumstances, this may cause major cardiac issues. ECT might be more dangerous if you have cardiac issues.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










