Effects of Acid Rain on Taj Mahal
What is Acid Rain?
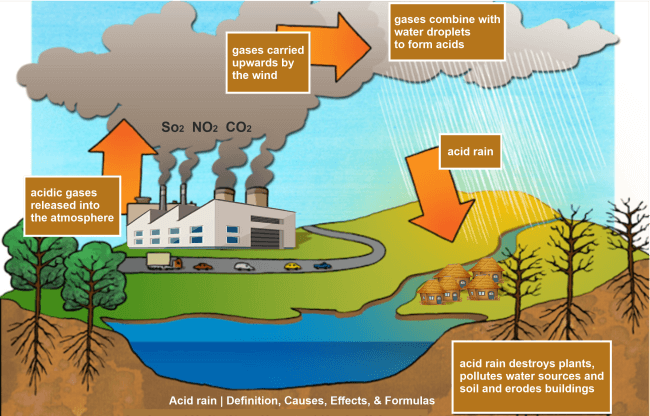
- Nitric acid and sulphuric acid are two examples of the numerous acidic compounds created when sulphur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) combine with water, air, and other substances in the atmosphere to form acid rain or acid precipitation.
- Acid rain is any downpour containing significant amounts of nitric and sulphuric acid.
- It can show as snowfall, mist, or even dry substances falling to the ground.
Formation
- Everyone is aware that rain clouds are made entirely of water.
- Under some circumstances, airborne chemicals like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide interact with the air or oxygen and water found in the atmosphere and descend to the earth as acid rain.
- However, how do these gases initially penetrate the atmosphere?
- There are two contributors to it.
- The first is a natural process that involves decaying flora and erupting volcanoes, emitting chemicals that can lead to acid rain.
- However, most acid rain is a consequence of human activity, such as the combustion of fossil fuels, transportation, and releasing chemicals from industries.
What causes the rain to turn acidic?
- It's crucial to realize that usual rain is a little acidic.
- Rain naturally has a pH of 6 because as it descends to the earth, it reacts with airborne carbon dioxide to create carbonic acid.
H2O(I)+CO2(g)→H2CO3(aq)
- However, due to the combustion of fossil fuels, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which are significantly more powerful acids, are emitted.
- This causes acid rain to develop a pH of 3, which greatly raises the acidity of rain.
- How much, in your opinion, does acidity rise when the pH falls from 6 to 3?
- Always keep in mind that a Ph shift of one corresponds to a tenfold shift in acidity.
- Therefore, going from 6 to 3 is a thousand times or ten times extra acidic.
- Let's investigate this in greater detail.
- It is widely known that plants require a specific proportion of sulphur to thrive, which they get from the potassium sulphate naturally found in the soil. Through the roots, these sulphates are absorbed.
- The carbon atoms in the leaves form a connection with the sulphur atoms.
- These sulphur and carbon molecules are still present in the coal that these plants inevitably turn into after millions of years.
- The sulphur and carbon particles in the fossilised remains of these extinct plants react with the oxygen found in the air to form sulphur dioxide and carbon dioxide, which are then released into the environment.
- When sunshine strikes these gases, sulphur dioxide interacts with additional oxygen to produce sulphur trioxide, which combines with rainwater to form sulphuric acid.
SO2(g)+O2(g)→2SO3(g)
SO3(g)+H2O(I)→H2SO4(aq)
- Similar to this, when nitrogen oxide from our automobiles is discharged into the atmosphere, it reacts with additional oxygen and interacts with rainwater to make nitric acid.
NO2+H20→HNO3
We now understand how rain becomes acidic.
Types of acid rain
Acid detaches from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms and sinks to the ground. This acidic fluid could travel long distances due to the wind. Wet deposition refers to the sort of acid rain that incorporates water. At the same time, dry deposition refers to acid rain from dust and gases.
Effects of acid rain on our environment
- Lakes, streams, and other freshwater environments are the primary targets of acid rain's numerous ecological repercussions.
- Acid rain elevates the acidity of such waterbodies, which causes more aluminium to be absorbed from the soil and transferred into streams and ponds, making the water poisonous to aquatic life.
- Acid rain penetrates the water system as runoff as it touches the ground and seeps into the soil.
- Crustaceans, crabs, fish, and other aquatic animals may become poisoned by the water as a result.
- Nonaquatic creatures like birds and the remainder of the food chain are also frequently impacted.
- Additionally, acid rain damages tree foliage, depletes the soil of essential minerals, and hinders trees' capacity to take in water.
- Because limestone and marble include a large amount of calcium carbonate, acid rain significantly impacts structures composed of these materials.
- The acid present in the rainwater interacts with the calcium molecules, causing damage to them.
- The Taj Mahal in Agra was significantly altered in colour by exhaust pollutants from the Mathura refinery.
How does acid rain significantly affect the Taj Mahal?
- Over the recent two decades, the Taj Mahal, one of the world's seven wonders, has drawn the attention of the Indian government.There are speculations that the Taj Mahal is fading.
- The structure's white luster is deteriorating, and in its place are green, brown, and other colours.
- Let's investigate why this is happening. The contamination is getting to the point where it is disturbing. This is primarily the result of three contributors:
- First, the Taj Mahal is surrounded by factories that spew hazardous fumes into the environment, including those that process rubber, make paper, build automobiles, make chemicals, and operate the renowned Mathura oil refinery.
- Second, a significant amount of smoke is emitted by the capital's growing automotive usage.
- Acids like sulphuric acid and nitric acid are created in the atmosphere when these gases (nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide) interact with moisture and air to create acid rain.
- The Taj Mahal's white marble deteriorates due to this acid rain.
- Acid rain also includes suspended materials such as ash, soot, and gases. SPM, or suspended particle matter, is the name of these particles.
- They adhere to the monument's surface, turning it pale and yellow.
- Another factor is the contamination of the Yamuna River, which is close to the landmark.
- The Taj Mahal's delicate inlay artistry is in danger because swarms of insects are thriving in the river Yamuna tributary.
- The marble's appearance is also affected by insect dung, which turns it from gleaming white to hues of brown and green.
Marble cancer
It is a condition wherein marble gets eroded by impurities like soot and acid rain, allowing the white marble to change to yellow.
Measures are undertaken to conserve the Taj Mahal
- The Indian government has taken significant steps to improve the town's and the region's air quality.
- Constructing a Taj Trapezium zone: a predetermined territory (10,400 km2) surrounding the monument where the new industrial development is prohibited.
- Industries are required to take steps to reduce the release of harmful gases. This lowers pollution levels.
- Moving to cleaner fuels: It has been enforced that LPG (Liquified Petroleum Gas) and CNG (Compact Natural Gas) be used to replace conventional fuels like coal and wood in industry and transportation.
- The Taj Mahal is being restored thanks to government investments in cutting-edge cleaning and beautification methods. To rejuvenate the luster and beauty of the Taj, fuller's earth, also known as Multani Miti, is applied.

Preventive measures
- Minimizing the utilization of fossil fuels for energy generation.
- We can lower the number of pollutants that cause acid rain by constructing more effective power stations that burn fossil fuels less frequently.
- By being aware of how the nitrogen in nitric acid and the sulphur in sulphuric acid initially penetrate the environment, we can try to minimize the effects of acid rain.
- In the chambers of automobiles, the combination of ambient nitrogen and oxygen produces nitrogen, while the combustion of sulphur-containing fossil fuels, particularly in energy plants, produces sulphur.
- Manufacturers have been disseminating sulphur dioxide through high chimneys for a long time, believing that dilution would reduce pollution.
- However, as opposed to being neutralized, the acid was diffused to distant locations by the wind.
- Scrubbing, a procedure that captures sulphur dioxide before it can penetrate the atmosphere is a much superior approach.
- Calcium sulphite is created due to the reaction between calcium oxide and sulphur dioxide.
- Gypsum, the fundamental component of all polymers, can be produced when sulphite and oxygen combine.
- As a scrubber, sulphur dioxide reacts with alkali, seawater, and lime (calcium oxide). These scrubbers have dramatically lowered our sulphur emissions levels and provided significantly better air quality in many nations.
- However, up to 10% less the power plants' efficiency, raising the price.
- Sulphur is eliminated from crude oil in oil refineries by combining it with hydrogen.
- In the industrial world, this phenomenon is known as hydrodesulphurization.
- It happens at a high temperature.
- By including a catalytic converter in every motor vehicle's exhaust pipe, we can lessen the amount of nitrogen released into the environment. In essence, they change the nitrogen oxides back into oxygen and nitrogen.
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now












