What is the full form of EDGEEDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM (Global System for Mobile) EvolutionEDGE is an enhanced version of GSM and offers high-speed 3G built on GSM. It is a type of data system used on the GSM network used to allow improved data transmission rates. It can transmit three times more bits than GPRR in the same length of time. EDGE is an "add-on" to GPRS; it cannot work alone. It was deployed on GSM networks by AT&T in 2003 in the United States. 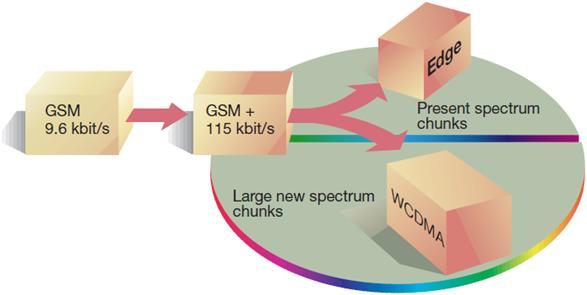
Data SpeedEDGE has successfully replaced GSM without disrupting the existing frequency reuse scheme. Technically, EDGE provides a speed of 384kbps (which is much higher than the data rate of GPRS) but is labelled as 2.75G by the industry. Key Elements added in EDGE
Features
EDGE's technological foundationThe first step towards third-generation wireless mobile services is the packet-switched technology known as General Packet Radio Services, or GPRS, which may attain speeds of up to 115 kbps (3G). The Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution (EDGE) technology is the best next step in a low-impact conversion if GPRS is already in use. Software updates and EDGE plug-in transceiver modules are all that is needed. The strategy protects operators' investments by enabling them to utilise their current radio and network equipment. EDGE offers an evolutionary migration path from GPRS to UMTS by applying modifications in modulation for UMTS deployment. The objective of EDGE is to boost data speeds on the existing 200 kHz GSM radio channel while preserving compatibility with the circuit (and packet) switches that are currently in use. Although EDGE is largely a radio interface improvement, it may also be seen as a system concept that allows the GSM and TDMA/136 networks to offer a variety of new services. Advantage
Disadvantage
Modulation and coding used in EDGE (MCS)Both GPRS and EGPRS/EDGE use a two-step channel encoding process: The Block Check Sequence, often known as the cyclic code, is used to add parity bits before coding with a potentially punctured convolutional code. The puncturing rate of the convolutional code and the number of parity bits generated by the cyclic code are both specified in the GPRS Coding Schemes CS-1 through CS-4. In GPRS Coding Schemes CS-1 through CS-3, each input bit is converted into two coded bits since the convolutional code works at a rate of 1/2. In Coding Schemes CS-2 and CS-3, the output of the convolutional code is punctured to achieve the proper coding rate. Convolutional coding is not utilised in the GPRS Coding Scheme CS-4. With EGPRS/EDGE, the GPRS coding schemes are replaced by the MCS-1 through MCS-9 modulation and coding schemes, which additionally specify whether GMSK or 8PSK is used as the modulation technique. MCS-1 through MCS-4 utilise GMSK and perform similarly to (but not nearly as well as) GPRS, whereas MCS-5 through MCS-9 use 8PSK. EGPRS codes the payload data separately from the Radio Link Control (RLC) and Media Access Control (MAC) headers, in contrast to GPRS.
Next TopicFull Form
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










